This section provides guidance on reporting genetic tests that involve sequencing the DNA, RNA or amino acid chains of the specimen. This includes direct sequencing, shot-gun sequencing, array-based variant testing and other mechanisms.
There are three profiles provided for describing the results of genetic testing that perform some degree of sequencing:
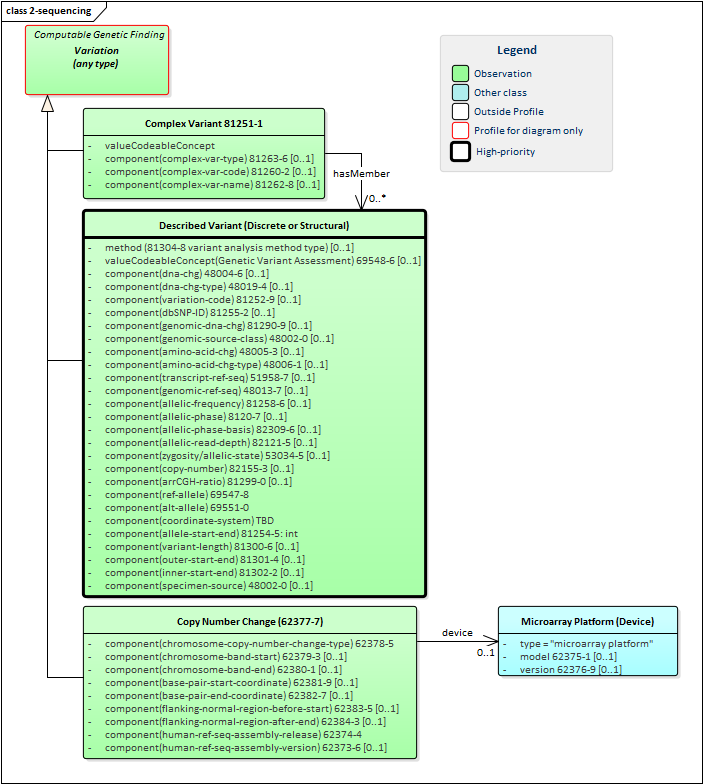
Figure 1: Sequencing Profiles
(Profile links:
Complex Variant,
Described Variant
)
Of these, the workhorse is Described Variant. It provides the details of exactly what sort of change was found, where that change was found, the degree of certainty around the type and location of the change and other information. It leverages the Sequence profile to convey information that would be part of a knowledge-base definition of the identified variant, but all information specific to the particular observed specimen is conveyed in the Described Variant profile.
The Complex Variant profile is used when there is a need to represent a named grouping of variants that do not correspond to a single Genotype or Haplotype. The details of what was found are left to the member Described Variants the Complex Variant points to.
TODO - provide additional guidance on the content and use of these profiles