This page is part of the Validated Healthcare Directory FHIR IG (v0.2.0: STU 1 Ballot 2) based on FHIR (HL7® FHIR® Standard) v3.5.0. The current version which supersedes this version is 1.0.0. For a full list of available versions, see the Directory of published versions
General Guidance and Background Information
Contents
- Background
- Healthcare Directory vs. Provider Directory
- ONC/FHA Healthcare Directory Effort
- Relation to US Core and other IGs
- The Validated Healthcare Directory Data Model
- Overview of Validated Healthcare Directory - Resource Relationships
Background
Healthcare directories play a critical role in enabling identification of individual providers and provider organizations, as well as characteristics about them, their relationships, and the means by which to access and exchange health information among them electronically. Healthcare directories support a variety of use cases, including:
- Electronic endpoint discovery
- Referrals and transitions of care
- Health plan enrollment
- Provider selection
- Provider credentialing/privileging
Today, many healthcare organizations maintain directories, including providers, payers, health information exchange organizations (HIEs/HIOs), health information service providers (HISPs), government agencies, and credentialing organizations. However, despite their importance, healthcare directory activities remain scattered, uncoordinated, and are often not interoperable. As a result, the healthcare industry collectively spends significant time and resources registering and validating demographic information for individual and organizational providers for purposes such as licensure, credentialing, certification, and payment.
Providers often have to submit and manage information about themselves and their places of employment to a variety of stakeholders. In the US, providers often contract with ten or more health plans, and are required to regularly submit similar information to each plan for inclusion in a provider directory. Likewise, provider credentialing and hospital privileging processes require similar documentation. The Council for Affordable Quality Healthcare has estimated that maintaining provider databases costs the US healthcare industry at least $2 billion annually.
Due to the high cost of acquiring and maintaining provider information and keeping it current, existing healthcare directories often contain information that is inaccurate, out of date, or not validated.
Healthcare Directory vs. Provider Directory
This implementation guide uses the term ‘healthcare directory’ instead of ‘provider directory’ because it encompasses all individuals and entities that provide services which may impact an individual’s health and well-being. We did not limit the definition of a directory to include only those individuals/entities that are licensed to practice medicine and/or bill for healthcare services. Rather, a validated healthcare directory may include data about community/social service entities and non-licensed administrative/support staff, among others.
Patient/caregiver information, however, is considered out of scope for a VHDir.
ONC/FHA Healthcare Directory Effort
On April 5th and 6th, 2016, the Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology (ONC) and the Federal Health Architecture (FHA) jointly hosted a Provider Directory Workshop to convene public and private stakeholders to review challenges, share successes, and generate new ideas around provider directory standards and solutions. Although participants described different use cases for healthcare directories, they agreed that provider data quality is a persistent challenge across the industry.
To address concerns about data quality, reduce administrative burden, and improve consumer satisfaction, ONC and FHA launched a new healthcare directory effort in July 2016. The project sought to: (1) define the architecture of a central source of validated healthcare directory data, and (2) develop a Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR) Implementation Guide describing the exchange of information between a central source of validated healthcare directory data and local environments (e.g. provider organizations, payers, HIEs).
Such a central source would include a broad set of provider data to support a variety of healthcare directory use cases. Data would be validated against primary sources (e.g. state licensing boards for licensure information) and available to local environments through a national FHIR-based exchange standard. Instead of submitting the same information to each payer and provider organization they worked with, providers would only have to attest to the majority of their information to the central source.
For more information on the ONC and FHA effort see the ONC Techlab Healthcare Directory Project
Relation to US Core and other IGs
This implementation guide was written for an international audience. We expect different jurisdictions considering implementating a VHDir will design their implementations in accordance with jurisdictional requirements, such as national profiles/IGs. In the United States, for example, we expect a VHDir would align with an R4 version of the US Core IG once it becomes available.
