|
The content in this section has not undergone work group review and may be significantly revised prior to the next ballot. |
This section provides guidance for genomic reporting about the impact of a patient's or tumor's genetics on the behavior of one or more medications. This includes making recommendations for medication adjustments. This portion of the implementation guide relies on the content in the General Genomic Reporting and Sequenced Variants portions of this implementation guide. Pharmacogenomic reports supplement this information with a set of pharmacogenomic-specific impact profiles. Implementers of pharmacogenomic reporting may also be interested in the Somatic Genomic Reporting section of this implementation guide as it includes several profiles dealing with the impact of medications on cancers.
1.5.1 General guidance

While not specifically profiled in this version of the IG, some additional constraints will typically apply to somatic profiles. Patient will usually be present, however pharmacogenomics can theoretically be relevant for environmental samples (e.g. to determine the most effective way to deal with a persistent environmental pathogen).
1.5.2 Pharmacogenomic-specific Genetic Impacts

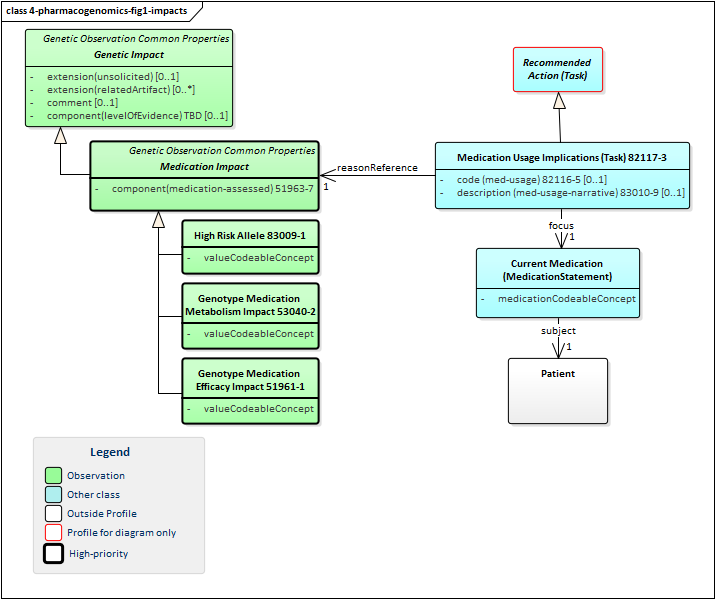
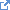
Figure 1: Pharmacogenomic Impacts
(Profile links:
Genetic Impact,
Medication Impact,
High Risk Allele,
Genotype Medication Metabolism Impact,
Genotype Medication Efficacy Impact
)
All pharmacogenomic impact profiles inherit from the abstract Genetic Impact profile. They also inherit from a commonabstract Medication Impact profile which includes the mandatory code that identifies the medication whose impact is being described. Because this is an international profile, no guidance is provided on drug coding systems. The typical or FHIR-mandated jurisdictional code system(s) should be used.
There are three types of impacts defined in this profile:
-
Genotype medication metabolism impact describes the impact of the associated genetic findings on how well the specified medication is metabolized by the patient - which can have impacts on appropriate dosage
-
Genotype medication efficacy impact describes how the associated genetic findings affect the effectiveness of the medication. This can influence the appropriateness of the medication for the patient.
-
High Risk Allele indicates if the associated genetic findings pose a particular risk for the patient independent of metabolism or efficacy. I.e. Does the medication have an unusual (and potentially dangerous) effect on patients with these genetic characteristics.
These impacts can all be associated with the Medication Usage Implications profile which allows making a recommendation for the patient's medication therapy (e.g. discontinuing a medication, altering dosage, etc.)
The modeling of the usage implications may also change if the modeling of impacts change as discussed in the General Genomic Reporting section.
1.5.3 Pharmacogenomic Example Instances

