This page is part of the FHIR Specification (v1.4.0: STU 3 Ballot 3). The current version which supercedes this version is 5.0.0. For a full list of available versions, see the Directory of published versions 

Definitions for the argonaut-careplan Profile.
| CarePlan(argonaut-careplan) | |
| Definition | Describes the intention of how one or more practitioners intend to deliver care for a particular patient, group or community for a period of time, possibly limited to care for a specific condition or set of conditions. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | CarePlan |
| Alternate Names | Care Team |
| CarePlan.id | |
| Definition | The logical id of the resource, as used in the URL for the resource. Once assigned, this value never changes. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | id |
| Comments | The only time that a resource does not have an id is when it is being submitted to the server using a create operation. Bundles always have an id, though it is usually a generated UUID. |
| CarePlan.meta | |
| Definition | The metadata about the resource. This is content that is maintained by the infrastructure. Changes to the content may not always be associated with version changes to the resource. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | Meta |
| CarePlan.implicitRules | |
| Definition | A reference to a set of rules that were followed when the resource was constructed, and which must be understood when processing the content. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | uri |
| Is Modifier | true |
| Comments | Asserting this rule set restricts the content to be only understood by a limited set of trading partners. This inherently limits the usefulness of the data in the long term. However, the existing health eco-system is highly fractured, and not yet ready to define, collect, and exchange data in a generally computable sense. Wherever possible, implementers and/or specification writers should avoid using this element as much as possible. |
| CarePlan.language | |
| Definition | The base language in which the resource is written. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Binding | A human language. The codes SHALL be taken from http://tools.ietf.org/html/bcp47 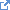 |
| Type | code |
| Comments | Language is provided to support indexing and accessibility (typically, services such as text to speech use the language tag). The html language tag in the narrative applies to the narrative. The language tag on the resource may be used to specify the language of other presentations generated from the data in the resource Not all the content has to be in the base language. The Resource.language should not be assumed to apply to the narrative automatically. If a language is specified, it should it also be specified on the div element in the html (see rules in HTML5 for information about the relationship between xml:lang and the html lang attribute). |
| CarePlan.text | |
| Definition | A human-readable narrative that contains a summary of the resource, and may be used to represent the content of the resource to a human. The narrative need not encode all the structured data, but is required to contain sufficient detail to make it "clinically safe" for a human to just read the narrative. Resource definitions may define what content should be represented in the narrative to ensure clinical safety. |
| Control | 0..1 This element is affected by the following invariants: dom-1 |
| Type | Narrative |
| Alternate Names | narrative, html, xhtml, display |
| Comments | Contained resources do not have narrative. Resources that are not contained SHOULD have a narrative. |
| CarePlan.contained | |
| Definition | These resources do not have an independent existence apart from the resource that contains them - they cannot be identified independently, and nor can they have their own independent transaction scope. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Resource |
| Alternate Names | inline resources, anonymous resources, contained resources |
| Comments | This should never be done when the content can be identified properly, as once identification is lost, it is extremely difficult (and context dependent) to restore it again. |
| CarePlan.extension | |
| Definition | May be used to represent additional information that is not part of the basic definition of the resource. In order to make the use of extensions safe and manageable, there is a strict set of governance applied to the definition and use of extensions. Though any implementer is allowed to define an extension, there is a set of requirements that SHALL be met as part of the definition of the extension. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Extension |
| Alternate Names | extensions, user content |
| Comments | There can be no stigma associated with the use of extensions by any application, project, or standard - regardless of the institution or jurisdiction that uses or defines the extensions. The use of extensions is what allows the FHIR specification to retain a core level of simplicity for everyone. |
| CarePlan.modifierExtension | |
| Definition | May be used to represent additional information that is not part of the basic definition of the resource, and that modifies the understanding of the element that contains it. Usually modifier elements provide negation or qualification. In order to make the use of extensions safe and manageable, there is a strict set of governance applied to the definition and use of extensions. Though any implementer is allowed to define an extension, there is a set of requirements that SHALL be met as part of the definition of the extension. Applications processing a resource are required to check for modifier extensions. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Extension |
