

This fragment is available on index.html
This publication includes IP covered under the following statements.
| Type | Reference | Content |
|---|---|---|
| web | pacioproject.org | The Personal Functioning and Engagement Encounter Diagnosis Profile was developed by the Personal Functioning and Engagement subgroup of the Post-Acute Care InterOperability (PACIO) project . The subgroup contained experts in: personal functioning and engagement related diagnoses (e.g., Physical Therapists), EHR implementation and interoperability, HL7 FHIR, and user-centered design. PACIO is sponsored by the US Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) and by the MITRE Corporation . |
| web | www.mitre.org | The Personal Functioning and Engagement Encounter Diagnosis Profile was developed by the Personal Functioning and Engagement subgroup of the Post-Acute Care InterOperability (PACIO) project . The subgroup contained experts in: personal functioning and engagement related diagnoses (e.g., Physical Therapists), EHR implementation and interoperability, HL7 FHIR, and user-centered design. PACIO is sponsored by the US Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) and by the MITRE Corporation . |
| web | pacioproject.org | The Personal Functioning and Engagement Condition Problems and Health Concerns Profile was developed by the Personal Functioning and Engagement subgroup of the Post-Acute Care InterOperability (PACIO) project . The subgroup contained experts in: supporting patients’ nutrition and diet (e.g., physical therapists, speech language pathologists), EHR implementation and interoperability, HL7 FHIR, and user-centered design. PACIO is sponsored by the US Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) and by the MITRE Corporation . |
| web | www.mitre.org | The Personal Functioning and Engagement Condition Problems and Health Concerns Profile was developed by the Personal Functioning and Engagement subgroup of the Post-Acute Care InterOperability (PACIO) project . The subgroup contained experts in: supporting patients’ nutrition and diet (e.g., physical therapists, speech language pathologists), EHR implementation and interoperability, HL7 FHIR, and user-centered design. PACIO is sponsored by the US Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) and by the MITRE Corporation . |
| web | www.who.int | The purpose of the Personal Functioning and Engagement Goal Profile is to facilitate exchange between post-acute care and other health care settings of personal functioning and engagement goals for post-acute care patients. For this profile, “post-acute care” is defined as “care that is provided to individuals who need additional help recuperating from an acute illness or serious medical procedure” cite ; “personal” is defined as relating to an individual person, as opposed to a group, system, or organization; “functioning” is defined as what the person can do, the help they need, and the effects of contributing factors, including physiological, environmental, and personal conditions and encompasses body functions, activities, and participation cite ; “engagement” is defined as participating in one’s life, as opposed to being a passive observer. |
| web | pacioproject.org | The Personal Functioning and Engagement Goal Profile was developed by the Personal Functioning and Engagement subgroup of the Post-Acute Care InterOperability (PACIO) project . The subgroup contained experts in: supporting patients’ nutrition and diet (e.g., physical therapists, speech language pathologists), EHR implementation and interoperability, HL7 FHIR, and user-centered design. PACIO is sponsored by the US Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) and by the MITRE Corporation . |
