This page is part of the US Core (v5.0.1: STU5) based on FHIR (HL7® FHIR® Standard) R4. The current version which supersedes this version is 8.0.1. For a full list of available versions, see the Directory of published versions. Page versions: R8 R7 R6 R5
The Profile elements consist of both Mandatory and Must Support elements. Mandatory elements are elements with an minimum cardinality of 1 (min=1). The base FHIR Must Support guidance requires specifications to define exactly the support expected for profile elements labeled Must Support. The sections below illustrate how these elements are displayed and define the rules for interpreting profile elements and subelements labeled Mandatory and Must Support for requesters and responders.
Each profile provides several different formal views of all the must support elements in a tree format under tabs labeled “Differential Table”, “Snapshot Table”, and “Snapshot Table (Must Support)”.
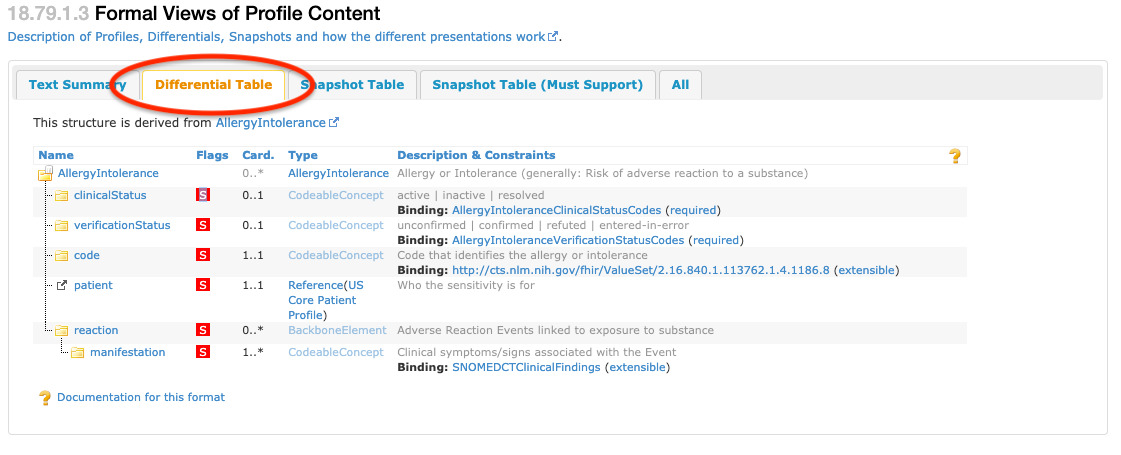
The elements labeled Must Support in the “Differential Table” view are flagged with an S. An example of this is illustrated in Figure 1.
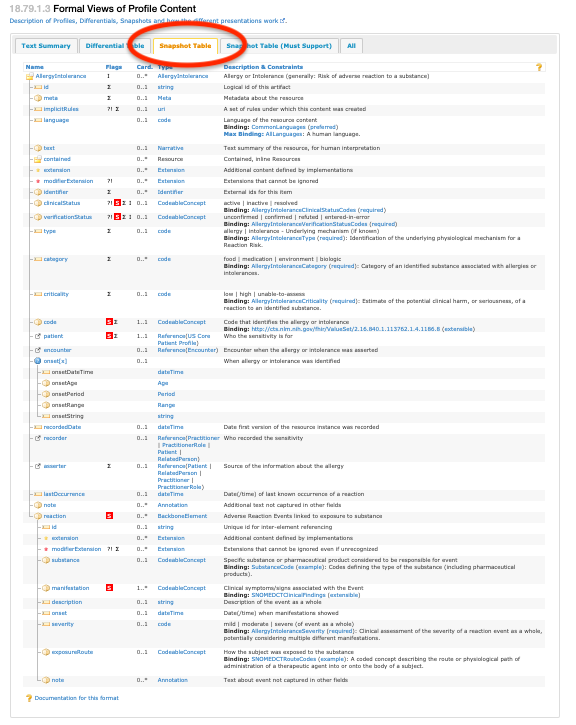
In the “Snapshot Table” view in Figure 2, all the must support elements defined for the profile, and any mandatory or must support elements inherited from a base profile (e.g. US Core Body Height Profile based on Vital Signs Profile), are flagged with an S. An example of the “Snapshot Table” is shown in Figure 2.