The following section walks through a specific pharmacogenomics example.
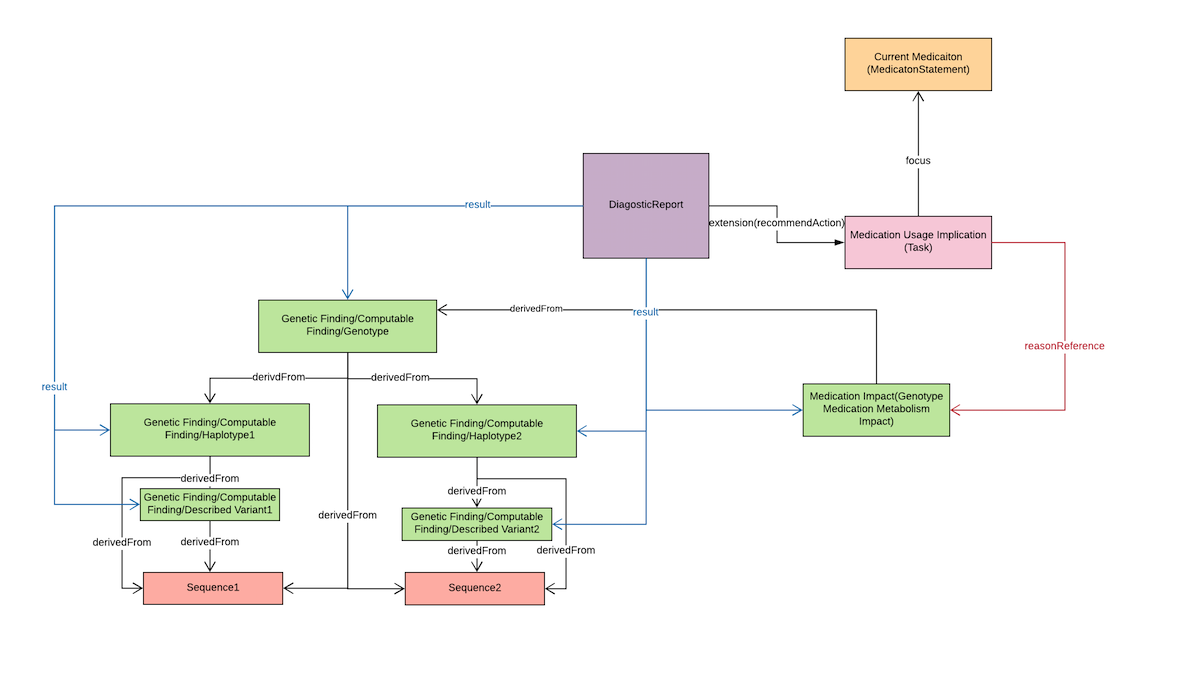
From the diagram above, Genotype Medication Metabolism Impact is used to store the phenotype detail which includes the following fields:
- code (LOINC|53040-2|Genetic variant effect on drug metabolism)
- valueCodeableConept (etc:LOINC|LA25390-8|Rapid metabolizer)
- derivedFrom(Observation/genotype)
- component
- code(LOINC|51963-7|medication assessed)
Medication Usage Impact is a Task resource, and it will store the specific recommendation of the specific phenotype which is stated on the Genotype Medication Metabolism Impact. Therefore, a reasonReference pointer will point to the Genotype Medication Metabolism Impact.
DiagnosticReport.result will be used to point to the Genotype Medication Metabolism Impact.
1.5.3.1 Pharmacogenomic-specific Computable Genetic Findings

