This page is part of the FHIR Specification (v1.0.2: DSTU 2). The current version which supercedes this version is 5.0.0. For a full list of available versions, see the Directory of published versions 

Definitions for the sdcde-dataelement Profile.
| DataElement(SDCDE-DataElement) | |
| Definition | Sets expectations for SDC conformant systems wishing to share data elements between registries. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | DataElement |
| Alternate Names | Master Observation, Data Element, CDE |
| Comments | Often called a clinical template. |
| Invariants | Defined on this element inv-2: One and only one DataElement.code must have is-data-element-concept set to "true" (xpath: count(f:code/f:extension[@uri='http://hl7.org/fhir/StructureDefinition/11179-de-is-data-element-concept'])=1) |
| DataElement.id | |
| Definition | The logical id of the resource, as used in the URL for the resource. Once assigned, this value never changes. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | id |
| Comments | The only time that a resource does not have an id is when it is being submitted to the server using a create operation. Bundles always have an id, though it is usually a generated UUID. |
| DataElement.meta | |
| Definition | The metadata about the resource. This is content that is maintained by the infrastructure. Changes to the content may not always be associated with version changes to the resource. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | Meta |
| DataElement.implicitRules | |
| Definition | A reference to a set of rules that were followed when the resource was constructed, and which must be understood when processing the content. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | uri |
| Is Modifier | true |
| Comments | Asserting this rule set restricts the content to be only understood by a limited set of trading partners. This inherently limits the usefulness of the data in the long term. However, the existing health eco-system is highly fractured, and not yet ready to define, collect, and exchange data in a generally computable sense. Wherever possible, implementers and/or specification writers should avoid using this element as much as possible. |
| DataElement.language | |
| Definition | The base language in which the resource is written. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Binding | A human language. The codes SHALL be taken from http://tools.ietf.org/html/bcp47 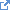 |
| Type | code |
| Comments | Language is provided to support indexing and accessibility (typically, services such as text to speech use the language tag). The html language tag in the narrative applies to the narrative. The language tag on the resource may be used to specify the language of other presentations generated from the data in the resource Not all the content has to be in the base language. The Resource.language should not be assumed to apply to the narrative automatically. If a language is specified, it should it also be specified on the div element in the html (see rules in HTML5 for information about the relationship between xml:lang and the html lang attribute). |
| DataElement.text | |
| Definition | A human-readable narrative that contains a summary of the resource, and may be used to represent the content of the resource to a human. The narrative need not encode all the structured data, but is required to contain sufficient detail to make it "clinically safe" for a human to just read the narrative. Resource definitions may define what content should be represented in the narrative to ensure clinical safety. |
| Control | 0..1 This element is affected by the following invariants: dom-1 |
| Type | Narrative |
| Alternate Names | narrative, html, xhtml, display |
| Comments | Contained resources do not have narrative. Resources that are not contained SHOULD have a narrative. |
| DataElement.contained | |
| Definition | These resources do not have an independent existence apart from the resource that contains them - they cannot be identified independently, and nor can they have their own independent transaction scope. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Resource |
| Alternate Names | inline resources, anonymous resources, contained resources |
| Comments | This should never be done when the content can be identified properly, as once identification is lost, it is extremely difficult (and context dependent) to restore it again. |
| DataElement.extension | |
| Definition | May be used to represent additional information that is not part of the basic definition of the resource. In order to make the use of extensions safe and manageable, there is a strict set of governance applied to the definition and use of extensions. Though any implementer is allowed to define an extension, there is a set of requirements that SHALL be met as part of the definition of the extension. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Extension |
| Alternate Names | extensions, user content |
| Comments | There can be no stigma associated with the use of extensions by any application, project, or standard - regardless of the institution or jurisdiction that uses or defines the extensions. The use of extensions is what allows the FHIR specification to retain a core level of simplicity for everyone. |
| Slicing | This element introduces a set of slices. The slicing rules are:
|
| DataElement.extension (http://hl7.org/fhir/StructureDefinition/11179-de-effective-period) | |
| Definition | Identifies the date on which the element became (or is expected to become) active and the date on which the element became (or is expected to become) retired. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | Extension (Extension Type: Period) |
| DataElement.extension (http://hl7.org/fhir/StructureDefinition/11179-de-document-reference) | |
| Definition | Identifies a document that conveys some sort of information related to the data element. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | Extension (Extension Type: Reference(DocumentReference)) |
| DataElement.extension (http://hl7.org/fhir/StructureDefinition/11179-de-administrative-status) | |
| Definition | Identifies internal processing status for the data element; e.g. "Under review". |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | Extension (Extension Type: CodeableConcept) |
| DataElement.extension (http://hl7.org/fhir/StructureDefinition/11179-de-change-description) | |
| Definition | Summarizes changes to the data element since the previous version. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | Extension (Extension Type: string) |
| DataElement.extension (http://hl7.org/fhir/StructureDefinition/11179-de-submitter-org) | |
| Definition | Organization responsible for submitting the data element to its registry. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | Extension (Extension Type: Reference(Organization)) |
| DataElement.extension (http://hl7.org/fhir/StructureDefinition/11179-de-registry-org) | |
| Definition | The organization that is the custodian for this data element. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | Extension (Extension Type: Reference(Organization)) |
| DataElement.modifierExtension | |
| Definition | May be used to represent additional information that is not part of the basic definition of the resource, and that modifies the understanding of the element that contains it. Usually modifier elements provide negation or qualification. In order to make the use of extensions safe and manageable, there is a strict set of governance applied to the definition and use of extensions. Though any implementer is allowed to define an extension, there is a set of requirements that SHALL be met as part of the definition of the extension. Applications processing a resource are required to check for modifier extensions. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Extension |
| Is Modifier | true |
| Alternate Names | extensions, user content |
| Comments | There can be no stigma associated with the use of extensions by any application, project, or standard - regardless of the institution or jurisdiction that uses or defines the extensions. The use of extensions is what allows the FHIR specification to retain a core level of simplicity for everyone. |
| DataElement.url | |
| Definition | An absolute URL that is used to identify this data element when it is referenced in a specification, model, design or an instance. This SHALL be a URL, SHOULD be globally unique, and SHOULD be an address at which this data element is (or will be) published. |
| Control | 1..1 |
| Type | uri |
| Must Support | true |
| DataElement.identifier | |
| Definition | Formal identifier that is used to identify this data element when it is represented in other formats, or referenced in a specification, model, design or an instance. |
| Control | 1..1 |
| Type | Identifier |
| Must Support | true |
| Comments | Typically, this is used for values that can go in a v3 II data type. |
| DataElement.version | |
| Definition | The identifier that is used to identify this version of the data element when it is referenced in a StructureDefinition, Questionnaire or instance. This is an arbitrary value managed by the definition author manually. |
| Control | 1..1 |
| Type | string |
| Must Support | true |
| Requirements | There may be multiple resource versions of the data element that have this same identifier. The resource version id will change for technical reasons, whereas the stated version number needs to be under the author's control. |
| Comments | N/A. |
| DataElement.name | |
| Definition | The term used by humans to refer to the data element. Should ideally be unique within the context in which the data element is expected to be used. |
| Control | 1..1 |
| Type | string |
| Must Support | true |
| Comments | This may be similar to the question used to prompt someone for a data element value, but the purpose is communicating about the data element, not asking the question. (Refer to the 'question' element for the latter.). |
| DataElement.status | |
| Definition | The status of the data element. |
| Control | 1..1 |
| Binding | The lifecycle status of a Value Set or Concept Map. The codes SHALL be taken from ConformanceResourceStatus |
| Type | code |
| Is Modifier | true |
| Must Support | true |
| Requirements | Allows filtering of data elements that are appropriate for use. |
| DataElement.experimental | |