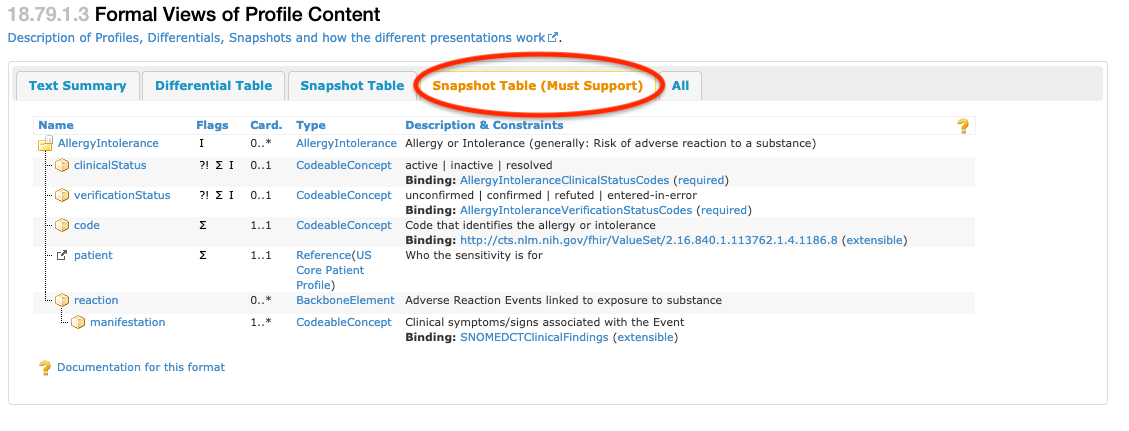
In the “Snapshot Table (Must Support)” view, all the elements presented in the view are either mandatory or must support elements for conformance to the profile. These elements are defined in the US Core Profile, mandatory elements inherited from the base specification and, for the US Core Vital Signs profiles, any mandatory or must support elements inherited from the FHIR base Vital Signs profile. An example of the “Snapshot Table (Must Support)” is shown in Figure 3.
When an element is mandatory (min=1), the data is expected to always be present. Very rarely it may not be and guidance for when data is missing is provided in the Missing Data section and in the next section. The convention in this guide is to mark all min=1 elements as must support unless the are nested under optional element. An example of this is CarePlan.status.
For querying and reading US Core Profiles, Must Support on any profile data element SHALL be interpreted as follows (see the Future of US Core page for writing and updating US Core Profiles):
unknown.The terms US Core Responder Actor US Core Requestor Actor are used throughout the guide and typically refer to a server or a client.
Readers are advised to understand FHIR Terminology requirements, FHIR RESTful API based on the HTTP protocol, along with FHIR Data Types, FHIR Search and FHIR Resource formats before implementing US Core requirements.
All the profile information for the US Core Implementation Guide is represented in a single CSV or Excel file. This may be useful to testers and analysts to review the must support and mandatory elements across profiles in a single table.
This Observation Summary Table compares Must Support Elements across all the US Core Observation Profiles.
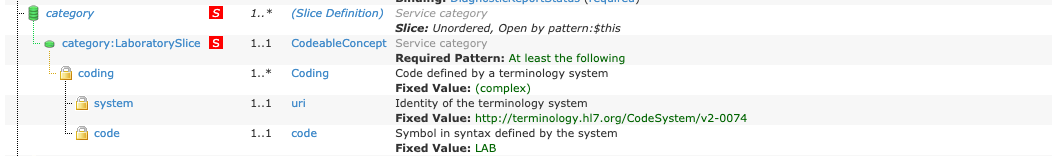
The StructureDefinitions define the US Core Profiles and the ElementDefinition.pattern which is used almost exclusively for the CodeableConcept and Coding datatypes. If the element is marked as must support and defined by a pattern then the pattern defines the elements and element values that the server SHALL be capable of providing.
For example the US Core DiagnosticReport Profile for Laboratory Results Reporting category element is defined with a pattern requiring fixed values in DiagnosticReport.category.coding.system and DiagnosticReport.category.coding.code for a Coding element. When claiming conformance to this profile:
DiagnosticReport.categoryUS Core Requestors SHALL be capable of processing these values in DiagnosticReport.category
Primitive elements are are single elements with a primitive value. If they are marked as must support, then the server SHALL be capable of providing the element value to meet the must support requirement.
For example, the US Core DiagnosticReport Profile for Laboratory Results Reporting issued element is a primitive instant datatype. When claiming conformance to this profile:
DiagnosticReport.issuedUS Core Requestors SHALL be capable of processing the value in DiagnosticReport.issued

Complex element are composed of primitive and/or other complex elements. Note that coded elements (CodeableConcept, Coding, and code datatypes) also have additional binding rules which are documented in the Coded Elements section.
For any complex element marked as must support, the server SHALL be capable of providing at least one of the sub-element values. If any sub-element is marked as must support it must meet the must support requirements as well and satisfy the must support requirement for the parent element.
