This page is part of the Potential Drug-Drug Interaction (PDDI) Clinical Decision Support (CDS) (FHIR IG) (v0.2.0: STU 1 Ballot 2) based on FHIR (HL7® FHIR® Standard) R4. No current official version has been published yet. For a full list of available versions, see the Directory of published versions
The Warfarin + NSAIDs knowledge artifact represents a relatively complex contextualized PDDI CDS algorithm. The knowledge artifact contains logic that uses both drug and patient contextual factors. The original rule was developed by clinical experts as part of the W3C Community Group effort to develop a minimum information model for representing clinically actionable knowedge about PDDIs. Table 1 is the Warfarin + NSAIDs knowledge artifact at the narrative level using the minimum information model.
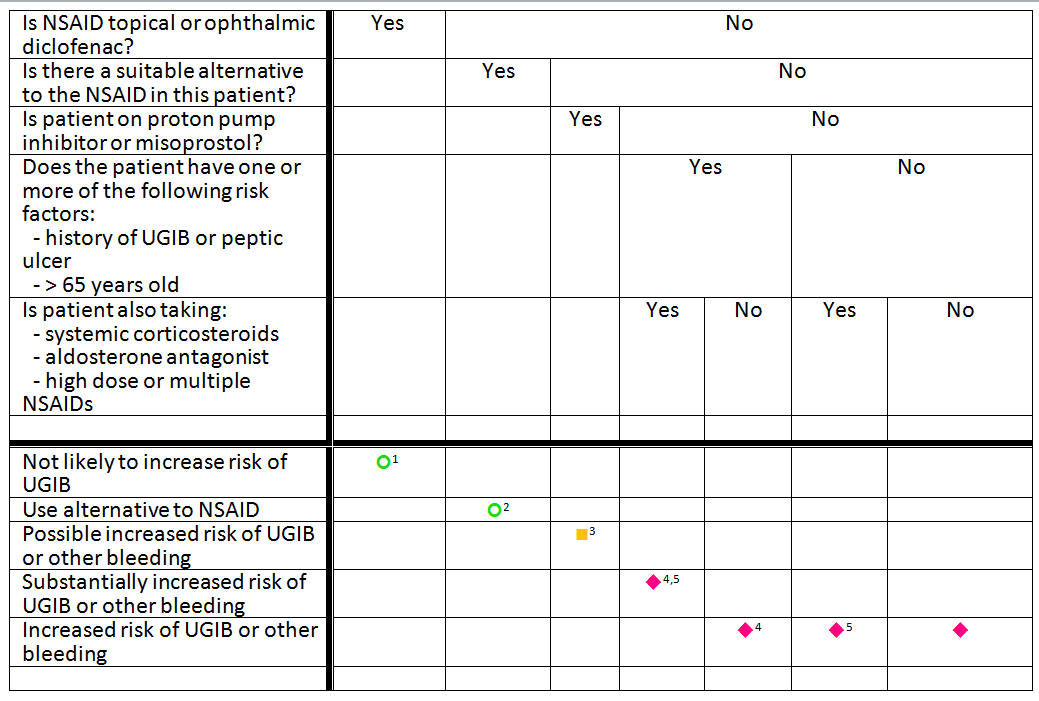
Footnotes:
| Drugs involved: Warfarin and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) |
| Comment: The drugs involved in a PDDI MUST be explicitly stated. To support a computable representation of the PDDI, the drugs involved SHOULD be listed as sets of terms from a terminology such as RxNorm or the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System (ATC). Such so called value sets MAY be referenced by a URI to a public repository such as the Value Set Authority Center that is maintained by the United States National Library of Medicine. |
| Clinical Consequences: Increased risk of bleeding including gastrointestinal bleeding, intracranial hemorrhage, and cerebral hemorrhage |
| Comment: The clinical consequences associated with a PDDI MUST be reported if known. Clinical consequences SHOULD refer health outcomes as specifically as possible. To support a computable representation of the PDDI, clinical consequences SHOULD be represented as one or more sets of terms from a terminology such as ICD-10 or SNOMED-CT. Such so called value sets MAY be referenced by a URI to a public repository such as the Value Set Authority Center that is maintained by the United States National Library of Medicine. |
| Seriousness: Bleeding is a serious potential clinical consequence because it can result in death, life-threatening hospitalization, and disability. |
| Comment: A PDDI clinical consequence MUST be noted as serious if it can result in death, life-threatening hospitalization, congenital anomaly, disability, or if it requires intervention to prevent permanent impairment or damage. |
| Mechanism of Interaction: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) have antiplatelet effects which increase the bleeding risk when combined with oral anticoagulants such as warfarin. The antiplatelet effect of NSAIDs lasts only as long as the NSAID is present in the circulation, unlike aspirin’s antiplatelet effect, which lasts for up to 2 weeks after aspirin is discontinued. NSAIDs also can cause peptic ulcers and most of the evidence for increased bleeding risk with NSAIDs plus warfarin is due to upper gastrointestinal bleeding (UGIB). |