| Definition | A flag to indicate that this search data element definition is authored for testing purposes (or education/evaluation/marketing), and is not intended to be used for genuine usage. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | boolean |
| Must Support | true |
| Comments | Allows filtering of search data element definitions that are appropriate for use vs. not. |
| DataElement.publisher | |
| Definition | The name of the individual or organization that published the data element. |
| Control | 1..1 |
| Type | string |
| Must Support | true |
| Requirements | Helps establish the "authority/credibility" of the data element. May also allow for contact. |
| Comments | Usually an organization, but may be an individual. This item SHOULD be populated unless the information is available from context. |
| DataElement.contact | |
| Definition | Contacts to assist a user in finding and communicating with the publisher. |
| Control | 1..* |
| Type | BackboneElement |
| Must Support | true |
| Comments | May be a web site, an email address, a telephone number (tel:), etc. |
| DataElement.contact.id | |
| Definition | unique id for the element within a resource (for internal references). |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | id |
| DataElement.contact.extension | |
| Definition | May be used to represent additional information that is not part of the basic definition of the element. In order to make the use of extensions safe and manageable, there is a strict set of governance applied to the definition and use of extensions. Though any implementer is allowed to define an extension, there is a set of requirements that SHALL be met as part of the definition of the extension. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Extension |
| Alternate Names | extensions, user content |
| Comments | There can be no stigma associated with the use of extensions by any application, project, or standard - regardless of the institution or jurisdiction that uses or defines the extensions. The use of extensions is what allows the FHIR specification to retain a core level of simplicity for everyone. |
| Slicing | This element introduces a set of slices. The slicing rules are:
|
| DataElement.contact.extension (http://hl7.org/fhir/StructureDefinition/11179-de-contact-address) | |
| Definition | Postal address for a contact for the data element. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | Extension (Extension Type: Address) |
| DataElement.contact.modifierExtension | |
| Definition | May be used to represent additional information that is not part of the basic definition of the element, and that modifies the understanding of the element that contains it. Usually modifier elements provide negation or qualification. In order to make the use of extensions safe and manageable, there is a strict set of governance applied to the definition and use of extensions. Though any implementer is allowed to define an extension, there is a set of requirements that SHALL be met as part of the definition of the extension. Applications processing a resource are required to check for modifier extensions. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Extension |
| Is Modifier | true |
| Alternate Names | extensions, user content, modifiers |
| Comments | There can be no stigma associated with the use of extensions by any application, project, or standard - regardless of the institution or jurisdiction that uses or defines the extensions. The use of extensions is what allows the FHIR specification to retain a core level of simplicity for everyone. |
| DataElement.contact.name | |
| Definition | The name of an individual to contact regarding the data element. |
| Control | 1..1 |
| Type | string |
| Must Support | true |
| Comments | If there is no named individual, the telecom is for the organization as a whole. |
| DataElement.contact.telecom | |
| Definition | Contact details for individual (if a name was provided) or the publisher. |
| Control | 1..1 |
| Type | ContactPoint |
| Must Support | true |
| DataElement.date | |
| Definition | The date this version of the data element was published. The date must change when the business version changes, if it does, and it must change if the status code changes. In addition, it should change when the substantive content of the data element changes. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | dateTime |
| Must Support | true |
| Comments | This refers to the "business" version, the DataElement.version which changes based on business processes. It does not refer to the date of the RESTful version which is part of the resource metadata. Additional specific dates may be added as extensions. |
| DataElement.useContext | |
| Definition | The content was developed with a focus and intent of supporting the contexts that are listed. These terms may be used to assist with indexing and searching of data element definitions. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Binding | Indicates the countries, regions, disciplines and other aspects of use within which this artifact is targeted for use. The codes SHALL be taken from Context of Use ValueSet; other codes may be used where these codes are not suitable |
| Type | CodeableConcept |
| Must Support | true |
| DataElement.useContext.id | |
| Definition | unique id for the element within a resource (for internal references). |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | id |
| DataElement.useContext.extension | |
| Definition | May be used to represent additional information that is not part of the basic definition of the element. In order to make the use of extensions safe and manageable, there is a strict set of governance applied to the definition and use of extensions. Though any implementer is allowed to define an extension, there is a set of requirements that SHALL be met as part of the definition of the extension. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Extension |
| Alternate Names | extensions, user content |
| Comments | There can be no stigma associated with the use of extensions by any application, project, or standard - regardless of the institution or jurisdiction that uses or defines the extensions. The use of extensions is what allows the FHIR specification to retain a core level of simplicity for everyone. |
| Slicing | This element introduces a set of slices. The slicing rules are:
|
| DataElement.useContext.extension (http://hl7.org/fhir/StructureDefinition/11179-de-classification-or-context) | |
| Definition | Identifies whether the useContext is a true context or a classification. |
| Control | 1..1 |
| Type | Extension (Extension Type: code) |
| DataElement.useContext.coding | |
| Definition | A reference to a code defined by a terminology system. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Coding |
| Requirements | Allows for translations and alternate encodings within a code system. Also supports communication of the same instance to systems requiring different encodings. |
| Comments | Codes may be defined very casually in enumerations, or code lists, up to very formal definitions such as SNOMED CT - see the HL7 v3 Core Principles for more information. Ordering of codings is undefined and SHALL NOT be used to infer meaning. Generally, at most only one of the coding values will be labelled as UserSelected = true. |
| DataElement.useContext.text | |
| Definition | A human language representation of the concept as seen/selected/uttered by the user who entered the data and/or which represents the intended meaning of the user. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | string |
| Requirements | The codes from the terminologies do not always capture the correct meaning with all the nuances of the human using them, or sometimes there is no appropriate code at all. In these cases, the text is used to capture the full meaning of the source. |
| Comments | Very often the text is the same as a displayName of one of the codings. |
| DataElement.copyright | |
| Definition | A copyright statement relating to the definition of the data element. Copyright statements are generally legal restrictions on the use and publishing of the details of the definition of the data element. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | string |
| Must Support | true |
| Alternate Names | License, Restrictions |
| Comments | The copyright statement does not apply to values for the data element, only to its definition. |
| DataElement.stringency | |
| Definition | Identifies how precise the data element is in its definition. |
| Control | 1..1 |
| Binding | Indicates the degree of precision of the data element definition. The codes SHALL be taken from DataElementStringency |
| Type | code |
| Must Support | true |
| Requirements | Allows determining the degree of comparability of data element instances. Less granular data elements result in data that is less comparable (or at least requires more work to compare). |
| Fixed Value | comparable |
| DataElement.mapping | |
| Definition | Identifies a specification (other than a terminology) that the elements which make up the DataElement have some correspondence with. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | BackboneElement |
| Slicing | This element introduces a set of slices. The slicing rules are:
|
| DataElement.mapping(ObjectClassPropertyMapping) | |
| Definition | Identifies a specification (other than a terminology) that the elements which make up the DataElement have some correspondence with. |
| Control | 1..1 |
| Type | BackboneElement |
| Must Support | true |
| DataElement.mapping.id | |
| Definition | unique id for the element within a resource (for internal references). |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | id |
| DataElement.mapping.extension | |
| Definition | May be used to represent additional information that is not part of the basic definition of the element. In order to make the use of extensions safe and manageable, there is a strict set of governance applied to the definition and use of extensions. Though any implementer is allowed to define an extension, there is a set of requirements that SHALL be met as part of the definition of the extension. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Extension |
| Alternate Names | extensions, user content |
| Comments | There can be no stigma associated with the use of extensions by any application, project, or standard - regardless of the institution or jurisdiction that uses or defines the extensions. The use of extensions is what allows the FHIR specification to retain a core level of simplicity for everyone. |