| Is Modifier | true |
| Alternate Names | extensions, user content |
| Comments | There can be no stigma associated with the use of extensions by any application, project, or standard - regardless of the institution or jurisdiction that uses or defines the extensions. The use of extensions is what allows the FHIR specification to retain a core level of simplicity for everyone. |
| CarePlan.identifier | |
| Definition | This records identifiers associated with this care plan that are defined by business processes and/or used to refer to it when a direct URL reference to the resource itself is not appropriate (e.g. in CDA documents, or in written / printed documentation). |
| Control | 0..0 |
| Type | Identifier |
| Requirements | Need to allow connection to a wider workflow. |
| CarePlan.subject | |
| Definition | Identifies the patient or group whose intended care is described by the plan. |
| Control | 1..1 |
| Type | Choice of: Reference(Patient), Reference(Group) |
| CarePlan.status | |
| Definition | Indicates whether the plan is currently being acted upon, represents future intentions or is now a historical record. |
| Control | 1..1 |
| Binding | Indicates whether the plan is currently being acted upon, represents future intentions or is now a historical record. The codes SHALL be taken from CarePlanStatus |
| Type | code |
| Is Modifier | true |
| Requirements | Allows clinicians to determine whether the plan is actionable or not. |
| Fixed Value | active |
| CarePlan.context | |
| Definition | Identifies the context in which this particular CarePlan is defined. |
| Control | 0..0 |
| Type | Choice of: Reference(Encounter), Reference(EpisodeOfCare) |
| Comments | Activities conducted as a result of the care plan may well occur as part of other encounters/episodes. |
| CarePlan.period | |
| Definition | Indicates when the plan did (or is intended to) come into effect and end. |
| Control | 0..0 |
| Type | Period |
| Requirements | Allows tracking what plan(s) are in effect at a particular time. |
| Comments | Any activities scheduled as part of the plan should be constrained to the specified period. |
| CarePlan.author | |
| Definition | Identifies the individual(s) or ogranization who is responsible for the content of the care plan. |
| Control | 0..0 |
| Type | Choice of: Reference(Patient), Reference(Practitioner), Reference(RelatedPerson), Reference(Organization) |
| Comments | Collaborative care plans may have multiple authors. |
| CarePlan.modified | |
| Definition | Identifies the most recent date on which the plan has been revised. |
| Control | 0..0 |
| Type | dateTime |
| Requirements | Indicates how current the plan is. |
| CarePlan.category | |
| Definition | Identifies what "kind" of plan this is to support differentiation between multiple co-existing plans; e.g. "Home health", "psychiatric", "asthma", "disease management", "wellness plan", etc. |
| Control | 0..0 |
| Binding | Identifies what "kind" of plan this is to support differentiation between multiple co-existing plans; e.g. "Home health", "psychiatric", "asthma", "disease management", etc. For example codes, see Care Plan Category |
| Type | CodeableConcept |
| Requirements | Used for filtering what plan(s) are retrieved and displayed to different types of users. |
| Comments | There may be multiple axis of categorization and one plan may serve multiple purposes. In some cases, this may be redundant with references to CarePlan.concern. |
| CarePlan.description | |
| Definition | A description of the scope and nature of the plan. |
| Control | 0..0 |
| Type | string |
| Requirements | Provides more detail than conveyed by category. |
| CarePlan.addresses | |
| Definition | Identifies the conditions/problems/concerns/diagnoses/etc. whose management and/or mitigation are handled by this plan. |
| Control | 0..0 |
| Type | Reference(Condition) |
| Requirements | Links plan to the conditions it manages. Also scopes plans - multiple plans may exist addressing different concerns. |
| CarePlan.support | |
| Definition | Identifies portions of the patient's record that specifically influenced the formation of the plan. These might include co-morbidities, recent procedures, limitations, recent assessments, etc. |
| Control | 0..0 |
| Type | Reference(Resource) |
| Requirements | Identifies barriers and other considerations associated with the care plan. |
| Comments | Use "concern" to identify specific conditions addressed by the care plan. |
| CarePlan.relatedPlan | |
| Definition | Identifies CarePlans with some sort of formal relationship to the current plan. |
| Control | 0..0 |
| Type | BackboneElement |
| Comments | Relationships are uni-directional with the "newer" plan pointing to the older one. |
| CarePlan.relatedPlan.id | |
| Definition | unique id for the element within a resource (for internal references). |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | id |
| CarePlan.relatedPlan.extension | |
| Definition | May be used to represent additional information that is not part of the basic definition of the element. In order to make the use of extensions safe and manageable, there is a strict set of governance applied to the definition and use of extensions. Though any implementer is allowed to define an extension, there is a set of requirements that SHALL be met as part of the definition of the extension. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Extension |
| Alternate Names | extensions, user content |