For example, the US Core DiagnosticReport Profile for Report and Note exchange presentedForm element is labeled must support and has no must support sub-elements. When claiming conformance to this profile:
DiagnosticReport.presentedForm sub-element.US Core Requestors SHALL be capable of processing the value in DiagnosticReport.presentedForm.

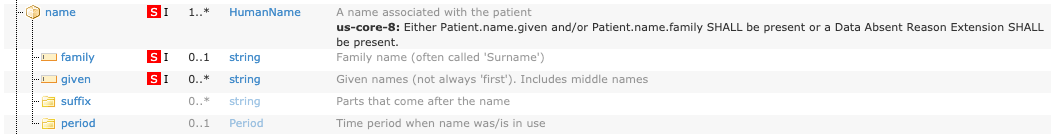
For example, the US Core Patient Profile name element is labeled must support and has must support sub-elements “family” and “given”. When claiming conformance to this profile:
Patient.name.family and Patient.name.given.US Core Requestors SHALL be capable of processing the value in value in Patient.name.family and Patient.name.given.
On the other hand, if any sub-element is marked as must support and the parent element is not, there is no expectation that you must support the parent. However, if the parent element is represented in the structure you must support the sub-element(s) marked as must support. There are no examples of US Core profiles that have this structure defined.
Systems can support the other elements, but this is not a requirement of US Core. The U.S. Core Data for Interoperability (USCDI) may require other elements, for example suffix.
This section documents additional must support requirements for the Reference element.
In certain profiles only specific resource references are labeled as Must Support.
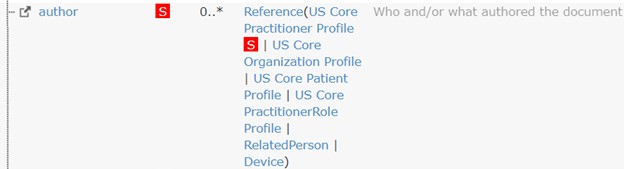
For example, the US Core DocumentReference Profile author US Core Practitioner Profile is labeled Must Support. When claiming conformance to the US Core DocumentReference Profile:
Systems can support other references but this is not a requirement of US Core.
In certain profiles only a single resource reference is present on an element labeled Must Support.
For example, the US Core AllergyIntolerance Profile patient is labeled Must Support. When claiming conformance to the US Core AllergyIntolerance Profile:
AllergyIntolerance.patient with a valid reference to a US Core Patient Profile.AllergyIntolerance.patient with a valid reference to a US Core Patient Profile.
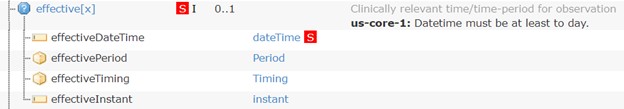
Some elements allow different data types (e.g. Observation.effective[x]) for their content. In these situations, only specific data type choice elements are labeled as Must Support.
For example, the US Core Laboratory Result Observation Profile effectiveDateTime is labeled Must Support. When claiming conformance to the US Core Laboratory Result Observation Profile:
Observation.effectiveDateTime.Observation.effectiveDateTime.Systems MAY support populating and processing other choice elements (such as, Observation.effectivePeriod) but this is not a requirement of US Core.
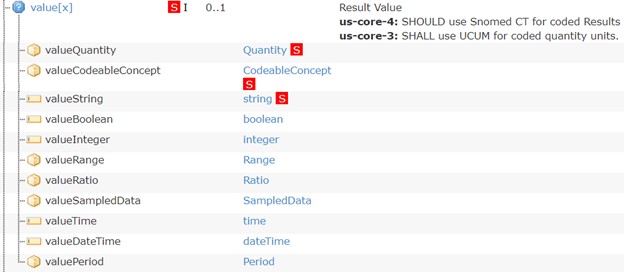
For the US Core Laboratory Result Observation Profile value element, multiple elements are labeled Must Support.
When claiming conformance to the US Core Laboratory Result Observation Profile:
Observation.valueQuantity, Observation.valueCodeableConcept, and Observation.valueString.Observation.valueQuantity, Observation.valueCodeableConcept, and Observation.valueString.Systems can support the other elements, but this is not a requirement of US Core.
There are several instances in this Guide where there is a choice of supporting one or another profile element to meet the must support requirement. In such instances, the server SHALL support at least one such element, and the client application SHALL support all such elements. There is no way to define this in a computable way, but these instances are clearly documented in the Profile specific implementation guidance sections.
For example:
US Core Medication Request Profile - The MedicationRequest resource can represent that information is from a secondary source using either a boolean flag or reference in MedicationRequest.reportedBoolean, or a reference using MedicationRequest.reportedReference to Practitioner or another resource type. Although both are marked as must support, servers are not required to support both a boolean and a reference, but SHALL choose to support at least one of these elements.