| DataElement.mapping.modifierExtension | |
| Definition | May be used to represent additional information that is not part of the basic definition of the element, and that modifies the understanding of the element that contains it. Usually modifier elements provide negation or qualification. In order to make the use of extensions safe and manageable, there is a strict set of governance applied to the definition and use of extensions. Though any implementer is allowed to define an extension, there is a set of requirements that SHALL be met as part of the definition of the extension. Applications processing a resource are required to check for modifier extensions. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Extension |
| Is Modifier | true |
| Alternate Names | extensions, user content, modifiers |
| Comments | There can be no stigma associated with the use of extensions by any application, project, or standard - regardless of the institution or jurisdiction that uses or defines the extensions. The use of extensions is what allows the FHIR specification to retain a core level of simplicity for everyone. |
| DataElement.mapping.identity | |
| Definition | An internal id that is used to identify this mapping set when specific mappings are made on a per-element basis. |
| Control | 1..1 |
| Type | id |
| Must Support | true |
| Comments | The specification is described once, with general comments, and then specific mappings are made that reference this declaration. |
| Fixed Value | objclass-prop |
| DataElement.mapping.uri | |
| Definition | An absolute URI that identifies the specification that this mapping is expressed to. |
| Control | 1..1 |
| Type | uri |
| Must Support | true |
| Comments | A formal identity for the specification being mapped to helps with identifying maps consistently. |
| Fixed Value | http://healthit.gov/sdc/objectclassproperty |
| DataElement.mapping.name | |
| Definition | A name for the specification that is being mapped to. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | string |
| Must Support | true |
| DataElement.mapping.comments | |
| Definition | Comments about this mapping, including version notes, issues, scope limitations, and other important notes for usage. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | string |
| Must Support | true |
| DataElement.mapping(OtherMapping) | |
| Definition | Identifies a specification (other than a terminology) that the elements which make up the DataElement have some correspondence with. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | BackboneElement |
| Must Support | true |
| Invariants | Defined on this element inv-1: Property extension can only be specified if ObjectClass extension is present (xpath: exists(f:extension[@url='http://hl7.org/fhir/StructureDefinition/11179-objectClass']) or not(exists(f:extension[@url='http://hl7.org/fhir/StructureDefinition/11179-property']))) |
| DataElement.mapping.id | |
| Definition | unique id for the element within a resource (for internal references). |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | id |
| DataElement.mapping.extension | |
| Definition | May be used to represent additional information that is not part of the basic definition of the element. In order to make the use of extensions safe and manageable, there is a strict set of governance applied to the definition and use of extensions. Though any implementer is allowed to define an extension, there is a set of requirements that SHALL be met as part of the definition of the extension. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Extension |
| Alternate Names | extensions, user content |
| Comments | There can be no stigma associated with the use of extensions by any application, project, or standard - regardless of the institution or jurisdiction that uses or defines the extensions. The use of extensions is what allows the FHIR specification to retain a core level of simplicity for everyone. |
| DataElement.mapping.modifierExtension | |
| Definition | May be used to represent additional information that is not part of the basic definition of the element, and that modifies the understanding of the element that contains it. Usually modifier elements provide negation or qualification. In order to make the use of extensions safe and manageable, there is a strict set of governance applied to the definition and use of extensions. Though any implementer is allowed to define an extension, there is a set of requirements that SHALL be met as part of the definition of the extension. Applications processing a resource are required to check for modifier extensions. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Extension |
| Is Modifier | true |
| Alternate Names | extensions, user content, modifiers |
| Comments | There can be no stigma associated with the use of extensions by any application, project, or standard - regardless of the institution or jurisdiction that uses or defines the extensions. The use of extensions is what allows the FHIR specification to retain a core level of simplicity for everyone. |
| DataElement.mapping.identity | |
| Definition | An internal id that is used to identify this mapping set when specific mappings are made on a per-element basis. |
| Control | 1..1 |
| Type | id |
| Must Support | true |
| Comments | The specification is described once, with general comments, and then specific mappings are made that reference this declaration. |
| DataElement.mapping.uri | |
| Definition | An absolute URI that identifies the specification that this mapping is expressed to. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | uri |
| Must Support | true |
| Comments | A formal identity for the specification being mapped to helps with identifying maps consistently. |
| DataElement.mapping.name | |
| Definition | A name for the specification that is being mapped to. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | string |
| Must Support | true |
| DataElement.mapping.comments | |
| Definition | Comments about this mapping, including version notes, issues, scope limitations, and other important notes for usage. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | string |
| Must Support | true |
| DataElement.element | |
| Definition | Defines the structure, type, allowed values and other constraining characteristics of the data element. |
| Control | 1..* |
| Type | ElementDefinition |
| Must Support | true |
| Requirements | 1. |
| Comments | For simple data types there will only be one repetition. For complex data types, multiple repetitions will be present defining a nested structure using the "path" element. |
| Invariants | Defined on this element dae-1: No base allowed (xpath: not(exists(f:base))) dae-2: No slicing allowed (xpath: not(exists(f:slicing))) |
| DataElement.element.id | |
| Definition | unique id for the element within a resource (for internal references). |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | id |
| DataElement.element.extension | |
| Definition | May be used to represent additional information that is not part of the basic definition of the element. In order to make the use of extensions safe and manageable, there is a strict set of governance applied to the definition and use of extensions. Though any implementer is allowed to define an extension, there is a set of requirements that SHALL be met as part of the definition of the extension. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Extension |
| Alternate Names | extensions, user content |
| Comments | There can be no stigma associated with the use of extensions by any application, project, or standard - regardless of the institution or jurisdiction that uses or defines the extensions. The use of extensions is what allows the FHIR specification to retain a core level of simplicity for everyone. |
| Slicing | This element introduces a set of slices. The slicing rules are:
|
| DataElement.element.extension (http://hl7.org/fhir/StructureDefinition/elementdefinition-question) | |
| Definition | The default/suggested phrasing to use when prompting a human to capture the data element in question form (e.g. In a survey). |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Extension (Extension Type: string) |
| Comments | Question and label serve similar purposes in they both can be used to prompt for capturing a data element. Whether the question form or label form should be used will depend on the type of instrument being used to capture the information. The ordering is in order of preference. I.e. Most preferred question form is listed first. Note that this is for alternate phrasings of the question. Language translations are handled using the ISO 21090 string translation extensions. |
| DataElement.element.extension (http://hl7.org/fhir/StructureDefinition/elementdefinition-allowedUnits) | |
| Definition | Identifies the units of measure in which the element should be captured or expressed. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | Extension (Extension Type: Choice of: CodeableConcept, Reference(ValueSet)) |
| Comments | Use a value set if more than one unit of measure is possible. Value sets will typically be short enough to display in a drop-down selection list. |
| DataElement.element.extension (http://hl7.org/fhir/StructureDefinition/minLength) | |
| Definition | The minimum number of characters that must be present in the simple data type to be considered a "valid" instance. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | Extension (Extension Type: integer) |
| Comments | For base64binary, reflects the number of characters representing the encoded data, not the number of bytes of the binary data. |
| DataElement.element.extension (http://hl7.org/fhir/StructureDefinition/regex) | |
| Definition | A regular expression that defines the syntax for the data element to be considered valid. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | Extension (Extension Type: string) |
| DataElement.element.extension (http://hl7.org/fhir/StructureDefinition/entryFormat) | |
| Definition | A syntax intended for display to the user to guide their input (i.e. a human readable version of a regular expression). For example "nnn-nnn-nnn". |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | Extension (Extension Type: string) |
| DataElement.element.extension (http://hl7.org/fhir/StructureDefinition/maxDecimalPlaces) | |
| Definition | Identifies the maximum number of decimal places that may be specified for the data element. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | Extension (Extension Type: integer) |
