This page is part of the Da Vinci Patient Cost Transparency Implementation Guide (v1.0.0: STU 1) based on FHIR (HL7® FHIR® Standard) R4. The current version which supersedes this version is 2.0.0. For a full list of available versions, see the Directory of published versions
| Official URL: http://hl7.org/fhir/us/davinci-pct/ImplementationGuide/hl7.fhir.us.davinci-pct | Version: 1.0.0 | |||
| Active as of 2023-03-30 | Computable Name: PatientCostTransparency | |||
This specification is a Standard for Trial Use. It is expected to continue to evolve and improve through HL7® FHIR® Connectathon testing and feedback from early adopters.
Criteria regarding what payers must verify in a good faith estimate (GFE) will be evaluated during the next phase of the project after the project stakeholders receive feedback on error handling during testing and implementation.
Feedback is welcome and may be submitted through the FHIR change tracker indicating "US Da Vinci PCT" as the specification.
This implementation guide (IG) is dependent on other specifications. Please submit any comments you have on these base specifications as follows:
- Feedback on the FHIR core specification should be submitted to the FHIR change tracker with "FHIR Core" as the specification.
- Feedback on the US core profiles should be submitted to the FHIR change tracker with "US Core" as the specification.
Individuals interested in participating in the Patient Cost Transparency project or other HL7 Da Vinci projects can find information about Da Vinci here.
This IG provides detailed guidance to support providers and payers exchanging financial information for specific services and items using FHIR-based standards. This exchange involves a provider submitting a Good Faith Estimate (GFE) to a payer, and the payer generating an Advanced Explanation of Benefits (AEOB) for a patient (which may optionally be returned to the submitting provider). This information about the cost of healthcare items or services may enable better decision making by the patient in consultation with the provider. Note: This exchange will be triggered via a “request” or “scheduled service”. The AEOB will also include the GFE used to inform the AEOB generation. This IG describes system interactions using the FHIR standard. This IG will reference where possible the “standards” defined by the Health Record exchange (HRex) Library/Framework IG, other FHIR IGs, and other industry standards where applicable.
There is no requirement or HIPAA mandate to use administration/payment transmission standards. However, HL7 and X12 work collaboratively to support implementers to align requirements with claim submission standards to ease the burden of implementation where possible.
This IG is informed by the No Surprises Act (see Division BB, Title I, Sections 111 and 112), which was enacted as part of the Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2021. The No Surprises Act specifically requires that a provider share GFEs with a payer and that a payer make an AEOB available to a patient in advance of service. The initial scope of this IG was inspired by this general requirement.
The IG supports different methods of information sharing between payers and providers and payers and patients. In this way, the IG can support providers and payers as they work to meet the legislative and future regulatory requirement as well as enable information sharing valuable to supporting patient care. Since the law does not require an API to share these data, the method used to share the required information – an API, a portal, email, etc. – is the decision of the parties engaged in the process. Should future rulemaking mandate a specific scenario, this IG can be revised IG accordingly.
By using the FHIR standard and implementing this guide, providers and payers can enhance their existing technologies, where applicable, for estimating patient costs securely and efficiently using common open web technologies. The anticipated benefit of using FHIR APIs is to enable applications of the patients’ choice to give greater transparency into patient-specific estimated costs of expected healthcare services and items.
FHIR is being used for consumer access to healthcare related data at significant scale today, and there are regulatory requirements in the form of the CMS Patient Access API for FHIR support for the related use case of post adjudicated claims. Use of an industry standard would keep the barrier to stakeholder adoption relatively low.
Acronyms used in this IG can be found here. The reader of this IG should become familiar with these before reading this IG.
AEOB Interaction Diagram Steps (High Level View)
A patient schedules a service which triggers the composition of a collection of one or more GFEs. Note: The composition of the collection of GFEs is currently not in scope for this IG.
The collection of GFEs in the form of a FHIR resource bundle (GFE Bundle) is submitted (via the gfe-submit operation to the payer’s endpoint for AEOB creation.
The payer would then process, adjudicate, and produce the AEOB bundle.
The patient can now request and receive the AEOB Bundle via FHIR query.
Note: Communication to the patient below could be through an app by a third-party or provider approved by the patient or directly to the patient by the payer.
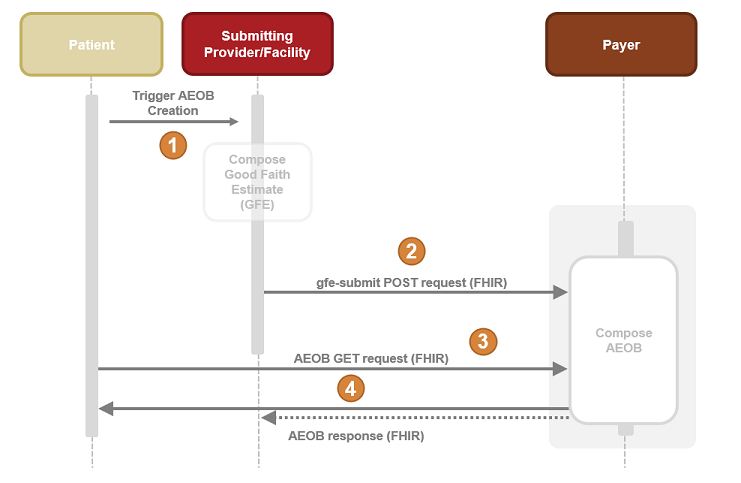
Figure 1: Advanced EOB Interactions
Primary Authors:
Technical Editing:
Da Vinci Project Coordination and Core Team:
Da Vinci Member Leadership Provided By:
This IG was developed under the auspices of the Financial Management Work Group.
Special thanks go to the numerous Da Vinci members and community who have participated on conference calls, provided reviews and feedback, supported sample data gathering, reference implementation development, and testing including, but not limited to:
If you are interested in participating in the PCT project, information about our calls, minutes of past discussions, and other information can be found here on our HL7 Confluence page.
The scope of this guide does not include coordination of benefits or more than one coverage. This does not serve as a replacement for eligibility, prior authorization or other financial and administrative use cases.
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| AEOB | The Consolidated Appropriations Act includes provisions whereby group health plans and health insurance issuers, based on charges, billing and diagnostic codes provided by the provider(s), provide an Advanced Explanation of Benefits for scheduled services or upon request to give patients transparency into their estimated healthcare costs. AEOBs need to include which providers are expected to provide treatment, the network status of providers, good faith estimates of cost, cost-sharing and progress towards meeting deductibles and out-of-pocket maximums, as well as whether a service is subject to medical management and relevant disclaimers of estimates; for example, the disclaimer might state that the information provided in the notification is only an estimate based on the items and services reasonably expected, at the time of scheduling (or requesting) and is subject to change. For a complete breakdown of what needs to be included in the AEOB see 42 U.S. Code 300gg-111(f)(1)(A) through (H). |
| Allowed Amount | The maximum amount a plan will pay for a covered healthcare service. May also be called “eligible expense,” “payment allowance,” “negotiated rate”, “contractual amount”, or “covered amount.” |
| CAA Consolidated Appropriations Act |
Also called “H.R. 133”. The CARES (Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security) Act implemented a variety of programs to address issues related to the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic. The Consolidated Appropriations Act continued many of these programs by adding new phases, new allocations, and new guidance to address issues related to the continuation of the COVID-19 pandemic. Title I (the No Surprises Act) of Division BB of the Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2021 establishes new protections from surprise billing and excessive cost sharing for consumers receiving healthcare items/services. The Consolidated Appropriations Act (2021) was passed by Congress on December 21, 2020 and signed into law on December 27, 2020. |
| Coinsurance | The percentage of costs of a covered healthcare service that is paid (20%, for example) after a member has paid the deductible. |
| Collection of Services | The list of services expected to be performed during the period of care as part of gathering the Good Faith Estimate for the expected charges, billing and diagnostic codes for one or multiple providers. |
| Copayment | A fixed amount ($20, for example) that is paid for a covered healthcare service after the deductible has been paid. For example, a health insurance plan’s allowable cost for a doctor’s office visit is $100 and the copayment for a doctor visit is $20. |
| Cost | To providers: the expense incurred to deliver healthcare services to patients. To payers: the amount they pay to providers for services rendered. To patients: the amount they pay out-of-pocket for healthcare services. |
| Data Exchange Method | The mechanism for sending and receiving the data (e.g. standard “transactions”, APIs, fax, email). |
| Data Payload | The bundle of data or collection of the data elements being sent. |
| Deductible | The amount that is paid for covered healthcare services before the insurance plan starts to pay. With a $2,000 deductible, for example, the first $2,000 of covered services is paid by the member out-of-pocket. After the deductible is paid, the member usually pays only a copayment or coinsurance for covered services. |
| EOB Explanation of Benefits |
An EOB is a statement from a health insurance plan describing what costs it will cover for medical care or products received. |
| GFE | The Good Faith Estimate is a notification of reasonably expected charges and billing codes for a scheduled or requested item or service. For a complete breakdown of what needs to be included in the GFE see 42 U.S. Code 300gg-136 |
| GFE Submitter | Any provider and/or facility that sends a Good Faith Estimate (GFE) to a payer to facilitate the creation of an Advanced Explanation of Benefits (AEOB). |
| Gross Charge | The charge for an individual item or service that is reflected on a hospital’s chargemaster absent any discounts. |
| HIPAA | The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (HIPAA) is a federal law that required the creation of national standards to protect sensitive patient health information from being disclosed without the patient’s consent or knowledge. The US Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) issued the HIPAA Privacy Rule to implement the requirements of HIPAA. The HIPAA Security Rule protects a subset of information covered by the Privacy Rule. |