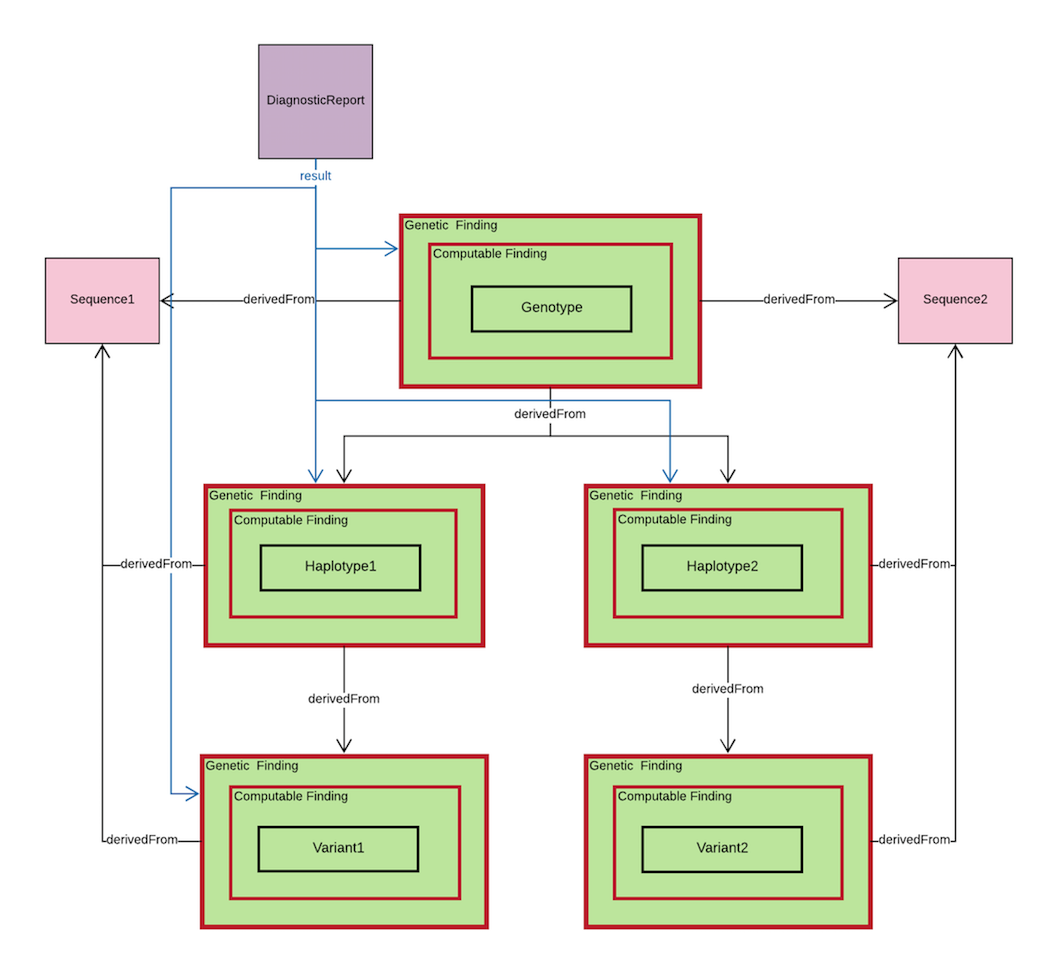
From the diagram above, Genotype, Haplotype and Variant profiles will are used. Each of the profile have the similar structure with Genetic Finding and Computable Finding, which means that Genotype, Haplotype and Variant profiles are inheriting the elements from Genetic Finding and Computable Finding.
Genotype contains the following fields:
- code(LOINC|84413-4|Genotype display name)
- valueString (etc:*4/*35B)
- derivedFrom
- Observation/Haplotype
- Observation/Variant
- Sequence/sequence
- component
- code (LOINC|48018-6|Gene studies ID)
Haplotype contains the following fields:
- code(LOINC|84414-2|Haplotype Name)
- valueString (etc: *35B)
- derivedFrom
- Observation/Variant
- Sequence/sequence
- component
- code (LOINC|48018-6|Gene studied ID)
Variant contains the following fields:
- code (LOINC|69548-6|genetic variant assessment)
- valueCodeableConcept(etc: LOINC|LA9633-4|Present)
- derivedFrom
- component
- code (LOINC|48013-7|Genomic reference sequence ID)
- code (LOINC|81255-2|dbSNP ID)
DiagnosticReport is used to record all these genetic finding elements by using “result” pointer, and each of these genetics finding elements will have a pointer point to their corresponding sequences.
1.5.4 Pharmacogenomic-specific Guidance and Recommendations

Recommendation for the medication usage will be stored on Task resource. Within the overall diagram, it is called Medication Usage Impact. It contains the following fields:
- code(etc: LOINC|LA26434-6|Increase dose)
- description(Any recommendation text for the medication usage suggestion)
- reasonReference(Obseration/GenomicImpact)