| DataElement.element.path | |
| Definition | The path identifies the element and is expressed as a "."-separated list of ancestor elements, beginning with the name of the resource or extension. |
| Control | 1..1 |
| Type | string |
| Must Support | true |
| DataElement.element.representation | |
| Definition | Codes that define how this element is represented in instances, when the deviation varies from the normal case. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Binding | How a property is represented on the wire. The codes SHALL be taken from PropertyRepresentation |
| Type | code |
| Comments | This is rarely used except for special cases where the representation deviates from the normal, which is done only very reluctantly, and can only be done in the base standard (and profiles must reproduce what the base standard does). |
| DataElement.element.name | |
| Definition | The name of this element definition (to refer to it from other element definitions using ElementDefinition.nameReference). This is a unique name referring to a specific set of constraints applied to this element. One use of this is to provide a name to different slices of the same element. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | string |
| Must Support | true |
| Requirements | Allows referencing a defined element. May also be used for code generation purposes. |
| Comments | The name SHALL be unique within the structure within the context of the constrained resource element. (Though to avoid confusion, uniqueness across all elements is recommended.). |
| DataElement.element.label | |
| Definition | The text to display beside the element indicating its meaning or to use to prompt for the element in a user display or form. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | string |
| Must Support | true |
| Comments | Question and label serve similar purposes in they both can be used to prompt for capturing a data element. Whether the question form or label form should be used will depend on the type of instrument being used to capture the information. |
| DataElement.element.code | |
| Definition | A code that provides the meaning for the element according to a particular terminology. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Binding | Codes representing the data element concept for a data element The codes SHALL be taken from DataElement SDC Concept; other codes may be used where these codes are not suitable |
| Type | Coding |
| Must Support | true |
| Requirements | Links the meaning of an element to an external terminology. |
| Comments | The data element definition and other constraints SHALL be a proper constraint on the meaning (as defined in the code system, including relationships) of any code listed here. Where multiple codes exist in a terminology that could correspond to the data element, the most granular code(s) should be selected, so long as they are not more restrictive than the data element itself. |
| DataElement.element.code.id | |
| Definition | unique id for the element within a resource (for internal references). |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | id |
| DataElement.element.code.extension | |
| Definition | May be used to represent additional information that is not part of the basic definition of the element. In order to make the use of extensions safe and manageable, there is a strict set of governance applied to the definition and use of extensions. Though any implementer is allowed to define an extension, there is a set of requirements that SHALL be met as part of the definition of the extension. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Extension |
| Alternate Names | extensions, user content |
| Comments | There can be no stigma associated with the use of extensions by any application, project, or standard - regardless of the institution or jurisdiction that uses or defines the extensions. The use of extensions is what allows the FHIR specification to retain a core level of simplicity for everyone. |
| Slicing | This element introduces a set of slices. The slicing rules are:
|
| DataElement.element.code.extension (http://hl7.org/fhir/StructureDefinition/11179-de-is-data-element-concept) | |
| Definition | If true, indicates that the specified coding corresponds to the data element concept for the data element. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | Extension (Extension Type: boolean) |
| DataElement.element.code.system | |
| Definition | The identification of the code system that defines the meaning of the symbol in the code. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | uri |
| Requirements | Need to be unambiguous about the source of the definition of the symbol. |
| Comments | The URI may be an OID (urn:oid:...) or a UUID (urn:uuid:...). OIDs and UUIDs SHALL be references to the HL7 OID registry. Otherwise, the URI should come from HL7's list of FHIR defined special URIs or it should de-reference to some definition that establish the system clearly and unambiguously. |
| DataElement.element.code.version | |
| Definition | The version of the code system which was used when choosing this code. Note that a well-maintained code system does not need the version reported, because the meaning of codes is consistent across versions. However this cannot consistently be assured. and when the meaning is not guaranteed to be consistent, the version SHOULD be exchanged. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | string |
| Comments | Where the terminology does not clearly define what string should be used to identify code system versions, the recommendation is to use the date (expressed in FHIR date format) on which that version was officially published as the version date. |
| DataElement.element.code.code | |
| Definition | A symbol in syntax defined by the system. The symbol may be a predefined code or an expression in a syntax defined by the coding system (e.g. post-coordination). |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | code |
| Requirements | Need to refer to a particular code in the system. |
| DataElement.element.code.display | |
| Definition | A representation of the meaning of the code in the system, following the rules of the system. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | string |
| Requirements | Need to be able to carry a human-readable meaning of the code for readers that do not know the system. |
| DataElement.element.code.userSelected | |
| Definition | Indicates that this coding was chosen by a user directly - i.e. off a pick list of available items (codes or displays). |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | boolean |
| Requirements | This has been identified as a clinical safety criterium - that this exact system/code pair was chosen explicitly, rather than inferred by the system based on some rules or language processing. |
| Comments | Amongst a set of alternatives, a directly chosen code is the most appropriate starting point for new translations. There is some ambiguity about what exactly 'directly chosen' implies, and trading partner agreement may be needed to clarify the use of this element and its consequences more completely. |
| DataElement.element.slicing | |
| Definition | Indicates that the element is sliced into a set of alternative definitions (i.e. in a structure definition, there are multiple different constraints on a single element in the base resource). Slicing can be used in any resource that has cardinality ..* on the base resource, or any resource with a choice of types. The set of slices is any elements that come after this in the element sequence that have the same path, until a shorter path occurs (the shorter path terminates the set). |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | Element |
| Comments | The first element in the sequence, the one that carries the slicing, is the unconstrained element, for reference purposes . This may include the unconstrained children. |
| Invariants | Defined on this element eld-1: If there are no discriminators, there must be a definition (xpath: (f:discriminator) or (f:description)) |
| DataElement.element.slicing.id | |
| Definition | unique id for the element within a resource (for internal references). |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | id |
| DataElement.element.slicing.extension | |
| Definition | May be used to represent additional information that is not part of the basic definition of the element. In order to make the use of extensions safe and manageable, there is a strict set of governance applied to the definition and use of extensions. Though any implementer is allowed to define an extension, there is a set of requirements that SHALL be met as part of the definition of the extension. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Extension |
| Alternate Names | extensions, user content |
| Comments | There can be no stigma associated with the use of extensions by any application, project, or standard - regardless of the institution or jurisdiction that uses or defines the extensions. The use of extensions is what allows the FHIR specification to retain a core level of simplicity for everyone. |
| DataElement.element.slicing.discriminator | |
| Definition | Designates which child elements are used to discriminate between the slices when processing an instance. If one or more discriminators are provided, the value of the child elements in the instance data SHALL completely distinguish which slice the element in the resource matches based on the allowed values for those elements in each of the slices. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | string |
| Comments | If there is no discriminator, the content is hard to process, so this should be avoided. If the base element has a cardinality of ..1, and there is a choice of types, the discriminator most be "@type". |
| DataElement.element.slicing.description | |
| Definition | A human-readable text description of how the slicing works. If there is no discriminator, this is required to be present to provide whatever information is possible about how the slices can be differentiated. |
| Control | 0..1 This element is affected by the following invariants: eld-1 |
| Type | string |
| Comments | If it's really not possible to differentiate them, the design should be re-evaluated to make the content usable. |
| DataElement.element.slicing.ordered | |
| Definition | If the matching elements have to occur in the same order as defined in the profile. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | boolean |