The Validated Healthcare Directory Data Model
To determine which resources to profile, extensions to create, etc. we reviewed a number of use cases supported by healthcare directories today:
- Basic Information Exchange
- A1. Enable electronic exchange (e.g. discovery of electronic end points such as IHE/EHR endpoints, FHIR server URLs, Direct addresses) - enables the electronic exchange of health information by supporting the ability to discover electronic service information including electronic endpoints or electronic addresses
- A2. Find an individual and/or organization (even if no electronic end point is available) - enables users to find contact and other identifying information about healthcare organizations and individual healthcare providers
- Patient/Payer focused
- B1. Find provider accessibility information (specialty, office hours, languages spoken, taking patients) - enables individuals and consumers to find contact and other accessibility information for individual healthcare providers and/or healthcare organizations
- B2. Relationship between provider and insurance plan (insurance accepted) or plan and provider (network) - enables individual healthcare providers, organizations, and payers to discover the relationships between providers, organizations, and payers, as well as additional details about the relationships and entities involved
- B3. Plan selection and enrollment - enables individuals and consumers to find information about health plans for the purposes of enrollment, including information about the health care providers and organizations that participate in a particular payer network, plan, or product and other information that can help the consumer make an informed choice about choosing the plan that best meets their health care needs
- B4. Claims management (adjudication, prior authorization, payment) - enables entities to discover information about providers to support claims processing, adjudication, prior authorization, and other reimbursement/payment related activities
- Care Delivery / Value Based Care
- C1. Provider relationship with a patient (e.g. for alerts) - supports discovery of provider-patient relationships to enable cross-organization workflows and processes for care coordination
- C2. Provider relationship with other providers in context of a patient (e.g. care team communications) - enables individual providers/organizations/care team members to identify each other, communicate and exchange information, expand the care team (e.g. referrals), and coordinate care within and across organizational boundaries
- Other
- D1. Provider credentialing - supports the process of establishing and evaluating the qualifications of a health care provider by verifying the provider’s experience, expertise, interests, and willingness to provide medical care
- D2. Quality or regulatory reporting (e.g. aggregate data, plan networks) - enables providers and health plans to consolidate and standardize the electronic exchange of quality-related data and performance results in addition to helping providers use their own information consistently to “report once”
- D3. Detection of fraud; inappropriate approval of services and/or payment for services - enables discovery of provider information for evaluating or responding to suspected cases of fraud or improper approval/payment for healthcare services
For each use case, we described the general information requirements necessary to support the use case. We then specified the general information requirements as discrete data elements using FHIR resources. Therefore, this implementation guide covers a broad set of data elements supporting a range of use cases that may reasonably be collected, validated, and exchanged from a central source of validated provider data.
Overview of Validated Healthcare Directory - Resource Relationships
Note: the following diagrams provide a high-level view of the relationships between resources used in this IG. They do not necessarily reflect all of the relationships/references between resources.
Practitioner
A practitioner is a person who is directly or indirectly involved in the provisioning of healthcare.
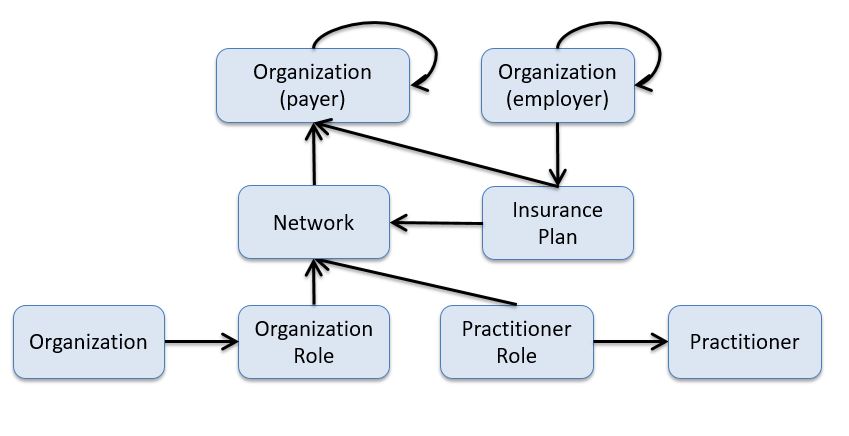
Practitioner Role
PractionerRole describes the relationship between a practitioner and an organization. A practitioner provides services to the organization at a location. Practitioners also participate in healthcare provider insurance networks through their role at an organization.
