This page is part of the Common Data Models Harmonization FHIR IG (v1.0.0: STU 1) based on FHIR R4. This is the current published version in its permanent home (it will always be available at this URL). For a full list of available versions, see the Directory of published versions 
Section 937(a)(£) of the Public Health Service Act (PHS Act), as amended by section 6301(b) of the Affordable Care Act of 2010 (ACA), PL 111-148, 124 Stat. 119 (March 23, 2010), authorizes the Secretary of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) to provide for the coordination of relevant Federal programs to build data capacity for patient-centered outcomes research. The Office of the Assistant Secretary for Planning and Evaluation (ASPE) is delegated to coordinate the Department’s effort.
The current project, titled Harmonization of Various Common Data Models and Open Standards for Evidence Generation, is a multi-agency collaboration led by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Other agencies include the National Cancer Institute (NCI), National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (NCATS), the Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology (ONC) and the National Library of Medicine (NLM).
The purpose of this project is to provide patient-centered outcomes researchers as well as other researcher at various Federal Government Agencies, academia, etc. with access to broader observational data by leveraging existing PCORTF investments such as US-Core, Data Access Framework Research Implementation Guide (DAF-Research IG). The project leverages the lessons learned from ONC Query Health initiative completed in 2013/2014. Subsequently efforts in HL7 towards a language for clinical decision support and quality measurement and subsequently a harmonization of those efforts into CQL which enabled specification of query semantics against various data models including FHIR. In addition FHIR has developed StructureMap and ConceptMap resources which can be used for mapping and transformation between models. CDMH uses many of these concepts to build the necessary mappings and profiles that can be leveraged to make data captured and stored in different models available for researchers.
The purpose and goals of the overall project are as follows
Develop a common data architecture to create user driven queries of the following four common data model (CDMs) of four networks (Sentinel, i2b2/ACT, OHDSI and PCORnet).
This section outlines the abstract model, the specific actors and definitions that will be used for creating the implementation guide. Figure 1 below shows a pictorial representation of the data flows and the actors for the CDMH IG.
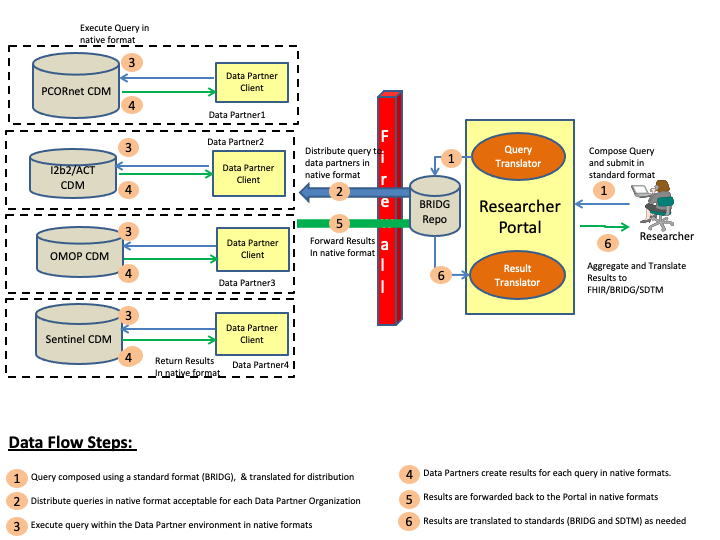
The steps involved in the CDMH project to includes creating a query, and then distributing the query to the various organizations (data partners), and collecting the results, and then finally viewing the results. These steps are is outlined in the above diagram and the definitions of the various actors can be found below.
Researcher Portal: Researcher Portal actor represents the capabilities that will be used by the researcher to compose the queries, distribute the queries and then view the returned results. Typically in a Researcher Portal implementation there will be many modular components, some of which are outlined below
Data Partner: Data Partner is any network or organization that is participating in the overall CDMH project and supports a data model or data models that can be queried by authorized researchers. The Data Partner holds the research data in a database conforming tousing one of the Common Data Models formats which and has appropriate security controls to verify/validate queries before releasing the results of a query.
Data Partner Client: Data Partner Client represents the capability that allows the Data Partner network or organization to control the queries being run and results being submitted to the Researchers.
CDMs: Common Data Models (CDMs) represent various physical representations of data that are commonly used by research networks and organizations currently. For CDMH project purposes, FDA’s Sentinel, PCORnet CDM, i2b2 and OMOP data models are being considered for mapping to FHIR.
The abstract model shown above allows researchers to compose queries in a uniform format and send them to the data partners for execution. In order to compose queries that can be executed against the different data models, the researcher has two options
For CDMH, Option 1 was not considered as it would add a significant burden on the researchers and the user interface to compose queries in each format and the maintenance of the overall solution would be complex. Hence Option 2 was chosen with BRIDG serving as the intermediary model. Leveraging BRIDG as the intermediary model has many benefits some of which are listed below
In the current phase of the project, BRIDG was chosen as the intermediary model to gain experience with the overall project and its implementation. In future phases, FHIR may be considered for playing the role of the intermediary model.
As as result of the architecture choices and decision made, the CDMH project developed a mapping between the various CDMs and BRIDG and then mapped BRIDG to FHIR. These mappings have been leveraged to finalize the mappings of the CDMs to FHIR and are outlined in the Mappings and Profiles section of the IG.
The following benefits will be realized by the industry using the CDMH project artifacts.
The DAF-Research FHIR IG outlines the overall workflows used to extract data from EHR systems, populate the CDMs and then allow the researcher to query these CDMs using mutliple formats embedded in FHIR resources and receive results using FHIR format. The CDMH FHIR IG complements the DAF-Research IG by providing the mappings from different CDMs to FHIR that can be used across multiple use cases. There are few overlaps between the CDMH and DAF-Research IG which will be harmonized on subsequent updates to DAF-Research and CDMH FHIR IGs.