| Comments | Order should only be required when it is a pressing concern for presentation. Profile authors should consider making the order a feature of the rules about the narrative, not the rules about the data - requiring ordered data makes the profile much less re-usable. |
| Default Value | false |
| DataElement.element.slicing.rules | |
| Definition | Whether additional slices are allowed or not. When the slices are ordered, profile authors can also say that additional slices are only allowed at the end. |
| Control | 1..1 |
| Binding | How slices are interpreted when evaluating an instance. The codes SHALL be taken from SlicingRules |
| Type | code |
| Comments | Allowing additional elements makes for a much for flexible template - it's open for use in wider contexts, but also means that the content of the resource is not closed, and applications have to decide how to handle content not described by the profile. |
| DataElement.element.short | |
| Definition | A concise description of what this element means (e.g. for use in autogenerated summaries). |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | string |
| Comments | May change the term to provide language more appropriate to the context of the profile or to reflect slicing. |
| DataElement.element.definition | |
| Definition | Provides a complete explanation of the meaning of the data element for human readability. For the case of elements derived from existing elements (e.g. constraints), the definition SHALL be consistent with the base definition, but convey the meaning of the element in the particular context of use of the resource. |
| Control | 1..1 |
| Type | markdown |
| Must Support | true |
| Requirements | To allow a user to state the usage of an element in a particular context. |
| Alternate Names | Description |
| Comments | It is easy for a different definition to change the meaning of an element and this can have nasty downstream consequences. Please be careful when providing definitions. |
| DataElement.element.comments | |
| Definition | Explanatory notes and implementation guidance about the data element, including notes about how to use the data properly, exceptions to proper use, etc. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | markdown |
| Must Support | true |
| Comments | If it is possible to capture usage rules using constraints, that mechanism should be used in preference to this element. |
| DataElement.element.requirements | |
| Definition | This element is for traceability of why the element was created and why the constraints exist as they do. This may be used to point to source materials or specifications that drove the structure of this element. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | markdown |
| Must Support | true |
| Comments | This element does not describe the usage of the element (that's done in comments), rather it's for traceability of why the element is either needed or why the constraints exist as they do. This may be used to point to source materials or specifications that drove the structure of this data element. |
| DataElement.element.alias | |
| Definition | Identifies additional names by which this element might also be known. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | string |
| Must Support | true |
| Requirements | Allows for better easier recognition of the element by multiple communities, including international communities. |
| Alternate Names | synonym, other name |
| DataElement.element.min | |
| Definition | The minimum number of times this element SHALL appear in the instance. |
| Control | 0..1 This element is affected by the following invariants: eld-2 |
| Type | integer |
| Must Support | true |
| DataElement.element.max | |
| Definition | The maximum number of times this element is permitted to appear in the instance. |
| Control | 0..1 This element is affected by the following invariants: eld-3, eld-2 |
| Type | string |
| Must Support | true |
| Invariants | Defined on this element eld-3: Max SHALL be a number or "*" (xpath: @value='*' or (normalize-space(@value)!='' and normalize-space(translate(@value, '0123456789',''))='')) |
| DataElement.element.base | |
| Definition | Information about the base definition of the element, provided to make it unncessary for tools to trace the deviation of the element through the derived and related profiles. This information is only provided where the element definition represents a constraint on another element definition, and must be present if there is a base element definition. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | Element |
| Comments | The base information does not carry any information that could not be determined from the path and related profiles, but making this determination requires both that the related profiles are available, and that the algorithm to determine them be available. So they are deformalised into this location for tooling convenience, and to ensure that the base information is available without dependencies. |
| DataElement.element.base.id | |
| Definition | unique id for the element within a resource (for internal references). |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | id |
| DataElement.element.base.extension | |
| Definition | May be used to represent additional information that is not part of the basic definition of the element. In order to make the use of extensions safe and manageable, there is a strict set of governance applied to the definition and use of extensions. Though any implementer is allowed to define an extension, there is a set of requirements that SHALL be met as part of the definition of the extension. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Extension |
| Alternate Names | extensions, user content |
| Comments | There can be no stigma associated with the use of extensions by any application, project, or standard - regardless of the institution or jurisdiction that uses or defines the extensions. The use of extensions is what allows the FHIR specification to retain a core level of simplicity for everyone. |
| DataElement.element.base.path | |
| Definition | The Path that identifies the base element - this matches the ElementDefinition.path for that element. Across FHIR, there is only one base definition of any element - that is, an element definition on a StructureDefinition without a StructureDefinition.base. |
| Control | 1..1 |
| Type | string |
| DataElement.element.base.min | |
| Definition | Minimum cardinality of the base element identified by the path. |
| Control | 1..1 |
| Type | integer |
| Comments | This is provided for consistency with max, and may affect code generation of mandatory elements of the base resource are generated differently (some reference implementations have done this). |
| DataElement.element.base.max | |
| Definition | Maximum cardinality of the base element identified by the path. |
| Control | 1..1 |
| Type | string |
| Comments | This is provided to code generation, since the wire representation in JSON differs depending on whether the base element has max > 1. Also, some forms of code generation may differ. |
| DataElement.element.type | |
| Definition | The data type or resource that the value of this element is permitted to be. |
| Control | 0..1 This element is affected by the following invariants: eld-13 |
| Type | Element |
| Must Support | true |
| Comments | The Type of the element can be left blank, in which case the type is inherited from the resource. The type can only be listed in this field if it is an allowed option in the base resource. |
| Invariants | Defined on this element eld-4: Aggregation may only be specified if one of the allowed types for the element is a resource (xpath: not(exists(f:aggregation)) or exists(f:code[@value = 'Reference'])) |
| DataElement.element.type.id | |
| Definition | unique id for the element within a resource (for internal references). |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | id |
| DataElement.element.type.extension | |
| Definition | May be used to represent additional information that is not part of the basic definition of the element. In order to make the use of extensions safe and manageable, there is a strict set of governance applied to the definition and use of extensions. Though any implementer is allowed to define an extension, there is a set of requirements that SHALL be met as part of the definition of the extension. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Extension |
| Alternate Names | extensions, user content |
| Comments | There can be no stigma associated with the use of extensions by any application, project, or standard - regardless of the institution or jurisdiction that uses or defines the extensions. The use of extensions is what allows the FHIR specification to retain a core level of simplicity for everyone. |
| DataElement.element.type.code | |
| Definition | Name of Data type or Resource that is a(or the) type used for this element. |
| Control | 1..1 |
| Binding | Either a resource or a data type. The codes SHALL be taken from FHIRDefinedType |
| Type | code |
| Must Support | true |
| Comments | If the element is a reference to another resource, this element contains "Reference", and the profile element refers to the profile of the allowed target of the resource, which may be a reference to the general definition of a resource (e.g. http://hl7.org/fhir/StructureDefinition/Patient). There would be one pair of type/code for each allowed target resource type. |
| DataElement.element.type.profile | |
| Definition | Identifies a profile structure or implementation Guide that SHALL hold for resources or datatypes referenced as the type of this element. Can be a local reference - to another structure in this profile, or a reference to a structure in another profile. When more than one profile is specified, the content must conform to all of them. When an implementation guide is specified, the resource SHALL conform to at least one profile defined in the implementation guide. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | uri |
| DataElement.element.type.aggregation | |
| Definition | If the type is a reference to another resource, how the resource is or can be aggregated - is it a contained resource, or a reference, and if the context is a bundle, is it included in the bundle. |
| Control | 0..* This element is affected by the following invariants: eld-4 |
| Binding | How resource references can be aggregated. The codes SHALL be taken from AggregationMode |