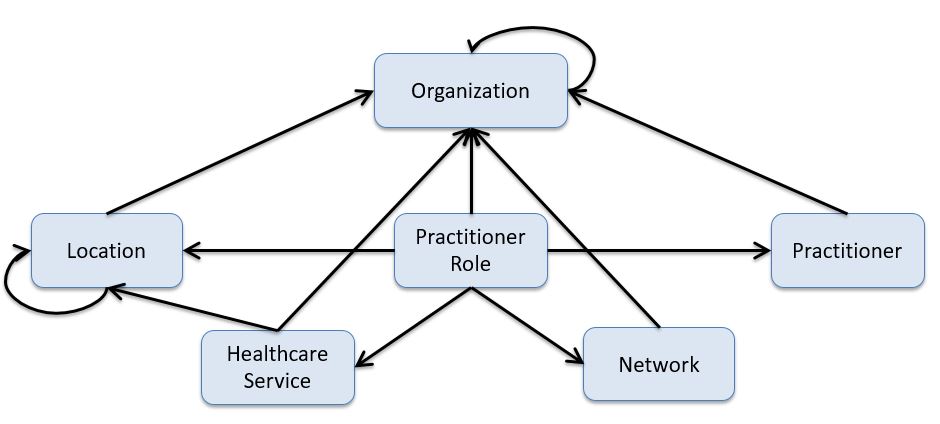
Organization Affiliation
Similar to PractitionerRole, OrganizationAffiliation describes relationships between organizations. For example: 1) the relationship between an organization and an association it is a member of (e.g. hospitals in a hospital association), 2) an organization that provides services to another organization, such as an organization contracted to provide mental health care for another organization as part of a healthcare provider insurance network, and 3) distinct organizations forming a partnership to provide services (e.g. a cancer center).
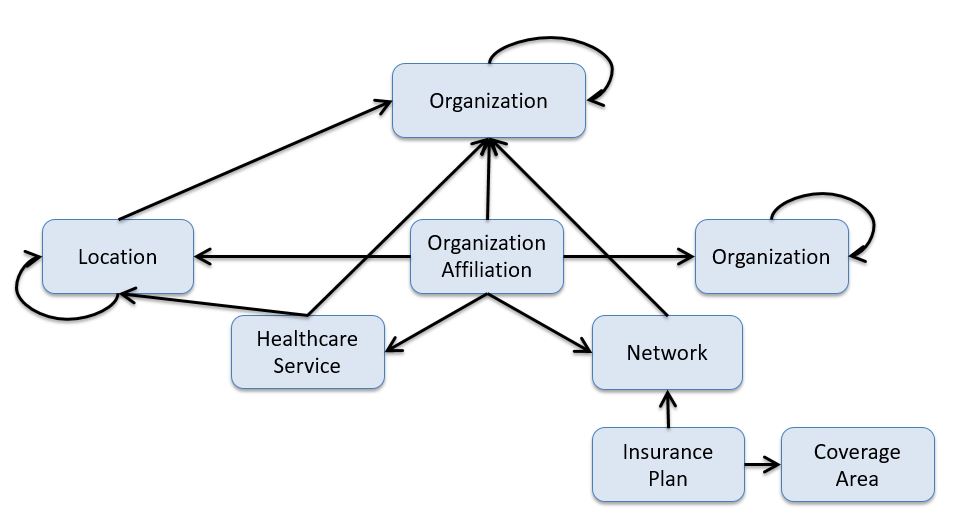
Network / Insurance Plan
A network is a group of practitioners and organizations that provide healthcare services for individuals enrolled in a health insurance product/plan (typically on behalf of a payer).