| web | www.mitre.org | The Personal Functioning and Engagement Goal Profile was developed by the Personal Functioning and Engagement subgroup of the Post-Acute Care InterOperability (PACIO) project . The subgroup contained experts in: supporting patients’ nutrition and diet (e.g., physical therapists, speech language pathologists), EHR implementation and interoperability, HL7 FHIR, and user-centered design. PACIO is sponsored by the US Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) and by the MITRE Corporation . |
| web | pacioproject.org | The Personal Functioning and Engagement Nutrition Order Profile was developed by the Personal Functioning and Engagement subgroup of the Post-Acute Care InterOperability (PACIO) project . The subgroup was comprised of clinical and technical experts including dieticians, speech language pathologists, physical therapists, occupational therapists, nurses, physicians, and home and community-based service professionals. |
| web | unitsofmeasure.org | The clinical test or procedure result value. If a numeric value, valueQuantity.code SHALL be selected from UCUM . A FHIR UCUM Codes value set that defines all UCUM codes is in the FHIR specification. |
| web | paciowg.github.io | Note: The Personal Functioning and Engagement IG replaces the previously published PACIO Functional Status and PACIO Cognitive Status FHIR IGs as well as the PACIO SPLASCH IG that had been under development. This decision was made because the profiles created for these IGs all had very similar structures. For the Observation-based profiles, the vocabulary used for the category (referenced in the Category Tag profile) is tied to the value set from which the code was to be pulled. The use of health domains based on ICF categories and corresponding value sets of observation codes for each domain replaces the need for multiple IGs, allowing this IG to define only a single set of profiles that cover all domains. |
| web | icd.who.int | This IG provides examples of some ICF domains and some of their associated, PACIO-vetted, preferred value sets. To view the ICF and all of its domains, please view the ICF browser maintained by the World Health Organization (WHO). |
| web | www.who.int | Functioning : in-scope data relates to what the person can do, the help they need, and the effects of contributing factors, including physiological, environmental, and personal conditions. The International Classification of Functioning, Disability, and Health (ICF), published by the World Health Organization (WHO), defines the term, “functioning,” as an umbrella term for body functions, activities, and participation. |
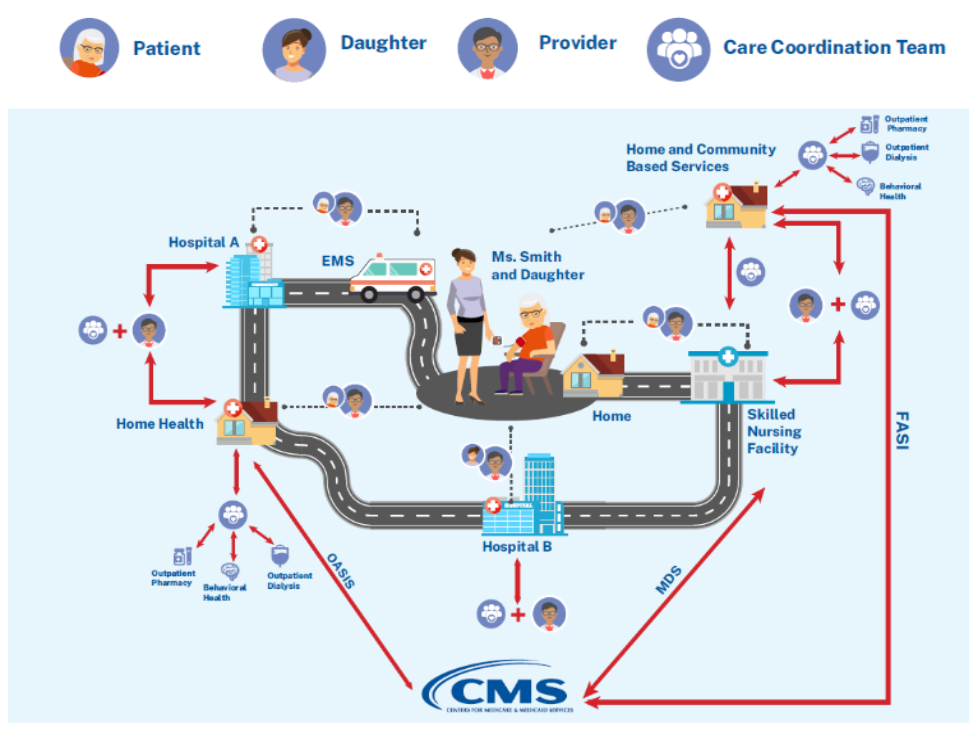
| web | jamanetwork.com | Unfortunately, healthcare providers across the spectrum of care, including at long-term care facilities and down-stream settings such as home- and community-based services, often face challenges sharing important assessment and observation data with and obtaining it from other healthcare providers involved in the person’s care. Forty-five percent of Medicare beneficiaries require post-acute care services after hospitalization (RTI International analysis of 2014 Medicare claims under contract with the Assistant Secretary for Planning and Evaluation, August 2018 (aea0315)), but a 2020 study that assessed continuity between hospitals and skilled nursing facilities (SNF) found that SNFs received complete mental status information at transition of care only 6% of the time. JAMA Network Open. 2021;4(1):e2033980. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.33980 . This failure to exchange accurate, timely data often leads to inefficient workflows, duplicative data entry, and increased risk of harm attributable to missing or inaccurate information. |
| web | nap.nationalacademies.org | The purpose of this IG is to offer a framework that providers and organizations across the spectrum of care can use to exchange observational assessment information. By using this framework to put accessible, usable, and timely data into the hands of providers, patients, and their caregivers, organizations can foster appropriate care for the whole person, promoting their ability to actively engage in daily life at home and in the community and supporting the person in achieving their optimal quality of life. This IG facilitates efforts to build more interoperable health IT systems that support data sharing, first outlined in the landmark Institute of Medicine Report To Err is Human: Building a Safer Health System , and is congruent with current federal efforts (e.g., The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services Promoting Interoperability Programs). |
| web | icd.who.int | Mental functions , captured as a part of evaluating an individual's cognitive status, |
| web | icd.who.int | Mobility and Self-care , captured as a part of evaluating an individual's functional status, and |
| web | icd.who.int | Mobility and Self-care , captured as a part of evaluating an individual's functional status, and |
| web | icd.who.int | Communication and Voice and speech functions , captured as a part of evaluating an individual's spoken language communication, swallowing, and hearing. |
| web | icd.who.int | Communication and Voice and speech functions , captured as a part of evaluating an individual's spoken language communication, swallowing, and hearing. |
| web | apps.who.int | More information on the domains currently defined in this IG, how codes are assigned to the domain-based value sets, and examples drawn from post-acute care assessments required by the IMPACT Act can be found on the Domain Support page. More information on all of the categories that ICF defines can be found in the ICF Browser . |
| web | www.iso.org |
ISO maintains the copyright on the country codes, and controls its use carefully. For further details see the ISO 3166 web page: https://www.iso.org/iso-3166-country-codes.html
Show Usage
|
| web | ucum.org |
The UCUM codes, UCUM table (regardless of format), and UCUM Specification are copyright 1999-2009, Regenstrief Institute, Inc. and the Unified Codes for Units of Measures (UCUM) Organization. All rights reserved. https://ucum.org/trac/wiki/TermsOfUse
Show Usage
|
| web | www.udap.org | Unified Data Access Profiles (UDAP) recommended by the ONC FHIR At Scale Taskforce (FAST) security tiger team. |
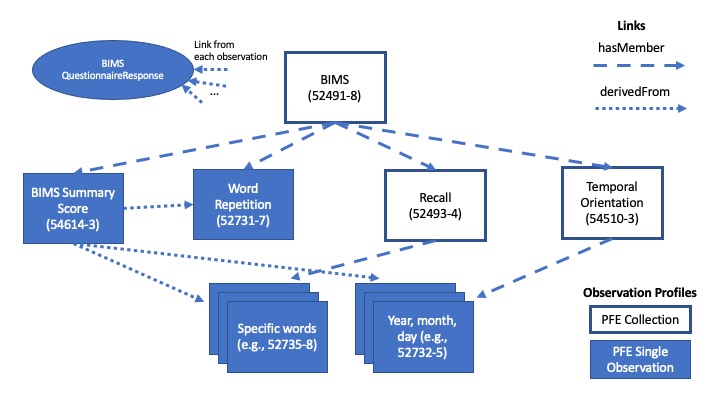
| web | www.mocatest.org | shorter assessments that target specific areas such as the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) or the swallowing panel that is part of the American Speech-Language-Hearing Association (ASHA) National Outcomes Measurement System (NOMS) program. |
| web | www.mocatest.org | Partially Codified – These instruments generally have standardized question and answer pairs and a code to describe the instrument and total score. However, critical meta data or other information may only be found on the assessment itself. For example, the MoCA has codes for only the summary score and not the component questions. |
| web | www.mocatest.org | Not all assessment tools have standardized codes for all of their questions. For example. the MoCA has a coded representation for the summary score, not the individual questions. In cases like this, QuestionnaireResponses MAY not be fully mapped to structured observations, meaning that some information remains only in the QuestionnaireResponse instance, or on the paper form. |
Patient_Journey.png 
|
StructureExample_BIMS.jpg 
|
pacio.png 
|
tree-filter.png 
|