| Type | code |
| DataElement.element.nameReference | |
| Definition | Identifies the name of a slice defined elsewhere in the profile whose constraints should be applied to the current element. |
| Control | 0..1 This element is affected by the following invariants: eld-5 |
| Type | string |
| Comments | If child components of this element are defined, they act as constraints on the referenced slice. |
| DataElement.element.defaultValue[x] | |
| Definition | The value that should be used if there is no value stated in the instance (e.g. 'if not otherwise specified, the abstract is false'). |
| Control | 0..1 This element is affected by the following invariants: eld-15 |
| Type | Choice of: boolean, integer, decimal, base64Binary, instant, string, uri, date, dateTime, time, code, oid, id, unsignedInt, positiveInt, markdown, Annotation, Attachment, Identifier, CodeableConcept, Coding, Quantity, Range, Period, Ratio, SampledData, Signature, HumanName, Address, ContactPoint, Timing, Reference, Meta |
| [x] Note | See Choice of Data Types for further information about how to use [x] |
| Comments | Default values can only be specified on a resource, data type, or extension definition, and never in a profile that applies to one of these. Specifying a default value means that the property can never been unknown - it must always have a value. Further, the default value can never be changed. For these reasons, default values are (and should be) used extremely sparingly. |
| DataElement.element.meaningWhenMissing | |
| Definition | The Implicit meaning that is to be understood when this element is missing (e.g. 'when this element is missing, the period is ongoing'. |
| Control | 0..1 This element is affected by the following invariants: eld-15 |
| Type | markdown |
| Comments | Implicit meanings for missing values can only be specified on a resource, data type, or extension definition, and never in a profile that applies to one of these. An implicit meaning for a missing value can never be changed, and specifying one has the consequence that constraining its use in profiles eliminates use cases as possibilities, not merely moving them out of scope. |
| DataElement.element.fixed[x] | |
| Definition | Specifies a value that SHALL be exactly the value for this element in the instance. For purposes of comparison, non-significant whitespace is ignored, and all values must be an exact match (case and accent sensitive). Missing elements/attributes must also be missing. |
| Control | 0..1 This element is affected by the following invariants: eld-5, eld-6, eld-8 |
| Type | Choice of: boolean, integer, decimal, base64Binary, instant, string, uri, date, dateTime, time, code, oid, id, unsignedInt, positiveInt, markdown, Annotation, Attachment, Identifier, CodeableConcept, Coding, Quantity, Range, Period, Ratio, SampledData, Signature, HumanName, Address, ContactPoint, Timing, Reference, Meta |
| [x] Note | See Choice of Data Types for further information about how to use [x] |
| Comments | This is not recommended for Coding and CodeableConcept since these often have highly contextual properties such as version or display. |
| DataElement.element.pattern[x] | |
| Definition | Specifies a value that the value in the instance SHALL follow - that is, any value in the pattern must be found in the instance. Other additional values may be found too. This is effectively constraint by example. The values of elements present in the pattern must match exactly (case-sensitive, accent-sensitive, etc.). |
| Control | 0..1 This element is affected by the following invariants: eld-5, eld-7, eld-8 |
| Type | Choice of: boolean, integer, decimal, base64Binary, instant, string, uri, date, dateTime, time, code, oid, id, unsignedInt, positiveInt, markdown, Annotation, Attachment, Identifier, CodeableConcept, Coding, Quantity, Range, Period, Ratio, SampledData, Signature, HumanName, Address, ContactPoint, Timing, Reference, Meta |
| [x] Note | See Choice of Data Types for further information about how to use [x] |
| Comments | Mostly used for fixing values of CodeableConcept. At present, pattern[x] is not recommended as a basis for slicing while issues related to this are investigated during the DSTU period. |
| DataElement.element.example[x] | |
| Definition | A sample value for this element demonstrating the type of information that would typically be captured. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | Choice of: boolean, integer, decimal, base64Binary, instant, string, uri, date, dateTime, time, code, oid, id, unsignedInt, positiveInt, markdown, Annotation, Attachment, Identifier, CodeableConcept, Coding, Quantity, Range, Period, Ratio, SampledData, Signature, HumanName, Address, ContactPoint, Timing, Reference, Meta |
| [x] Note | See Choice of Data Types for further information about how to use [x] |
| Must Support | true |
| Comments | This will most commonly be present for data where it's not implicitly obvious from either the data type or value set what the values might be. (I.e. Example values for dates or quantities would generally be unnecessary.) If the example value is fully populated, the publication tool can generate an instance automatically. |
| DataElement.element.minValue[x] | |
| Definition | The minimum allowed value for the element. The value is inclusive. This is allowed for the types date, dateTime, instant, time, decimal, integer, and Quantity. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | Choice of: boolean, integer, decimal, base64Binary, instant, string, uri, date, dateTime, time, code, oid, id, unsignedInt, positiveInt, markdown, Annotation, Attachment, Identifier, CodeableConcept, Coding, Quantity, Range, Period, Ratio, SampledData, Signature, HumanName, Address, ContactPoint, Timing, Reference, Meta |
| [x] Note | See Choice of Data Types for further information about how to use [x] |
| Must Support | true |
| Comments | Except for date/date/instant, the type of the minValue[x] SHALL be the same as the specified type of the element. For the date/dateTime/instant values, the type of minValue[x] SHALL be either the same, or a a Duration which specifies a relative time limit to the current time. The duration value is positive, and is subtracted from the current clock to determine the minimum allowable value. A minimum value for a Quantity is interpreted as an canonical minimum - e.g. you cannot provide 100mg if the minimum value is 10g. |
| DataElement.element.maxValue[x](l) | |
| Definition | The maximum allowed value for the element. The value is inclusive. This is allowed for the types date, dateTime, instant, time, decimal, integer, and Quantity. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | Choice of: boolean, integer, decimal, base64Binary, instant, string, uri, date, dateTime, time, code, oid, id, unsignedInt, positiveInt, markdown, Annotation, Attachment, Identifier, CodeableConcept, Coding, Quantity, Range, Period, Ratio, SampledData, Signature, HumanName, Address, ContactPoint, Timing, Reference, Meta |
| [x] Note | See Choice of Data Types for further information about how to use [x] |
| Must Support | true |
| Comments | Except for date/date/instant, the type of the maxValue[x] SHALL be the same as the specified type of the element. For the date/dateTime/instant values, the type of maxValue[x] SHALL be either the same, or a a Duration which specifies a relative time limit to the current time. The duration value is positive, and is added to the current clock to determine the maximum allowable value. A maximum value for a Quantity is interpreted as an canonical maximum - e.g. you cannot provide 10g if the maximum value is 50mg. |
| DataElement.element.maxLength | |
| Definition | Indicates the maximum length in characters that is permitted to be present in conformant instances and which is expected to be supported by conformant consumers that support the element. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | integer |
| Must Support | true |
| Comments | Receivers are not required to reject instances that exceed the maximum length. The full length could be stored. In some cases, data might be truncated, though truncation should be undertaken with care and an understanding of the consequences of doing so. If not specified, there is no conformance expectation for length support. |
| DataElement.element.condition | |
| Definition | A reference to an invariant that may make additional statements about the cardinality or value in the instance. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | id |
| Must Support | true |
| DataElement.element.constraint | |
| Definition | Formal constraints such as co-occurrence and other constraints that can be computationally evaluated within the context of the instance. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Element |
| Must Support | true |
| Comments | Constraints should be declared on the "context" element - the lowest element in the hierarchy that is common to all nodes referenced by the constraint. |
| DataElement.element.constraint.id | |
| Definition | unique id for the element within a resource (for internal references). |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | id |
| DataElement.element.constraint.extension | |
| Definition | May be used to represent additional information that is not part of the basic definition of the element. In order to make the use of extensions safe and manageable, there is a strict set of governance applied to the definition and use of extensions. Though any implementer is allowed to define an extension, there is a set of requirements that SHALL be met as part of the definition of the extension. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Extension |
| Alternate Names | extensions, user content |
| Comments | There can be no stigma associated with the use of extensions by any application, project, or standard - regardless of the institution or jurisdiction that uses or defines the extensions. The use of extensions is what allows the FHIR specification to retain a core level of simplicity for everyone. |
| DataElement.element.constraint.key | |
| Definition | Allows identification of which elements have their cardinalities impacted by the constraint. Will not be referenced for constraints that do not affect cardinality. |
| Control | 1..1 This element is affected by the following invariants: eld-14 |
| Type | id |
| Must Support | true |
| DataElement.element.constraint.requirements | |
