This page is part of the Making EHR Data MOre available for Research and Public Health (MedMorph) Healthcare Surveys Reporting Content IG (v1.0.0: STU1 Release 1) based on FHIR R4. This is the current published version. For a full list of available versions, see the Directory of published versions 
The section identifies the business needs including specific user stories outlining the health care surveys reporting data exchange needs.
The purpose of the Health Care Surveys Content Implementation Guide (IG) is to identify the hospital (e.g., emergency department (ED), inpatient care) and ambulatory care data that will be extracted from Data Sources (e.g., Electronic Health Records (EHR), clinical data repository) via Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR®) Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) and sent to a system hosted at the federal level. This use case will help define how electronic data can be used in automated data collection, reducing burden for the healthcare provider and data dource with the goal of increasing the submission of timely quality health care data to the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS). In the past predominate ambulatory (manual medical record abstraction) and hospital (claims) data collection methods are burdensome for providers, lack clinical richness, and are inefficient for NCHS. The HL7 Clinical Document Architecture (CDA®) R2 Implementation Guide: National Health Care Surveys Release 1, Draft Standard for Trial Use (DSTU) Release 1.2 - US Realm, 2016, is available-as a standards-based as well as a Promoting Interoperability measure-data submission option for providers. This CDA IG has improved NCHS EHR data submissions, but some providers have found it burdensome and NCHS has identified some data quality issues in submissions by this method.