| Comment: The mechanism of a PDDI MUST be reported if known. The description SHOULD be written for a clinician audience and include details that help the clinician decide what course of management action to take. To reduce ambiguity, the description MAY refer to specific drugs or health conditions using codes from terminologies. |
| Recommended Action: If the NSAID is being used as an analgesic or antipyretic, it would be prudent to use an alternative such as acetaminophen. In some people, acetaminophen can increase the anticoagulant effect of warfarin, so monitor the INR if acetaminophen is used in doses over 2 g/day for a few days. For more severe pain consider short-term opioids in place of the NSAID. |
| Comment: Any recommended actions that apply to all patient exposures SHOULD be stated using clear and concise language. The recommended action statement SHOULD also provide citations to evidence for a suspected drug-drug interaction (not provided in this example). Recommendations that depend on contextual information/modifying factors SHOULD be mentioned separately to support context-specific presentation of such information. |
Contextual information/modifying factors:
|
| Comment: Contextual information/modifying factors are necessary for alerts that are both sensitive and specific. Like clinical consequences, each known factor SHOULD be stated as specifically as possible. The factors SHOULD be amenable to implementation as executable logic using value sets from clinical terminologies such as RxNorm, the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System (ATC), ICD-10, and SNOMED-CT. As is used in this example, each factor SHOULD be related to a specific recommended action that is supported by the evidence for a suspected drug-drug interaction |
| Frequency of Exposure to the PDDI: Unknown |
| Comment: Frequency of exposure and frequency of harm information is rarely available but can help a clinician assess the risk/benefit trade-off of exposure to PDDI. Such information SHOULD be provided if available. |
| Frequency of Harm for persons who have been exposed to the PDDI: Unknown |
| Comment: Frequency of exposure and frequency of harm information is rarely available but can help a clinician assess the risk/benefit trade-off of exposure to PDDI. Such information SHOULD be provided if available. |
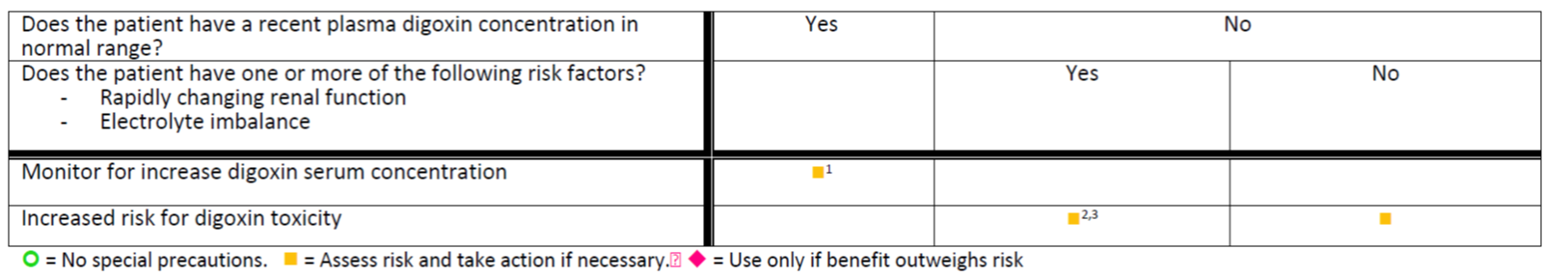
Footnotes:
| Drugs involved: Digoxin and Cyclosporine |
| Comment: The drugs involved in a PDDI MUST be explicitly stated. To support a computable representation of the PDDI, the drugs involved SHOULD be listed as sets of terms from a terminology such as RxNorm or the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System (ATC). Such so called value sets MAY be referenced by a URI to a public repository such as the Value Set Authority Center that is maintained by the United States National Library of Medicine. |
| Clinical Consequences: Increased risk of digitalis toxicity that may lead to cardiac arrhythmias |
