This page is part of the Da Vinci Prior Authorization Support (PAS) FHIR IG (v1.0.0: STU 1) based on FHIR R4. The current version which supercedes this version is 1.1.0. For a full list of available versions, see the Directory of published versions 
This specification is currently published as a Standard for Trial Use (STU). Feedback is welcome and may be submitted through the FHIR change tracker indicating "US Da Vinci PAS" as the specification.
This implementation guide is dependent on other specifications. Please submit any comments you have on these base specifications as follows:
- Feedback on the FHIR core specification should be submitted to the FHIR change tracker with "FHIR Core" as the specification.
- Feedback on the US core profiles should be submitted to the FHIR change tracker with "US Core" as the specification.
Individuals interested in participating in the Prior Authorization Support or other HL7 Da Vinci projects can find information about Da Vinci here.
Note that this implementation guide is intended to support mapping between FHIR and X12 transactions. To respect X12 intellectual property, all mapping and X12-specific terminology information will be solely published by X12 and made available in accordance with X12 rules - which may require membership and/or payment. Please see this Da Vinci External Reference page for details on how to get this mapping.
Several of the profiles will require use of terminologies that are part of X12 which we anticipate being made publicly available. At such time as this occurs, the implementation guide will be updated to bind to these as external terminologies.
Prior authorization is a process commonly used by payer organizations to manage healthcare costs. However, the process of requesting and receiving prior authorizations can be slow and inefficient. The Administrative Simplification provisions of HIPAA mandate that the X12 278 Health Care Services Review Request for Review and Response be used for communicating prior authorization requests and responses. While few electronic health record (EHR) systems have implemented this interface, this functionality is often implemented as a portal solution and/or as a part of Practice Management and Revenue Cycle Management solutions. As a result, prior authorizations are often solicited by fax or by using payer-specific portals where clinicians re-key relevant information. Fax submission requires manual transcription on the payer side - and may result in significant back-and-forth requesting additional information prior to a decision being made. Re-keying information is inefficient and can result in data entry errors.
This implementation guide strives to enable direct submission of prior authorization requests from EHR systems using a standard already widely supported by most EHRs - FHIR. To meet regulatory requirements, these FHIR interfaces will communicate with an intermediary who, when necessary, can convert the FHIR requests to the corresponding X12 instances prior to passing the requests to the payer. Responses are handled by a reverse mechanism (payer to intermediary as X12, then converted to FHIR and passed to the EHR). Direct submission of prior authorization requests from the EHR will reduce costs for both providers and payers. It will also result in faster prior authorization decisions which will lead to improved patient care and experience.
When combined with the Da Vinci Coverage Requirements Discovery (CRD) and Documentation Templates and Rules (DTR) implementation guides, direct submission of prior authorization requests will further increase efficiency by ensuring that authorizations are always sent when (and only when) necessary, and that such requests will almost always contain all relevant information needed to make the authorization decision on initial submission.
The implementation guide also defines capabilities around the management of prior authorization requests, including checking the status of a previously submitted request, revising a previously submitted request and cancelling a request.
A high-level summary of how all of these IGs will work together can be seen below:
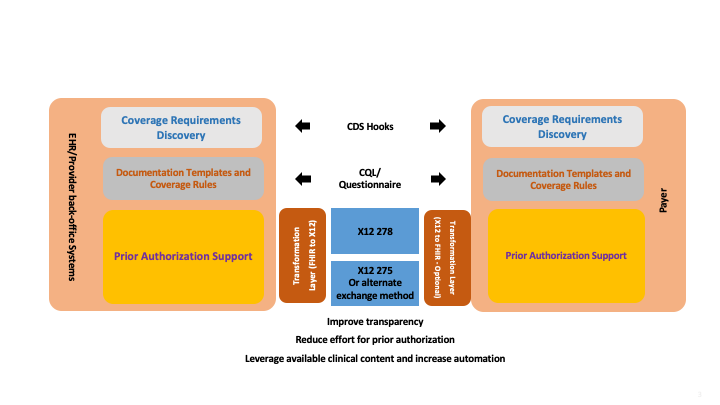
The implementation guide is organized into the following sections:
This implementation guide relies on the following other specifications:
This implementation guide defines additional constraints and usage expectations above and beyond the information found in these base specifications.