Utilizing this IG, which is tightly aligned with newly available standards such as FHIR R4 APIs and the United States Core Date for Interoperability (USCDI)/US Core Profiles, for electronic reporting will increase the response rate of sampled hospitals and ambulatory health care providers to the National Hospital Care Survey (NHCS) and the National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey (NAMCS) over other data collection approaches. This will also increase the volume, quality, completeness, and timeliness of the data submitted to the NHCS and NAMCS. This reporting approach via automated means (without provider involvement) will reduce the burden associated with survey participation and reduce costs associated with recruiting hospital and ambulatory health care providers.
The goals of the Health Care Survey submission use case include:
In-Scope
Out-of-Scope
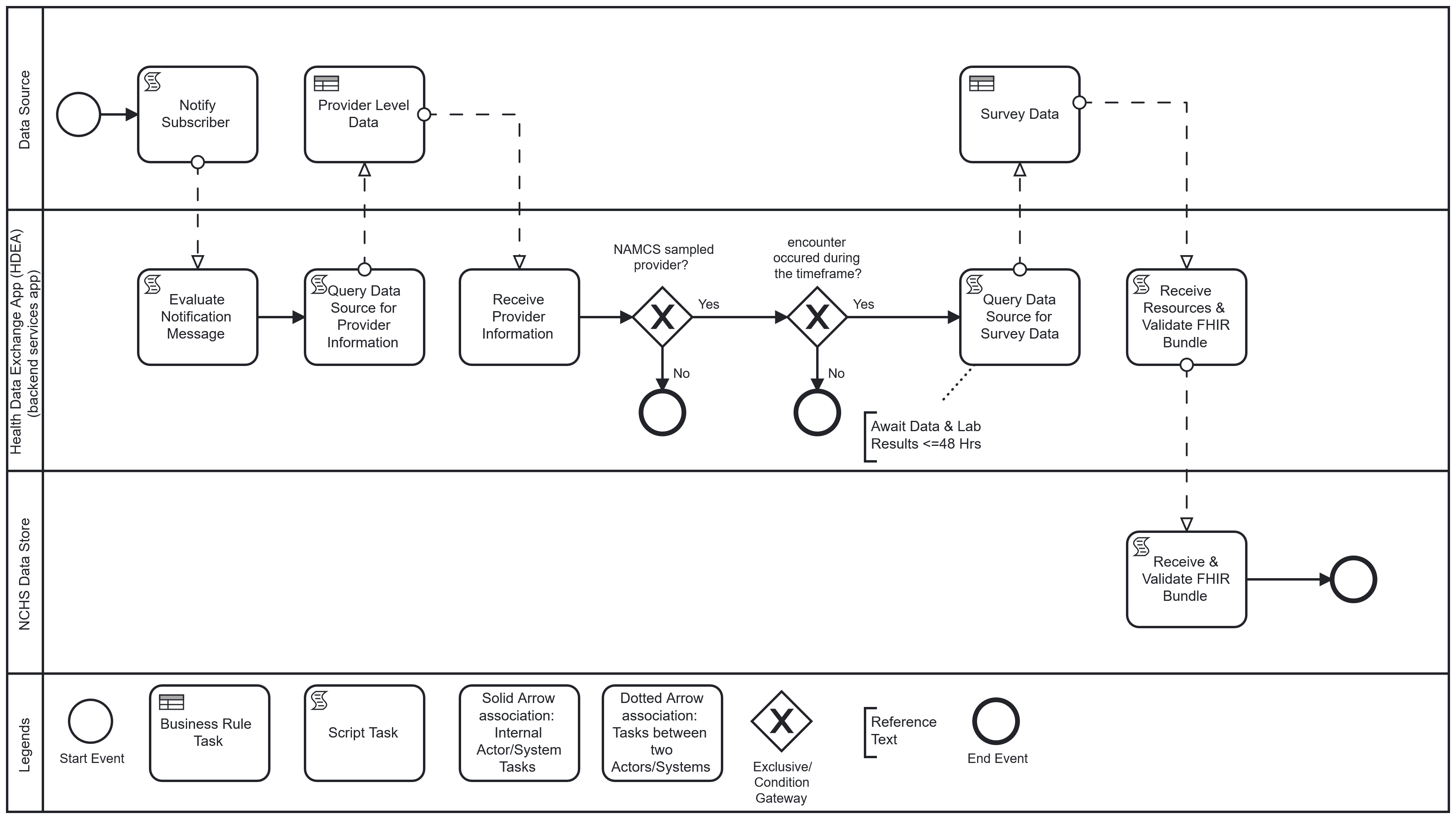
Background: The National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey (NAMCS) is based on a sample of patient visits to non-federally employed office-based physicians (primary care or specialist) who are primarily engaged in direct patient care. Starting in 2006, a separate sample of visits to community health centers (CHC) was added; in 2021, the former CHC sample of NAMCS was redesigned and launched as the health center (HC) component. NAMCS collects an encounter-based set of demographic and clinical data generally available in a medical record for any type of visit.
Workflow: Upon completion of an encounter, the physician or licensed clinician, using the EHR, completes and closes the clinical encounter (“sign off”). This “sign off” triggers the Health Data Exchange App (HDEA), MedMorph’s backend services app, to evaluate the completed encounter. The completed encounter evaluation by the HDEA includes validating that the provider associated with the encounter is a “sampled” NAMCS provider and the encounter occurred within a specified timeframe. If the encounter meets the criteria, and after a lag period to allow for lab results to post when applicable, the HDEA requests a set of FHIR resources representing patient-level and select provider-level data of the encounter from the Data Source. The obtained resources are validated (e.g., conformant to the appropriate FHIR profiles) and transmitted to NCHS where they are received, acknowledged, and loaded into the NCHS Data Store.
