This page is part of the Documentation Templates and Rules (v1.0.0: STU 1) based on FHIR R4. This is the current published version. For a full list of available versions, see the Directory of published versions 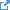
Da Vinci is an HL7-sponsored project that brings together the U.S. payer, providers, and technology suppliers (including EHR vendors) to help payers and providers to positively impact clinical, quality, cost, and care management outcomes using FHIR-related technologies. The project organizes meetings (face-to-face and conference calls) as well as Connectathons to find ways to leverage FHIR technologies to support and integrate value-based care (VBC) data exchange across communities. Da Vinci identifies value-based care use cases of interest to its member and the community as a whole.
The process that Da Vinci has adopted includes:
Additional information about Da Vinci, its members, the use cases and the implementation guides being developed can all be found on the HL7 website. Meeting minutes and other materials can be found on the Da Vinci Confluence page.
This implementation guide is part of a set of interrelated implementation guides that are focused on reducing clinician and payer burden. The Da Vinci ‘Burden Reduction’ implementation guides are:
The general flow of activity across all three IGs can be seen in the following diagram:
The guides overlap in the following ways:
All three implementation guides can be used together and intersect in that they perform business functions related to prior authorization. However the first two IGs also offer functionality that’s unrelated to prior authorization. The guides can function independently in a number of ways:
As such, implementers can choose to roll out these three implementation guides in whatever order or combination best meets their particular business objectives - though obviously coordinating with their communication partners so that there are other systems to interoperate with will also be important.
This IG uses terminology, notations and design principles that are specific to FHIR. It’s important to be familiar with some of the basic principles of FHIR as well as general guidance on how to read FHIR specifications. Readers who are unfamiliar with FHIR are encouraged to read the following prior to reading the rest of this IG.
This IG leverages and builds on the US Core IG defined by HL7 for sharing human EHR data in the US. Implementers need to familiarize themselves with the profiles in US Core.
This IG supports the R4 version of the FHIR standard.
| FHIR Version |
|---|
| FHIR R4 US Core |
Implementers should also familiarize themselves with the FHIR resources used within this IG.
| Resources |
|---|
| Questionnaire |
| QuestionnaireResponse |
| Task |
Clinical systems SHALL use the specification defined by US Core in exchanging information with payers. Implementers should be familiar with this specification.
Clinical systems and payer systems SHALL use the specification and workflows defined by Clinical Decision Support (CDS) Hooks to initiate CRD. Implementers should be familiar with this specification.
Clinical systems SHOULD use the specification and workflows defined by Coverage Requirements Discovery (CRD) to initiate DTR functionality with payers, where it is appropriate. Implementers should be familiar with this specification.
Client systems conformant to this IG SHALL also serve as a SMART on FHIR client. This is to allow DTR functionality to be invoked outside of regular EHR clinical workflows using a SMART on FHIR app to provide a consistent way of evaluating payer rules and documentation requirements across EHR implementations. As such client implementers will also need to be familiar with the SMART on FHIR specification. Payer implementers only need to be familiar with the SMART on FHIR specification if they plan to develop SMART apps for launch by CDS Hooks or other purposes.
Clinical systems SHALL use the specification and workflows defined by Structured Data Capture (SDC) to initiate DTR functionality with the payers. Implementers should be familiar with this specification.
Payer systems SHALL use the specification and workflows defined by Clinical Quality Language CQL to facilitate DTR functionality within clinical systems. Implementers should be familiar with this specification. Older versions of CQL such as STU 2 can be used provided they work with FHIR R4.
This IG does NOT mark any elements with the Must Support flag in its own profiles.
This IG also references the US Core IG. Da Vinci DTR implementations SHALL conform to the US Core IG Must Support Guidance where US Core IG resources are used.