This page is part of the FHIRcast (v2.1.0-ballot: STU3 Ballot 1) based on FHIR (HL7® FHIR® Standard) R4. This version is a pre-release. The current official version is 2.0.0. For a full list of available versions, see the Directory of published versions
This chapter consists of the following sections:
| 2.1 Session Discovery |
| 2.2 FHIRcast scopes |
| 2.3 Event format |
| 2.4 Subscribing to events |
| 2.5 Event notification |
| 2.6 Request context change |
| 2.7 Conformance |
| 2.8 Extensions |
| 2.9 Get Current Context |
The FHIRcast specification describes the APIs used to synchronize disparate healthcare applications’ user interfaces in real time, allowing them to show the same clinical content to a user (or group of users).
Once the subscribing app knows about the session, the app subscribes to specific workflow-related events for the given session. The app is then notified when those workflow-related events occur; for example, when the clinician opens a patient’s chart. The subscribing app can also initiate context changes by accessing APIs defined in this specification; for example, closing the patient’s chart. The app unsubscribes from its subscription to no longer receive notifications. The notification messages describing the workflow event are defined as a simple JSON wrapper around one or more FHIR resources.
FHIRcast recommends the HL7 SMART on FHIR launch protocol for both session discovery and API authentication. FHIRcast enables a subscriber to receive notifications either through a webhook or over a WebSocket connection. This protocol is modeled on the W3C WebSub RFC, such as its use of GET vs POST interactions and a Hub for managing subscriptions. The Hub exposes APIs for subscribing and unsubscribing, requesting context changes, and distributing event notifications. The flow diagram presented below illustrates the series of interactions specified by FHIRcast, their origination and their outcome.
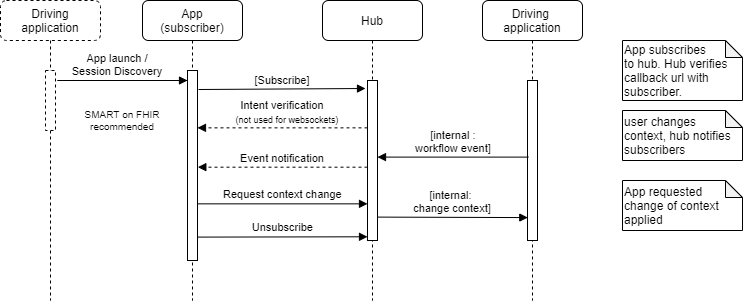
All data exchanged through the HTTP APIs SHALL be formatted, sent and received as JSON structures, and SHALL be transmitted over channels secured using the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) over Transport Layer Security (TLS), also known as HTTPS which is defined in RFC2818.
All data exchanged through WebSockets SHALL be formatted, sent and received as JSON structures, and SHALL be transmitted over Secure Web Sockets (WSS) as defined in RFC6455.