The following is a diagram of the workflow based on the above user story used for Health Care Surveys Reporting in the Ambulatory Setting:
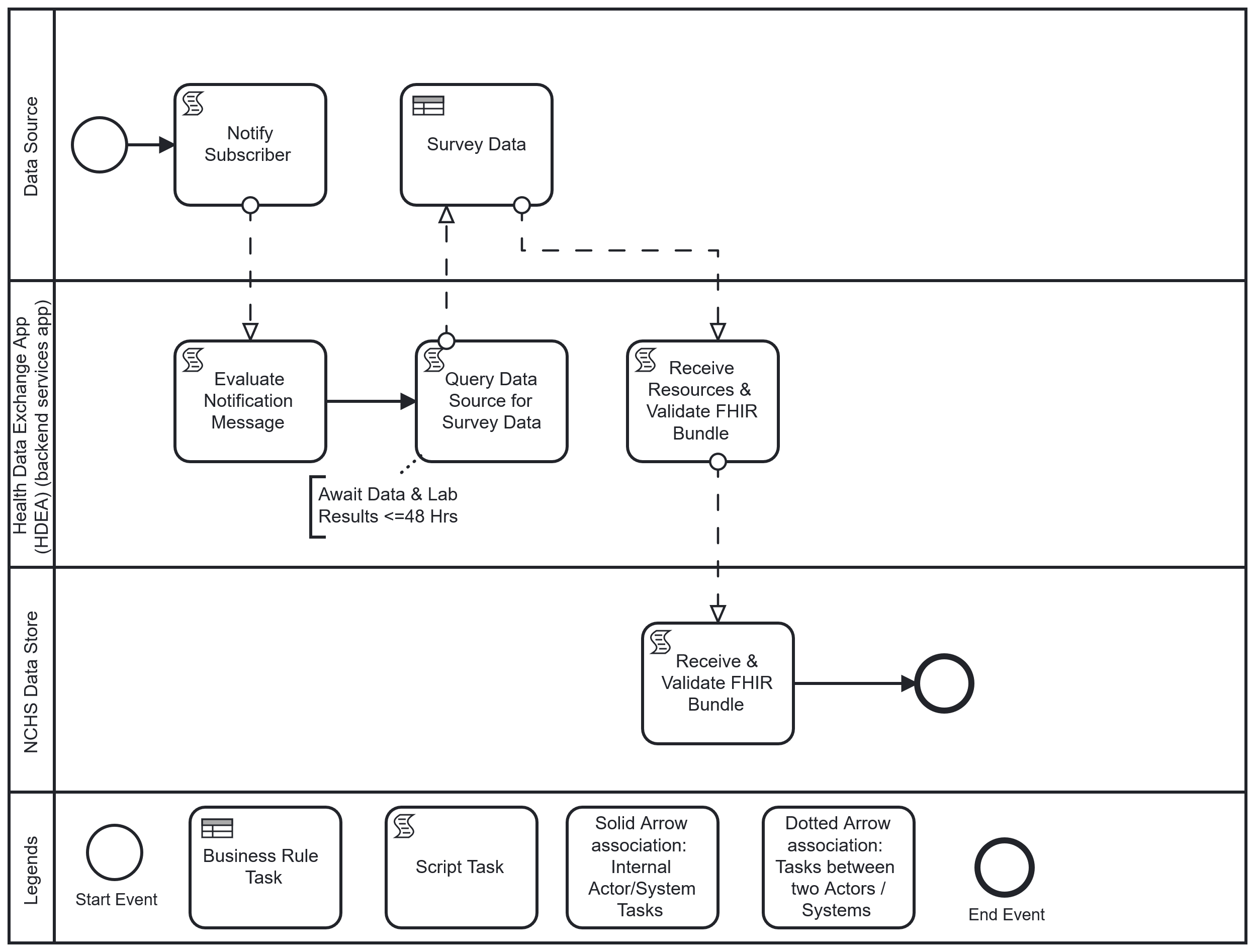
Background: The National Hospital Care Survey (NHCS) is an electronic data collection, gathering Uniform Bill (UB) 04 administrative claims data or electronic data from sampled hospitals. NHCS is designed to provide reliable and timely nationally representative healthcare utilization data for hospital-based settings. NHCS collects all inpatient discharges, and ED encounters from sampled hospitals for a survey period of one year. NHCS’ sample is drawn from all non-federal US hospitals with a bed size > 6.
Workflow: Upon completion of an inpatient or ED encounter, the physician or licensed clinician completes and closes the clinical encounter (“sign off”). This “sign off” triggers the HDEA to evaluate the completed encounter against the NHCS criteria. If the encounter meets the survey criteria, and after a lag period to allow for lab results to post when applicable, the HDEA requests a set of FHIR resources representing patient-level and select provider-level data of the encounter from the Data Source. Once obtained and validated, these resources are transmitted to NCHS where they are received, acknowledged, validated, and loaded into the NCHS Data Store.
The following is a diagram of the workflow based on the above user story used for Health Care Surveys Reporting for the Hospital Setting:
The following actors from the MedMorph RA IG are used by the Health Care Surveys Reporting use cases.