| Comment: The clinical consequences associated with a PDDI MUST be reported if known. Clinical consequences SHOULD refer health outcomes as specifically as possible. To support a computable representation of the PDDI, clinical consequences SHOULD be represented as one or more sets of terms from a terminology such as ICD-10 or SNOMED-CT. Such so called value sets MAY be referenced by a URI to a public repository such as the Value Set Authority Center that is maintained by the United States National Library of Medicine. |
| Seriousness: Digitalis toxicity is a serious potential clinical consequence because it can result in death, life-threatening hospitalization, and disability. |
| Comment: A PDDI clinical consequence MUST be noted as serious if it can result in death, life-threatening hospitalization, congenital anomaly, disability, or if it requires intervention to prevent permanent impairment or damage. |
| Mechanism of Interaction: The mechanism of this interaction appears to be mediated through P-glycoprotein inhibition by cyclosporine. P-glycoprotein is a major transporter for digoxin efflux. |
| Comment: The mechanism of a PDDI MUST be reported if known. The description SHOULD be written for a clinician audience and include details that help the clinician decide what course of management action to take. To reduce ambiguity, the description MAY refer to specific drugs or health conditions using codes from terminologies. |
| Recommended Action: For patients with a reliable plasma digoxin concentration in normal range, it is reasonable to anticipate an increase in plasma concentrations after the initiation of cyclosporine. Following initiation, close monitoring and adjusting the digoxin dose as needed is recommended. |
| Comment: Any recommended actions that apply to all patient exposures SHOULD be stated using clear and concise language. The recommended action statement SHOULD also provide citations to evidence for a suspected drug-drug interaction (not provided in this example). Recommendations that depend on contextual information/modifying factors SHOULD be mentioned separately to support context-specific presentation of such information. |
Contextual information/modifying factors:
|
| Comment: Contextual information/modifying factors are necessary for alerts that are both sensitive and specific. Like clinical consequences, each known factor SHOULD be stated as specifically as possible. The factors SHOULD be amenable to implementation as executable logic using value sets from clinical terminologies such as RxNorm, the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System (ATC), ICD-10, and SNOMED-CT. As is used in this example, each factor SHOULD be related to a specific recommended action that is supported by the evidence for a suspected drug-drug interaction |
| Frequency of Exposure to the PDDI: Unknown |
| Comment: Frequency of exposure and frequency of harm information is rarely available but can help a clinician assess the risk/benefit trade-off of exposure to PDDI. Such information SHOULD be provided if available. |
| Frequency of Harm for persons who have been exposed to the PDDI: Unknown |
| Comment: Frequency of exposure and frequency of harm information is rarely available but can help a clinician assess the risk/benefit trade-off of exposure to PDDI. Such information SHOULD be provided if available. |