This page is part of the SDOH Clinical Care for Multiple Domains (v2.0.0: STU 2) based on FHIR R4. This is the current published version. For a full list of available versions, see the Directory of published versions 
Functional Use Cases
Note: SDOH IG related Patient Stories are available on the Gravity Project Confluence site here
These use cases are represented by workflow diagrams on the Exchange Workflow Page
The following numbering is use throughout this section where N is an integer number:
- N (e.g. 1-14) are steps common to all functional use cases
- IN (e.g. I1-I12) are additional steps used only by Indirect use cases
- INa (e.g. I8,I9) are steps used by the Indirect use case when communicating with a FHIR API enabled CBO
- INb (e.g. I8b, I9b) are steps used by the Indirect use case when communicating with a FHIR application enabled CBO
Overview
The functional use cases defined below are based on specific exchanges of information between the relevant actors. These use cases include:
- A direct referral between a requesting entity and a performing entity where both entities have FHIR APIs to facilitate the exchanges
- A “light” version of the direct referral where the performing entity uses a application that can access the referring entities API (but does not have FHIR API capability)
- An indirect referral, where the communication between the referring entity and the performing entity is through an intermediary (such as a Coordination Platform as defined below) that has FHIR API capability
- Finally, a patient application may optionally communicate directly with any of the entities that support a FHIR API and provides a mechanism for secure exchange
Actors
- Provider (includes licensed providers and others that interact with the patient to assess social risk, set goal, and determine/recommend referrals)
- Care Coordinator (coordinates the care and referral activities but normally does not make assessment, goal, or referral decisions)
- Patient (consumer, client, etc.) –the subject of the assessment, goals, referrals and services delivered)
- Community Based Organization (CBO) – organizations that deliver social requested services (e.g. food pantry)
- Coordination Platform (CP) – an intermediary that receives referrals, assesses patient needs, and works with one or more CBOs to deliver the services
Business Associates
- CBOs and CPs are not covered entities under HIPAA. (Covered entities only includes Providers, Payers, and Clearing Houses)
- However, a CBO and/or CP may be a Business Associate (BA) of a covered entity. This requires a Business Associate Agreement (BAA) between the covered entity and the BA.
- Entities covered under a BAA may be able to receive Protected Health Information (PHI) as part of the agreement without consent of the patient. However, they are required to observe the same limitation as covered entities with regard the protection and disclosure of PHI.
- Typically, a BAA is required by a covered entity to avoid disclosure of PHI by non-covered entities and in particular in situations where clinical information is shared to help manage the needs of the patient (e.g., if the patient is diabetic and therefore has specific dietary constraints)
- For a covered entity or business associate to share PHI with an entity that is not a covered entity or does not have a BAA, consent of the patient is generally required (there are specific exception allowed by HIPAA)
Direct Referral
Applies to Providers, Payers and CPs as the referral requester
Patient assessed by provider and referred to CBO to deliver the service
Actors
- Provider / Care Coordinator
- Patient
- Community Based Organization (CBO)
Assumptions
- Provider has a FHIR API
- Patient has a FHIR enabled personal application
- CBO has a FHIR API
Provider Actions
- Patient takes standardized assessment tool to identify risks
- Provider evaluates assessment and identifies Food Insecurity and Transportation Insecurity
- Provider and patient determine that it is most important to address the Food Insecurity first – provider promotes the health concern to the problem list
- Provider and patient add a goal related to this problem to pursue enrollment in a SNAP program
- Provider and patient agree that a referral to a contracted or non-contracted CBO is an appropriate next step
- Patient consents to be referred to the CBO and consents to have the information that will be provided sent to the CBO
- Optional: Provider makes information regarding the referral available to the patient’s application
Provider – CBO Actions
8a. Provider or Care Coordinator creates and sends an electronic referral to the C
9a. CBO receives and accepts referral
CBO Actions
10a. Optional: CBO communicates with the patient via their application to schedule appointments, collect additional information, etc.