| Definition | Description of why this constraint is necessary or appropriate. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | string |
| Must Support | true |
| Comments | To be used if the reason for the constraint may not be intuitive to all implementers. |
| DataElement.element.constraint.severity | |
| Definition | Identifies the impact constraint violation has on the conformance of the instance. |
| Control | 1..1 |
| Binding | SHALL applications comply with this constraint? The codes SHALL be taken from ConstraintSeverity |
| Type | code |
| Must Support | true |
| Comments | This allows constraints to be asserted as "shall" (error) and "should" (warning). |
| DataElement.element.constraint.human | |
| Definition | Text that can be used to describe the constraint in messages identifying that the constraint has been violated. |
| Control | 1..1 |
| Type | string |
| Must Support | true |
| Comments | Should be expressed in business terms as much as possible. |
| DataElement.element.constraint.xpath | |
| Definition | An XPath expression of constraint that can be executed to see if this constraint is met. |
| Control | 1..1 |
| Type | string |
| Must Support | true |
| Requirements | Used in Schematron tests of the validity of the resource. |
| Comments | Elements SHALL use "f" as the namespace prefix for the FHIR namespace, and "x" for the xhtml namespace, and SHALL NOT use any other prefixes. |
| DataElement.element.mustSupport | |
| Definition | If true, implementations that produce or consume resources SHALL provide "support" for the element in some meaningful way. If false, the element may be ignored and not supported. |
| Control | 0..0 |
| Type | boolean |
| Requirements | Allows a profile to set expectations for system capabilities beyond merely respecting cardinality constraints. |
| Comments | "Something useful" is context dependent and impossible to describe in the base FHIR specification. For this reason, tue mustSupport flag is never set to true by the FHIR specification itself - it is only set to true in profiles. This is done in Resource Profiles, where the profile labels an element as mustSupport=true. When a profile does this, it SHALL also make clear exactly what kind of "support" is required, as this can mean many things. Note that an element that has the property IsModifier is not necessarily a "key" element (e.g. one of the important elements to make use of the resource), nor is it automatically mustSupport - however both of these things are more likely to be true for IsModifier elements than for other elements. |
| Default Value | false |
| DataElement.element.isModifier | |
| Definition | If true, the value of this element affects the interpretation of the element or resource that contains it, and the value of the element cannot be ignored. Typically, this is used for status, negation and qualification codes. The effect of this is that the element cannot be ignored by systems: they SHALL either recognize the element and process it, and/or a pre-determination has been made that it is not relevant to their particular system. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | boolean |
| Requirements | Allows elements to be introduced into a specification that can't safely be ignored by applications that don't recognize them. |
| Comments | Only the definition of an element can set IsModifier true - either the specification itself or where an extension is originally defined. Once set, it cannot be changed in derived profiles. An element/extension that has isModifier=true SHOULD also have a minimum cardinality of 1, so that there is no lack of clarity about what to do if it is missing. If it can be missing, the definition SHALL make the meaning of a missing element clear. |
| Default Value | false |
| DataElement.element.isSummary | |
| Definition | Whether the element should be included if a client requests a search with the parameter _summary=true. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | boolean |
| Requirements | Allow clients to search through large resources quickly. |
| Comments | Some resources include a set of simple metadata, and some very large data. This element is used to reduce the quantity of data returned in searches. Note that servers may pre-cache summarized resources for optimal performance, so servers may not support per-profile use of the isSummary flag. |
| Default Value | false |
| DataElement.element.binding | |
| Definition | Binds to a value set if this element is coded (code, Coding, CodeableConcept). |
| Control | 0..1 This element is affected by the following invariants: eld-11 |
| Type | Element |
| Must Support | true |
| Invariants | Defined on this element eld-10: provide either a reference or a description (or both) (xpath: (exists(f:valueSetUri) or exists(f:valueSetReference)) or exists(f:description)) |
| DataElement.element.binding.id | |
| Definition | unique id for the element within a resource (for internal references). |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | id |
| DataElement.element.binding.extension | |
| Definition | May be used to represent additional information that is not part of the basic definition of the element. In order to make the use of extensions safe and manageable, there is a strict set of governance applied to the definition and use of extensions. Though any implementer is allowed to define an extension, there is a set of requirements that SHALL be met as part of the definition of the extension. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Extension |
| Alternate Names | extensions, user content |
| Comments | There can be no stigma associated with the use of extensions by any application, project, or standard - regardless of the institution or jurisdiction that uses or defines the extensions. The use of extensions is what allows the FHIR specification to retain a core level of simplicity for everyone. |
| DataElement.element.binding.strength | |
| Definition | Indicates the degree of conformance expectations associated with this binding - that is, the degree to which the provided value set must be adhered to in the instances. |
| Control | 1..1 |
| Binding | Indication of the degree of conformance expectations associated with a binding. The codes SHALL be taken from BindingStrength |
| Type | code |
| Must Support | true |
| Alternate Names | conformance, extensibility |
| Comments | For further discussion, see Using Terminologies. |
| DataElement.element.binding.description | |
| Definition | Describes the intended use of this particular set of codes. |
| Control | 0..1 This element is affected by the following invariants: eld-10 |
| Type | string |
| Must Support | true |
| DataElement.element.binding.valueSetReference | |
| Definition | Points to the value set or external definition (e.g. implicit value set) that identifies the set of codes to be used. |
| Control | 1..1 This element is affected by the following invariants: eld-10, eld-12 |
| Type | Reference(Structured Data Capture Data Element Exchange Value Set) |
| Must Support | true |
| Comments | For value sets with a referenceResource, the display can contain the value set description. The reference may be version-specific or not. |
| Invariants | Defined on this element eld-12: URI SHALL start with http:// or https:// (xpath: starts-with(string(@value), 'http:') or starts-with(string(@value), 'https:')) inv-3: Must have data element permitted value concept map extension if and only if data element permitted value valueset extension is present (xpath: count(f:extension[@url='http://hl7.org/fhir/StructureDefinition/11179-permitted-value-valueset'])=count(f:extension[@url='http://hl7.org/fhir/StructureDefinition/11179-permitted-value-conceptmap'])) |
| DataElement.element.binding.valueSetReference.id | |
| Definition | unique id for the element within a resource (for internal references). |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | id |
| DataElement.element.binding.valueSetReference.extension | |
| Definition | May be used to represent additional information that is not part of the basic definition of the element. In order to make the use of extensions safe and manageable, there is a strict set of governance applied to the definition and use of extensions. Though any implementer is allowed to define an extension, there is a set of requirements that SHALL be met as part of the definition of the extension. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Extension |
| Alternate Names | extensions, user content |
| Comments | There can be no stigma associated with the use of extensions by any application, project, or standard - regardless of the institution or jurisdiction that uses or defines the extensions. The use of extensions is what allows the FHIR specification to retain a core level of simplicity for everyone. |
| Slicing | This element introduces a set of slices. The slicing rules are:
|
| DataElement.element.binding.valueSetReference.extension (http://hl7.org/fhir/StructureDefinition/11179-permitted-value-valueset) | |
| Definition | Allows expressing the value set that must be stored internally by the system (as distinct from the base value set which defines values for exchange). |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | Extension (Extension Type: Reference(ValueSet)) |
| Comments | The permitted value set must have a 1..1 set of codes for each code in the value meaning value set. |
| DataElement.element.binding.valueSetReference.extension (http://hl7.org/fhir/StructureDefinition/11179-permitted-value-conceptmap) | |
| Definition | Expresses the linkage between the internal codes used for storage and the codes used for exchange. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | Extension (Extension Type: Reference(ConceptMap)) |
| Comments | The permitted value set must have a 1..1 set of codes for each code in the value meaning value set. The source for the concept map is the value set the extension appears on. The target is the permitted-value-valueset. |
| DataElement.element.binding.valueSetReference.reference | |
| Definition | A reference to a location at which the other resource is found. The reference may be a relative reference, in which case it is relative to the service base URL, or an absolute URL that resolves to the location where the resource is found. The reference may be version specific or not. If the reference is not to a FHIR RESTful server, then it should be assumed to be version specific. Internal fragment references (start with '#') refer to contained resources. |
| Control | 0..1 This element is affected by the following invariants: ref-1 |
| Type | string |
| Comments | Using absolute URLs provides a stable scalable approach suitable for a cloud/web context, while using relative/logical references provides a flexible approach suitable for use when trading across closed eco-system boundaries. Absolute URLs do not need to point to a FHIR RESTful server, though this is the preferred approach. If the URL conforms to the structure "/[type]/[id]" then it should be assumed that the reference is to a FHIR RESTful server. |
| DataElement.element.binding.valueSetReference.display | |
| Definition | Plain text narrative that identifies the resource in addition to the resource reference. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | string |
| Comments | This is generally not the same as the Resource.text of the referenced resource. The purpose is to identify what's being referenced, not to fully describe it. |
| DataElement.element.mapping | |
| Definition | Identifies a concept from an external specification that roughly corresponds to this element. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Element |
| Requirements | Provides guidance to implementers familiar with or converting content from other specifications. |
| Comments | Mappings are not necessarily specific enough for safe translation. |
| Slicing | This element introduces a set of slices. The slicing rules are:
|
| DataElement.element.mapping(ClassPropertyMapping) | |
| Definition | A mapping that defines the data element in terms of the SDC project's ObjectClass and Property value sets. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | Element |
| Must Support | true |
| Requirements | Provides guidance to implementers familiar with or converting content from other specifications. |
| Comments | Mappings are not necessarily specific enough for safe translation. |
| DataElement.element.mapping.id | |
| Definition | unique id for the element within a resource (for internal references). |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | id |
| DataElement.element.mapping.extension | |
| Definition | May be used to represent additional information that is not part of the basic definition of the element. In order to make the use of extensions safe and manageable, there is a strict set of governance applied to the definition and use of extensions. Though any implementer is allowed to define an extension, there is a set of requirements that SHALL be met as part of the definition of the extension. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Extension |
| Alternate Names | extensions, user content |
| Comments | There can be no stigma associated with the use of extensions by any application, project, or standard - regardless of the institution or jurisdiction that uses or defines the extensions. The use of extensions is what allows the FHIR specification to retain a core level of simplicity for everyone. |
| Slicing | This element introduces a set of slices. The slicing rules are:
|
| DataElement.element.mapping.extension (http://hl7.org/fhir/StructureDefinition/11179-objectClass) | |
| Definition | A concept that represents a set of ideas, abstractions, or things in the real world that can be identified with explicit boundaries and meaning and whose properties and behavior follow the same rules. It may be either a single or a group of associated concepts, abstractions, or things. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | Extension (Extension Type: Coding) |
| Comments | ObjectClass and Property are treated as a data model that can be mapped to like any other. This extension merely captures the ObjectClass element as a discrete code. The information conveyed here should also be conveyed in human-readable form in the mapping.map element. |
| DataElement.element.mapping.extension.id | |
| Definition | unique id for the element within a resource (for internal references). |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | id |
| DataElement.element.mapping.extension.extension(extension) | |
| Definition | An Extension |
| Control | 0..0 |
| Type | Extension |
| DataElement.element.mapping.extension.url | |
| Definition | Source of the definition for the extension code - a logical name or a URL. |
| Control | 1..1 |
| Type | uri |
| Comments | The definition may point directly to a computable or human-readable definition of the extensibility codes, or it may be a logical URI as declared in some other specification. The definition should be version specific. This will ideally be the URI for the Resource Profile defining the extension, with the code for the extension after a #. |
| Fixed Value | http://hl7.org/fhir/StructureDefinition/11179-objectClass |
| DataElement.element.mapping.extension.valueCoding | |
| Definition | Value of extension - may be a resource or one of a constrained set of the data types (see Extensibility in the spec for list). |
| Control | 1..1 |
| Binding | Codes representing the ISO 11179 Object Class for a data element The codes SHALL be taken from DataElement SDC Concept; other codes may be used where these codes are not suitable |
| Type | Coding |
| Must Support | true |
| DataElement.element.mapping.extension (http://hl7.org/fhir/StructureDefinition/11179-objectClassProperty) | |
| Definition | A quality common to all members of an object class. A property may be any feature that humans naturally use to distinguish one individual object from another. It is the human perception of a single quality of an object class in the real world. It is conceptual and thus has no particular associated means of representation by which the property can be communicated. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | Extension (Extension Type: Coding) |
| Comments | ObjectClass and Property are treated as a data model that can be mapped to like any other. This extension merely captures the Property element as a discrete code. The information conveyed here should also be conveyed in human-readable form in the mapping.map element. |
| DataElement.element.mapping.extension.id | |
| Definition | unique id for the element within a resource (for internal references). |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | id |
| DataElement.element.mapping.extension.extension(extension) | |
| Definition | An Extension |
| Control | 0..0 |
| Type | Extension |
| DataElement.element.mapping.extension.url | |
| Definition | Source of the definition for the extension code - a logical name or a URL. |
| Control | 1..1 |
| Type | uri |
| Comments | The definition may point directly to a computable or human-readable definition of the extensibility codes, or it may be a logical URI as declared in some other specification. The definition should be version specific. This will ideally be the URI for the Resource Profile defining the extension, with the code for the extension after a #. |
| Fixed Value | http://hl7.org/fhir/StructureDefinition/11179-objectClassProperty |
| DataElement.element.mapping.extension.valueCoding | |
| Definition | Value of extension - may be a resource or one of a constrained set of the data types (see Extensibility in the spec for list). |
| Control | 1..1 |
| Binding | Codes representing the ISO 11179 Object Class Property for a data element The codes SHALL be taken from DataElement SDC Concept; other codes may be used where these codes are not suitable |
| Type | Coding |
| Must Support | true |
| DataElement.element.mapping.identity | |
| Definition | An internal reference to the definition of a mapping. |
| Control | 1..1 |
| Type | id |
| Must Support | true |
| Fixed Value | objclass-prop |
| DataElement.element.mapping.language | |
| Definition | Identifies the computable language in which mapping.map is expressed. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Binding | The mime type of an attachment. Any valid mime type is allowed. The codes SHALL be taken from http://www.rfc-editor.org/bcp/bcp13.txt  |
| Type | code |
| Comments | If omitted, then there can be no expectation of computational interpretation of the mapping. |
| DataElement.element.mapping.map | |
| Definition | This should be expressed as "[uri for object class code system]#[code for object class code system] | [uri for property code system]#[code for property code system]". |
| Control | 1..1 |
| Type | string |
| Must Support | true |
| Comments | We express the mapping even though the class and property extensions already convey the data to ensure that systems that don't recognize the extensions still understand the mappings. |
| DataElement.element.mapping(OtherElementMapping) | |
| Definition | Identifies a concept from an external specification that roughly corresponds to this element. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Element |
| Must Support | true |
| Requirements | Provides guidance to implementers familiar with or converting content from other specifications. |
| Comments | Mappings are not necessarily specific enough for safe translation. |
| DataElement.element.mapping.id | |
| Definition | unique id for the element within a resource (for internal references). |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | id |
| DataElement.element.mapping.extension (http://hl7.org/fhir/StructureDefinition/elementdefinition-equivalence) | |
| Definition | The level of equivalence between the element containing the mapping and the element mapped to. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | Extension (Extension Type: code) |
| DataElement.element.mapping.identity | |
| Definition | An internal reference to the definition of a mapping. |
| Control | 1..1 |
| Type | id |
| Must Support | true |
| DataElement.element.mapping.language | |
| Definition | Identifies the computable language in which mapping.map is expressed. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Binding | The mime type of an attachment. Any valid mime type is allowed. The codes SHALL be taken from http://www.rfc-editor.org/bcp/bcp13.txt  |
| Type | code |
| Must Support | true |
| Comments | The most common languages will be application/sparql-results+xml, application/sql and application/xquery. |
| DataElement.element.mapping.map | |
| Definition | Expresses what part of the target specification corresponds to this element. |
| Control | 1..1 |
| Type | string |
| Must Support | true |
| Comments | For most mappings, the syntax is undefined. Syntax will be provided for mappings to the RIM. Multiple mappings may be possible and may include constraints on other resource elements that identify when a particular mapping applies. |