This page is part of the Da Vinci Patient Cost Transparency Implementation Guide (v0.1.0: STU 1 Draft) based on FHIR (HL7® FHIR® Standard) R4. The current version which supersedes this version is 2.0.0. For a full list of available versions, see the Directory of published versions
The below describes the process of initiating the creation of an AEOB and the process of receiving or retrieving an AEOB. Note: An AEOB includes all GFEs as well as other required information.
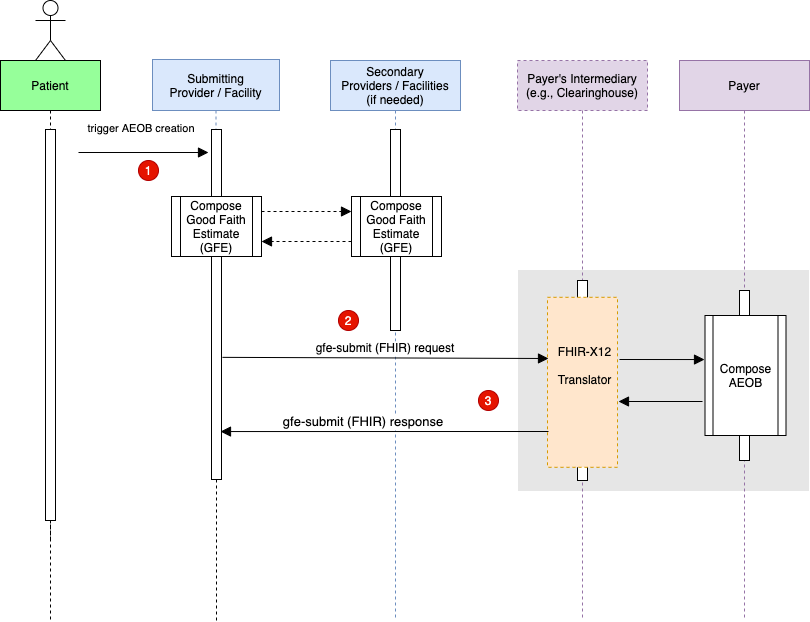
A patient schedules a service which triggers the composition of a collection of 1 or more GFEs. Note: The composition of the collection of GFEs is currently not in scope for this IG. In other words, how the scheduling provider coordinates with other providers is currently not in scope for this IG.
The provider uses the gfe-submit operation to submit the GFE bundle to the payer or payer intermediary endpoint. This is a POST request.
The AEOB bundle is created asynchronously. Because of this the AEOB bundle is not complete at this point. This is because the GFE processing and adjudication has not taken place yet. Therefore, each AEOB instance in the bundle should now contain one of these ExplanationOfBenefit.outcome: queued, error, or partial. The gfe-submit response will also contain a Bundle.identifier.
The Bundle.identifier can now be used to run a AEOB FHIR query to check the AEOB ExplanationOfBenefit.outcome(s) and receive the completed bundle. The AEOB is complete when ExplanationOfBenefit.outcome is equal to complete. This process is explained in more detail in the Get completed AEOB from payer section.
Note: The translation from FHIR to X12 and back to FHIR is not required to be conformant with this IG.

The patient receives a notification that the AEOB is complete along with an Bundle.identifier which identifies their AEOB.
The patient authorizes/authenticates and receives an access token.
The patient requests the AEOB by using the access token and Bundle.identifier. The patient receives the AEOB Bundle.
Note: The patient above could be a third-party portal or provider portal.
MRI Scenario
Assumptions:
• Patient has single commercial insurance coverage and plans to use it
• This is clinically appropriate (Clinical Decision Support (CDS) Score)
• Service Location is known (e.g., Address)
• All providers are in network - PCP, imaging facility, and reading radiologist
• If a medical management technique, such as Prior Authorization is required, a disclaimer indicating this will be included in the Advanced EOB and does not impact the GFE, per the No Surprises Act (Section 111(a)(f)(1)(F)).
GFE Professional
GFE Institutional
| Term | Proposed Definition |
|---|---|
| AEOB | The No Surprises Act requires that group health plans and insurers provide advance cost estimates, called Advanced Explanations of Benefits (AEOBs), for scheduled services. |
| Allowed Amount | The maximum amount a plan will pay for a covered health care service. May also be called “eligible expense,” “payment allowance,” “negotiated rate", "contractual amount", or "covered amount." |
| CAA Consolidated Appropriations Act |
Also called "H.R. 133". The CARES (Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security) Act implemented a variety of programs to address issues related to the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic. The Consolidated Appropriations Act continued many of these programs by adding new phases, new allocations, and new guidance to address issues related to the continuation of the COVID-19 pandemic. The Consolidated Appropriations Act (2021) was passed by Congress on December 21, 2020 and signed into law on December 27, 2020. |
| CDM Chargemaster |
Also called the Charge Description Master. A comprehensive listing of items billable to a hospital patient or a patient's health insurance provider. ... The chargemaster typically serves as the starting point for negotiations with patients and health insurance providers of what amount of money will actually be paid to the hospital. It is described as "the central mechanism of the revenue cycle" of a hospital. |
| Coinsurance | The percentage of costs of a covered health care service you pay (20%, for example) after a member has paid the deductible. |
| Collection of Services | The list of services expected to be performed as part of gathering the good faith estimate. Note: Purposely not using loaded words like "grouper" or "episode" Note: this may span across Providers (NPIs) |
| Copayment | A fixed amount ($20, for example) you pay for a covered health care service after you've paid your deductible. Let's say your health insurance plan's allowable cost for a doctor's office visit is $100. Your copayment for a doctor visit is $20. |
| Cost | To providers: the expense incurred to deliver health care services to patients. To payers: the amount they pay to providers for services rendered. To patients: the amount they pay out-of-pocket for health care services. |
| Data Exchange Method | The mechanism for sending and receiving the data (e.g. standard "transactions", APIs, fax, email). |
| Data Payload | The bundle of data or collection of the data elements being sent. |
| Deductible | The amount you pay for covered health care services before your insurance plan starts to pay. With a $2,000 deductible, for example, you pay the first $2,000 of covered services yourself. After you pay your deductible, you usually pay only a copayment or coinsurance for covered services. |
| De-identified minimum negotiated charge | The lowest charge that a hospital has negotiated with all third-party payers for an item or service. |
| De-identified maximum negotiated charge | The highest charge that a hospital has negotiated with all third-party payers for an item or service. |
| EOB Explanation of Benefits |
An EOB is a statement from a health insurance plan describing what costs it will cover for medical care or products received. |
| Fee Schedule | A complete listing of fees used by Medicare and commercial payers to pay doctors or other providers/suppliers. This comprehensive listing of fee maximums is used to reimburse a physician and/or other providers on a fee-for-service basis. |
| GFE | Good Faith Estimate |
| GFE Submitter | Any provider and/or facility that sends a Good Faith Estimate (GFE) to a payer to facilitate the creation of an advanced Explanation of Benefits (AEOB). |
| Gross Charge | The charge for an individual item or service that is reflected on a hospital's chargemaster absent any discounts. |
| HIPAA | The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (HIPAA) is a federal law that required the creation of national standards to protect sensitive patient health information from being disclosed without the patient’s consent or knowledge. The US Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) issued the HIPAA Privacy Rule to implement the requirements of HIPAA. The HIPAA Security Rule protects a subset of information covered by the Privacy Rule. |