This section outlines the high-level interactions between the various MedMorph Actors and Systems listed above. These interactions are shown in Figure 2.3 along with the descriptions of each step.
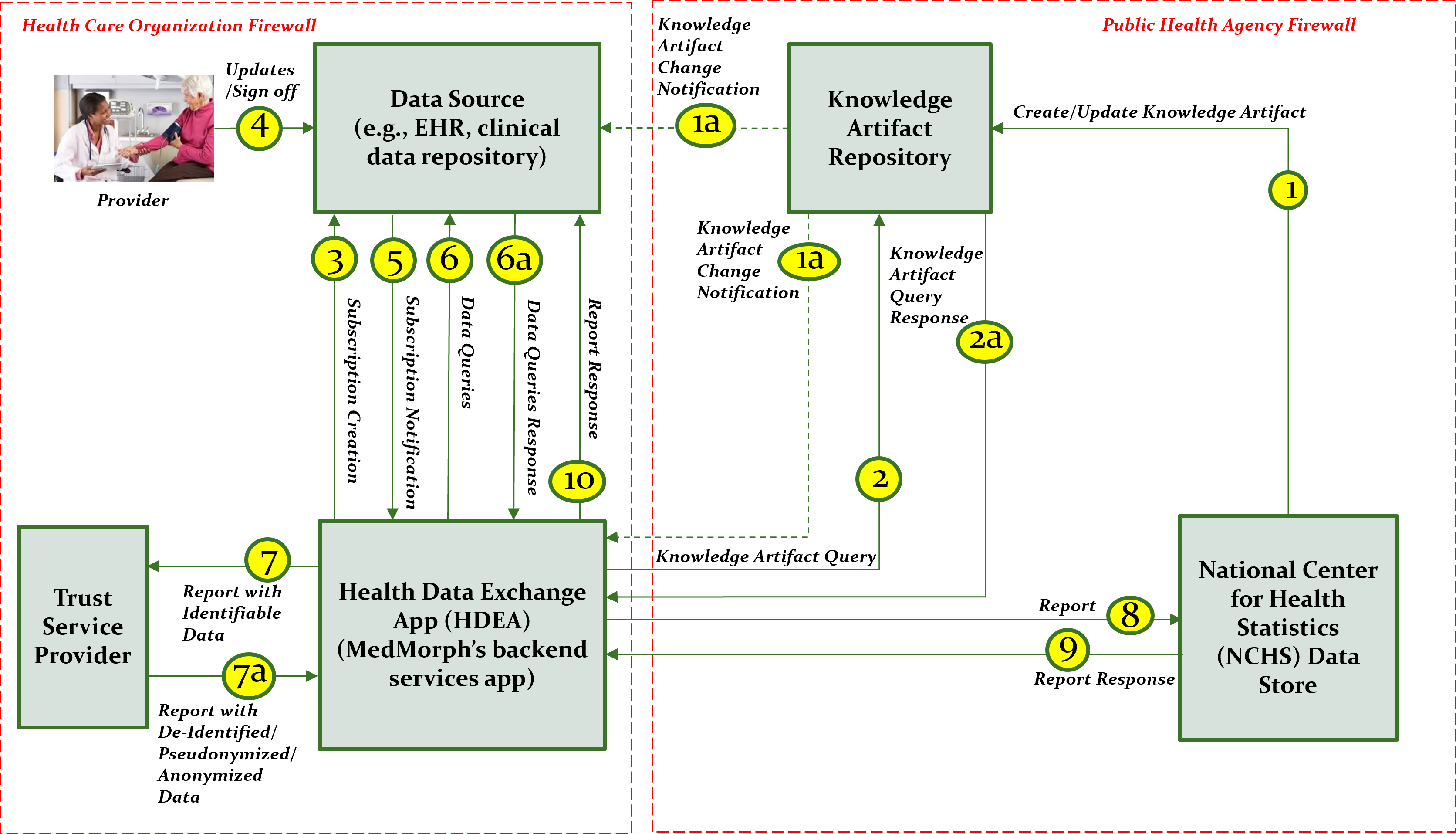
The descriptions for each step in the above diagram include: