This page is part of the Da Vinci Coverage Requirements Discovery (CRD) FHIR IG (v2.1.0: STU 2.1) based on FHIR (HL7® FHIR® Standard) R4. This is the current published version in its permanent home (it will always be available at this URL). For a full list of available versions, see the Directory of published versions
| Page standards status: Informative |
The current CRD, DTR, PAS, and CDex supporting the electronic Prior Authorization (ePA) workflow only focus on the interactions between the provider Health Information Technology (HIT) in total and the payer HIT in total, not the necessary interactions among the respective HIT solutions that make up the provider and payer HIT environment that need to participate in the ePA workflow.
Organizations might need a variety of combinations of HIT components to support new prior authorization regulatory requirements. The U.S. Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information (ONC) is considering a certification process where certified software can use generic (or generically referenced) relied-upon software to meet certain requirements and can clearly specify the capabilities they rely on without the need to test each permutation of relied-upon software with which they support the ePA workflow. Further guidance is needed for the interactions necessary within each of the provider and payer HIT configurations based on the functions/roles of those HIT solutions, and requires the relied upon software approach using predictable, standards-based capabilities to participate in an ePA workflow and for HIT that provides full support for ePA workflow through its certified HIT.
The following drawing demonstrates the CRD workflow exchanges between an integrated provider HIT environment and an integrated payer HIT environment in the upper portion. The lower portion of the CRD workflow drawing represents the potential for electronic Prior Authorization (ePA) coordinator functionality to play a role between the provider HIT and the payer HIT. It should be noted that the exchanges between the provider HIT (including any ePA) and the payer HIT (including any ePA) SHALL replicate all of the defined exchanges between provider and payer (represented by the green and orange arrows). The red and purple arrows are representative of information exchange between the Provider ePA and the Provider systems (red arrows) or the information exchange between the Payer ePA and the Payer systems (purple arrows).
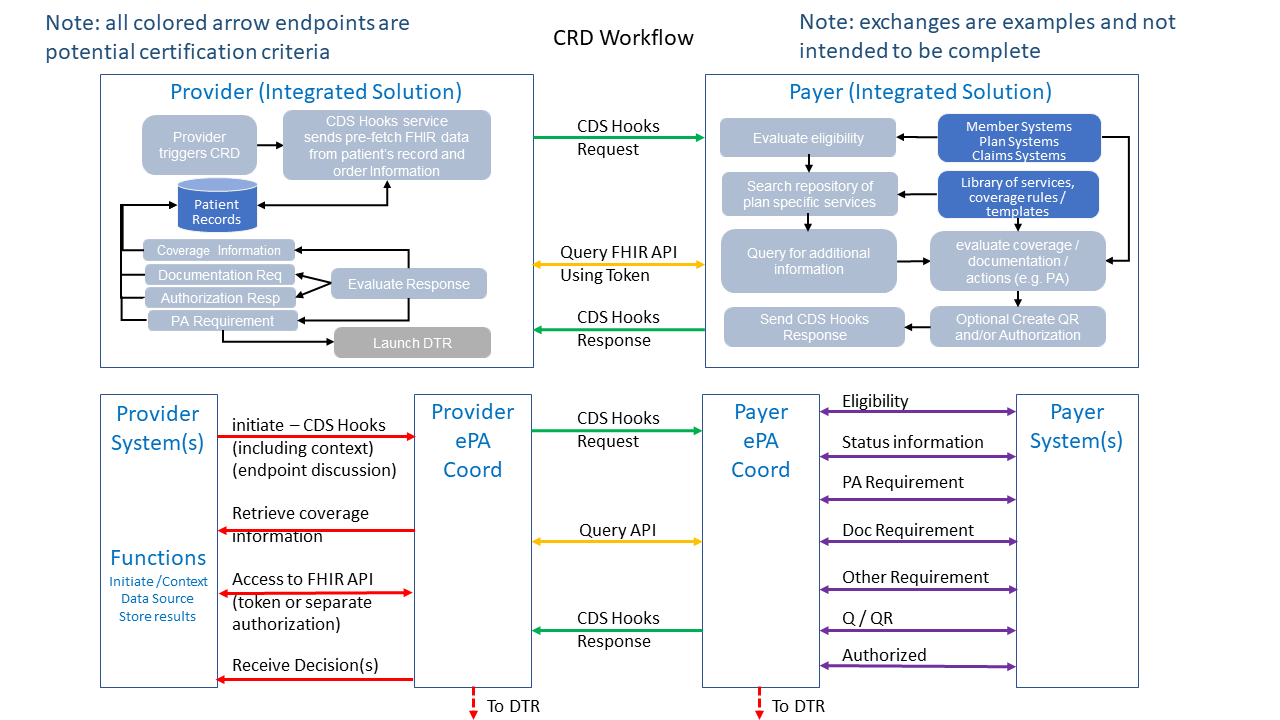 Figure 1 - CRD workflow with and without ePA coordinators
Figure 1 - CRD workflow with and without ePA coordinators
The following drawing provides additional detail regarding the exchanges between a provider ePA coordinator, multiple provider HIT systems and the payer. The boxes below the workflow drawing indicate the activities of the various components. From left to right:
The numbered workflow in the provider ePA coordinator box indicates the inputs from the provider HIT systems that are involved in creating the exchanges between the provider and the Payer. This includes:
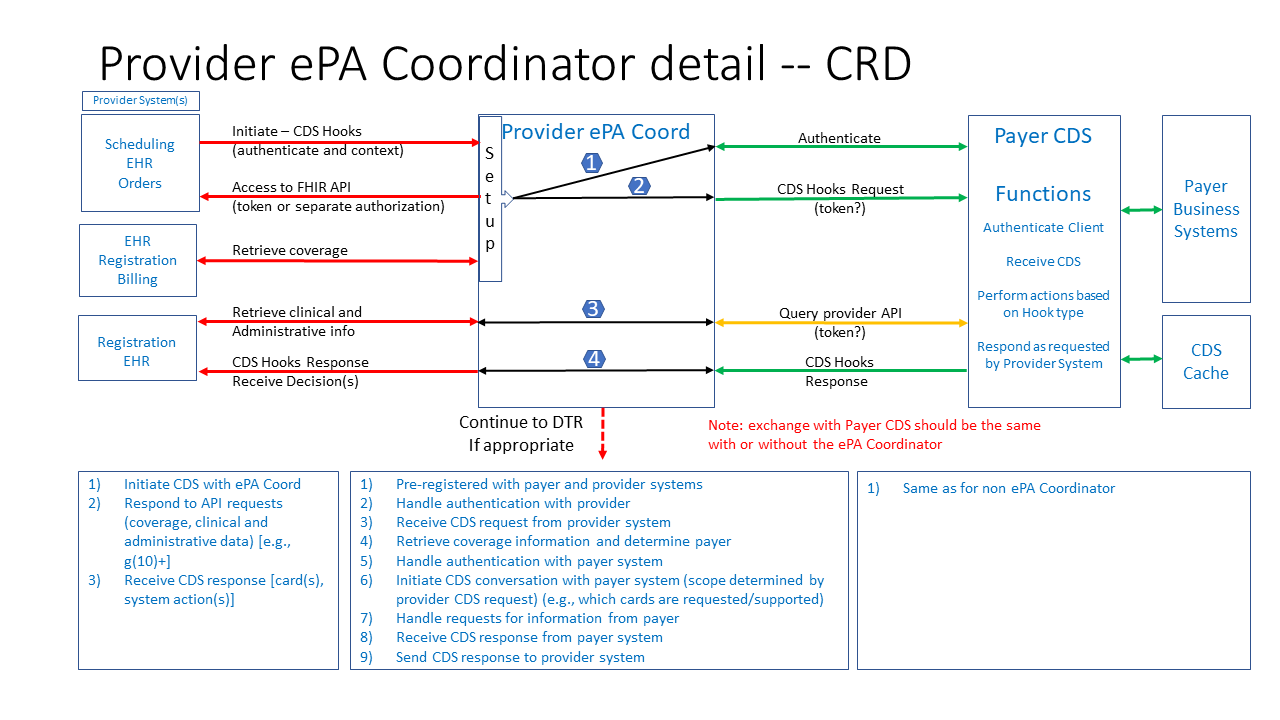 Figure 2 - Provider ePA coordinator detail
Figure 2 - Provider ePA coordinator detail
The following graphic and table provides an example of the type of interactions that will need to be supported between an ePA coordinator and the various provider HIT components. These interactions include:
The table briefly describes each action along with:
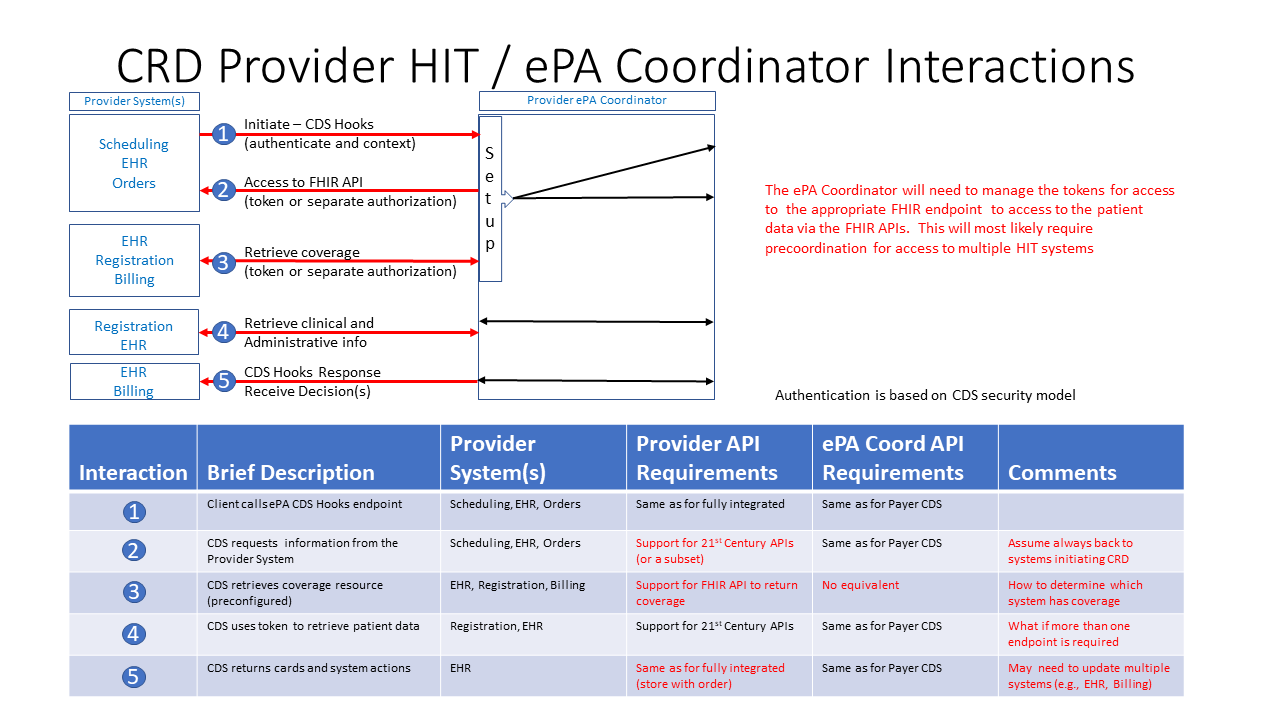 Figure 3 - Provider ePA coordinator interactions
Figure 3 - Provider ePA coordinator interactions
The above graphics and descriptions outline the relevant interactions that will be further documented in subsequent releases of this IG as implementations of various combinations of HIT further inform the specifications.