This page is part of the FHIRcast (v2.1.0-ballot: STU3 Ballot 1) based on FHIR (HL7® FHIR® Standard) R4. This version is a pre-release. The current official version is 2.0.0. For a full list of available versions, see the Directory of published versions
The Hub SHALL notify subscribed apps of workflow-related events to which the app is subscribed. The notification is a JSON object communicated over the webhook or websocket channel.
The HTTP request notification interaction to the subscriber SHALL include a description of the subscribed event that just occurred, an ISO 8601-2 formatted timestamp in UTC and an event identifier that is universally unique for the Hub. The timestamp SHOULD be used by subscribers to establish message affinity (message ordering) through the use of a message queue. Subscribers SHALL ignore messages with older timestamps than the message that established the current context. The event identifier MAY be used to differentiate retried messages from user actions.
| Field | Optionality | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
timestamp |
Required | string | ISO 8601-2 timestamp in UTC describing the time at which the event occurred. |
id |
Required | string | Event identifier used to recognize retried notifications. This id SHALL be unique for the Hub, for example a UUID. |
event |
Required | object | A JSON object describing the event see Event Definition. |
webhook Event Notification Request DetailsFor webhook subscriptions, the Hub SHALL generate an HMAC signature of the payload (using the hub.secret from the subscription request) and include that signature in the request headers of the notification. The X-Hub-Signature header’s value SHALL be in the form method=signature where method is one of the recognized algorithm names and signature is the hexadecimal representation of the signature. The signature SHALL be computed using the HMAC algorithm (RFC6151) with the request body as the data and the hub.secret as the key.
POST https://app.example.com/session/callback/v7tfwuk17a HTTP/1.1
Host: subscriber
X-Hub-Signature: sha256=dce85dc8dfde2426079063ad413268ac72dcf845f9f923193285e693be6ff3ae
{ ... json object ... }
For both webhook and websocket subscriptions, the event notification content is the same.
{
"timestamp": "2018-01-08T01:37:05.14",
"id": "q9v3jubddqt63n1",
"event": {
"hub.topic": "fdb2f928-5546-4f52-87a0-0648e9ded065",
"hub.event": "patient-open",
"context": [
{
"key": "patient",
"resource": {
"resourceType": "Patient",
"id": "ewUbXT9RWEbSj5wPEdgRaBw3",
"identifier": [
{
"type": {
"coding": [
{
"system": "http://terminology.hl7.org/CodeSystem/v2-0203",
"value": "MR",
"display": "Medication Record Number"
}
"text": "MRN"
]
}
}
]
}
}
]
}
}
The subscriber SHALL respond to the event notification with an appropriate HTTP status code. In the case of a successful notification, the subscriber SHALL respond with an any of the response codes indicated below: HTTP 200 (OK) or 202 (Accepted) response code to indicate a success; otherwise, the subscriber SHALL respond with an HTTP error status code.
| Code | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| 200 | OK | The subscriber is able to implement the context change. |
| 202 | Accepted | The subscriber has successfully received the event notification, but has not yet taken action. If it decides to refuse the event, it will send a syncerror event. Clients are RECOMMENDED to do so within 10 seconds after receiving the context event. |
| 500 | Server Error | There is an issue in the client preventing it from processing the event. The hub SHALL send a syncerror indicating the event was not delivered. |
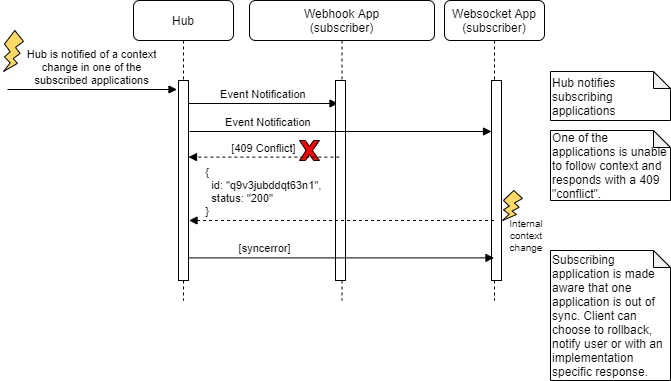
| 409 | Conflict | The client refuses to follow the context change. The hub SHALL send a syncerror indicating the event was refused. |
The Hub MAY use these statuses to track synchronization state.
webhook Event Notification Response ExampleFor webhook subscriptions, the HTTP status code is communicated in the HTTP response, as expected.
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
websocket Event Notification Response ExampleFor websocket subscriptions, the id of the event notification and the HTTP status code is communicated from the client to Hub through the existing WebSocket channel, wrapped in a JSON object. Since the WebSocket channel does not have a synchronous request/response, this id is necessary for the Hub to correlate the response to the correct notification.
| Field | Optionality | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
id |
Required | string | Event identifier from the event notification to which this response corresponds. |
status |
Required | numeric HTTP status code | Numeric HTTP response code to indicate success or failure of the event notification within the subscribing app. Any 2xx code indicates success, any other code indicates failure. |
{
"id": "q9v3jubddqt63n1",
"status": "200"
}
webhook and websocket Event Notification Sequence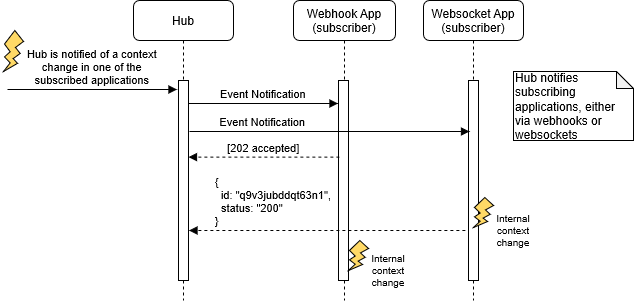
If the subscriber cannot follow the context of the event, for instance due to an error or a deliberate choice to not follow a context, the subscriber SHALL communicate the error to the Hub in one of two ways.
syncerror event to the Hub. If the application cannot determine whether it will follow context within 10 seconds after reception of the event it SHOULD send a syncerror event.If the Hub receives an error notification from a subscriber, it SHALL generate a syncerror event to the other subscribers of that topic. syncerror events are like other events in that they need to be subscribed to in order for an app to receive the notifications and they have the same structure as other events, the context being a single FHIR OperationOutcome resource.
The figure below illustrates the webhook and websocket Event Notification Error Sequence.
More information on the source of notification errors and how to resolve them can be found in Synchronization Considerations.
More information on the source of notification errors and how to resolve them can be found in Synchronization Considerations.
syncerror EventsIn addition to distributing syncerror events sent by one application to other subscribed applications, the Hub MAY generate and communicate syncerror events to applications under the following conditions –
A subscribed application’s WebSocket connection is closed with any Connection Close Reason other than 1000 (normal closure) or 1001 (going away) (see WebSocket RFC and WebSocket Status Codes)
And, the subscribed application, does not respond to a FHIRcast event within 10 seconds or an order of magnitude lower than the subscription time-out.
Implementer input is solicited on the amount and specificity of time, in the above.
syncerror events are distributed only to applications which have subscribed to syncerrors.
Upon communicating a syncerror resulting from an unresponsive app, the Hub SHALL unsubscribe the application.
The Hub SHALL NOT generate syncerror events in the following situations:
heartbeat eventDuring a normal shutdown of an application, it SHALL unsubscribe, and provide a WebSocket Connection Close Reason of 1000 and not rely upon the Hub recognizing and unsubscribing it as an unresponsive app.
Implementer feedback is solicited on Hub Generated `syncerror` Events particularly on the following topics:
syncerror indicating that an application is not responsive, should the nonresponsive application be automatically unsubscribed (removed from the Hub’s list of applications subscribed to the topic)? This would avoid syncerror events being sent after subsequent operations; however, it may conflict with the approach of syncerror events generated by the Hub only being distributed to subscribers of the event which triggered the syncerror event to be generated.syncerror events generated by the Hub be distributed only to subscribers of the event which triggered the syncerror event to be generated? However, this could conflict automatically unsubscribe a non-responsive application after the initial syncerror is generated and distributed.syncerror events to be generated by the Hub for an unresponsive application or only when a context change is requested ([FHIR Resource]-open or [FHIR Resource]-close)?