- CBO completes the evaluation and enrollment, updates the status of the referral to completed, and includes information on what was completed
Provider Actions
- Provider receives the updated status
- Optional: Provider closes loop with patient via questionnaire available to a patient’s application
- Provider determines if the goal has been satisfied and/or progress has been made on the goal and updates the goal appropriately
Considerations
- CBOs are typically not BAs of covered entities and therefore not bound by HIPAA’s privacy and security requirements
- Provider may not always have the relationship with the CBO
- CBO may not accept the referral or be unable to perform the requested service
- Closing the loop via patient reported outcome
Direct Referral Light
Note: same as Direct Referral with the following exceptions
Actors (same as Direct Referral)
Note: Community Based Organization (CBO) has an application that can interact with a FHIR API and does not have a FHIR server
Assumptions
- Provider has a FHIR API
- Patient has a FHIR enabled personal application
- CBO has a FHIR enabled application
- Applications cannot talk to each other
Provider Actions (same as Direct Referral)
CBO - Provider Actions (changed based on CBO application vs FHIR API)
8b. CBO application queries Provider or Care Coordinator API for new or updated referrals.
9b. CBO finds new referral and accepts the referral
CBO Actions (changed step 10 does not occur)
10b. Optional exchange with Patient does not occur electronically (no app to app exchange)
- CBO completes the evaluation and enrollment, updates the status of the referral to completed, and includes information on what was completed
Provider Actions (same as Direct Referral)
Considerations (same as Direct Referral)
Indirect Referral with Direct CBO
Note: applies to Providers and Payers as the referral requester
Patient is assessed by a practitioner and referred to a Coordination Platform (CP). CP refers to a Community Based Organization (CBO) to deliver the service
Actors
- Provider / Care Coordinator
- Patient
- Coordination Platform (CP)
- Community Based Organization (CBO)
Assumptions
- Provider has a FHIR API
- Patient has a FHIR enabled persona application
- CP has a FHIR API
- CBO has a FHIR API
Provider Actions (same as Direct Referral)
Provider – CP – CBO workflow
I1. Provider or Care Coordinator creates and sends an electronic referral (and a copy of the consent) to the CP
I2. CP receives and accepts referral
I3. Optional: CP communicates with patient via their application to schedule appointments, collect additional information, etc.
I4a. CP refers patient to a CBO, with which they have a relationship, to evaluate the patient’s eligibility and help the patient enroll in a SNAP program, if appropriate
I5a. CBO receives and accepts the referral
I6a. Optional: CP makes information regarding the referral available to the patient’s application
I7. CP updates status of the initial referral
I8a. Optional: CBO communicates with patient via their application to schedule appointments, collect additional information, etc.
- step 11. CBO completes the evaluation and enrollment
I9a. CBO updates the status of the referral to completed, and includes information on what was completed
I10. Optional: CP communicates with the patient via their application to close loop on service(s) delivered by the CBO
I11. CP uses the input from the CBO and Patient to update the status of the referral and includes information on what was completed
I12. Provider receives the updated status
Provider Actions (same as Direct Referral)
Considerations in addition to Direct Referral
- CPs may not be a BA of the covered entity and therefore not bound by HIPAA’s privacy and security requirements
- CP may not always have a formal relationship with a CBO
- Provider may request to have the service delivered by a specific CBO
- CP may not accept the referral or be unable to perform the requested service
- CP may need to split the request into multiple tasks to be performed by more than one CBO
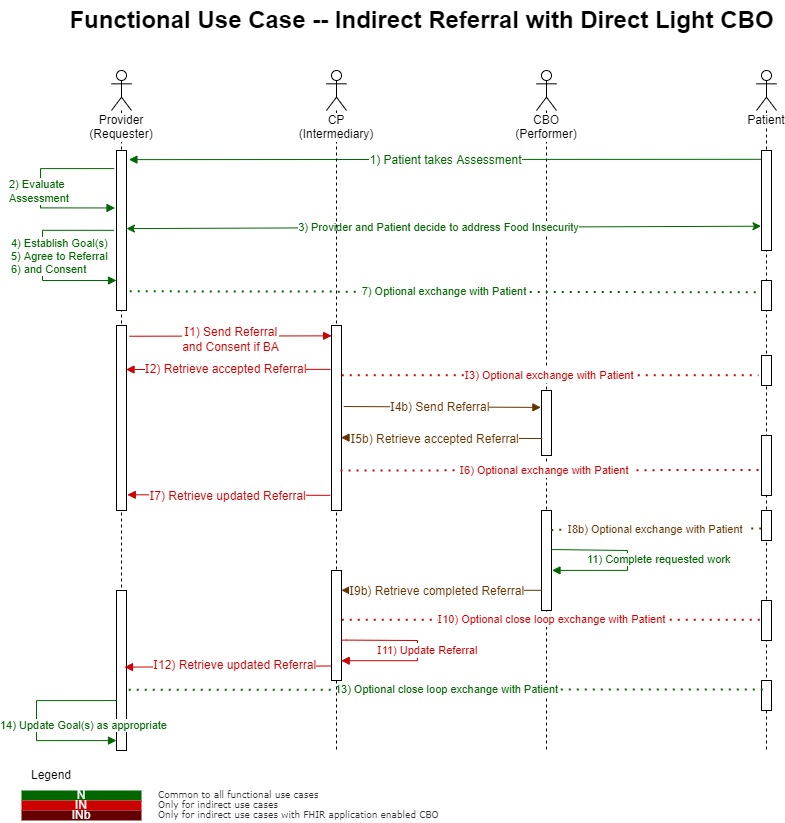
Indirect Referral with Direct Light CBO
Note: applies to Providers and Payers as the referral requester
Patient is assessed by a practitioner and referred to a Coordination Platform (CP). CP refers to a Community Based Organization (CBO) to deliver the service
Actors
- Provider / Care Coordinator
- Patient
- Coordination Platform (CP)
- Community Based Organization (CBO)
Assumptions
- Provider has a FHIR API
- Patient has a FHIR enabled persona application
- CP has a FHIR API
- CBO has a FHIR enabled application
- Applications cannot talk to each other
Provider Actions (same as Direct Referral)
Provider – CP – CBO workflow (note: steps with a “b” suffix are specific to this referral)
I1. Provider or Care Coordinator creates and sends an electronic referral (and a copy of the consent) to the CP
I2. CP receives and accepts referral
I3. Optional: CP communicates with patient via their application to schedule appointments, collect additional information, etc.
I4b. CBO application queries the CP for new or updated referrals
I5b. CBO finds new referral and accepts the referral
I6a. Optional: CP makes information regarding the referral available to the patient’s application
I7. CP updates status of the initial referral
I8b. Optional exchange with Patient does not occur electronically (no app to app exchange)
- step 11. CBO completes the evaluation and enrollment
I9b. CBO updates the status of the referral to completed, and includes information on what was completed
I10. Optional: CP communicates with the patient via their application to close loop on service(s) delivered by the CBO
I11. CP uses the input from the CBO and Patient to update the status of the referral and includes information on what was completed
I12. Provider receives the updated status
Provider Actions (same as Direct Referral)
Considerations (same as Indirect Referral with Direct CBO)
Closing the loop with the patient
Note: applies to Providers, Payers, CPs and CPOs
Assumes patient is using a personal application (e.g., Smart Phone application) that has already been registered and authenticated with the provider’s EHR API, the CP API and the CBO API.
Actors
- Practitioner / Care Coordinator
- Patient
- CP
- CBO (FHIR API)
Patient Workflow (from above functional use cases)
Note: all exchanges are optional
-
Provider - Patient
- Provider makes information regarding the referral available to the patient’s application
-
CP - Patient
I3. CP communicates with patient via their application to schedule appointments, collect additional information, etc.
-
CBO - Patient (assumes CBO has FHIR API)
I8a. CBO communicates with patient via their application to schedule appointments, collect additional information, etc.
-
CP - Patient
I10. CP communicates with the patient via their application to close loop on service(s) delivered by the CBO
-
Provider - Patient
- Provider closes loop with patient via questionnaire available to a patient’s application
Considerations
- Patient may not have an appropriate application or completed process to register and authenticate with the API(s)
- Patient may not be willing or able to respond to the questionnaires