| Comments | There can be no stigma associated with the use of extensions by any application, project, or standard - regardless of the institution or jurisdiction that uses or defines the extensions. The use of extensions is what allows the FHIR specification to retain a core level of simplicity for everyone. |
| CarePlan.relatedPlan.modifierExtension | |
| Definition | May be used to represent additional information that is not part of the basic definition of the element, and that modifies the understanding of the element that contains it. Usually modifier elements provide negation or qualification. In order to make the use of extensions safe and manageable, there is a strict set of governance applied to the definition and use of extensions. Though any implementer is allowed to define an extension, there is a set of requirements that SHALL be met as part of the definition of the extension. Applications processing a resource are required to check for modifier extensions. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Extension |
| Is Modifier | true |
| Alternate Names | extensions, user content, modifiers |
| Comments | There can be no stigma associated with the use of extensions by any application, project, or standard - regardless of the institution or jurisdiction that uses or defines the extensions. The use of extensions is what allows the FHIR specification to retain a core level of simplicity for everyone. |
| CarePlan.relatedPlan.code | |
| Definition | Identifies the type of relationship this plan has to the target plan. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Binding | Codes identifying the types of relationships between two plans. The codes SHALL be taken from CarePlanRelationship |
| Type | code |
| Comments | Read the relationship as "this plan" [relatedPlan.code] "relatedPlan.plan"; e.g. This plan includes Plan B. Additional relationship types can be proposed for future releases or handled as extensions. |
| CarePlan.relatedPlan.plan | |
| Definition | A reference to the plan to which a relationship is asserted. |
| Control | 1..1 |
| Type | Reference(CarePlan) |
| CarePlan.participant | |
| Definition | Identifies all people and organizations who are expected to be involved in the care envisioned by this plan. |
| Control | 0..0 |
| Type | BackboneElement |
| Requirements | Allows representation of care teams, helps scope care plan. In some cases may be a determiner of access permissions. |
| Alternate Names | Care Team |
| CarePlan.participant.id | |
| Definition | unique id for the element within a resource (for internal references). |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | id |
| CarePlan.participant.extension | |
| Definition | May be used to represent additional information that is not part of the basic definition of the element. In order to make the use of extensions safe and manageable, there is a strict set of governance applied to the definition and use of extensions. Though any implementer is allowed to define an extension, there is a set of requirements that SHALL be met as part of the definition of the extension. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Extension |
| Alternate Names | extensions, user content |
| Comments | There can be no stigma associated with the use of extensions by any application, project, or standard - regardless of the institution or jurisdiction that uses or defines the extensions. The use of extensions is what allows the FHIR specification to retain a core level of simplicity for everyone. |
| CarePlan.participant.modifierExtension | |
| Definition | May be used to represent additional information that is not part of the basic definition of the element, and that modifies the understanding of the element that contains it. Usually modifier elements provide negation or qualification. In order to make the use of extensions safe and manageable, there is a strict set of governance applied to the definition and use of extensions. Though any implementer is allowed to define an extension, there is a set of requirements that SHALL be met as part of the definition of the extension. Applications processing a resource are required to check for modifier extensions. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Extension |
| Is Modifier | true |
| Alternate Names | extensions, user content, modifiers |
| Comments | There can be no stigma associated with the use of extensions by any application, project, or standard - regardless of the institution or jurisdiction that uses or defines the extensions. The use of extensions is what allows the FHIR specification to retain a core level of simplicity for everyone. |
| CarePlan.participant.role | |
| Definition | Indicates specific responsibility of an individual within the care plan; e.g. "Primary physician", "Team coordinator", "Caregiver", etc. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Binding | Indicates specific responsibility of an individual within the care plan; e.g. "Primary physician", "Team coordinator", "Caregiver", etc. For example codes, see Participant Roles |
| Type | CodeableConcept |
| Comments | Roles may sometimes be inferred by type of Practitioner. These are relationships that hold only within the context of the care plan. General relationships should be handled as properties of the Patient resource directly. |
| CarePlan.participant.member | |
| Definition | The specific person or organization who is participating/expected to participate in the care plan. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | Choice of: Reference(Practitioner), Reference(RelatedPerson), Reference(Patient), Reference(Organization) |
| Comments | Patient only needs to be listed if they have a role other than "subject of care". Member is optional because some participants may be known only by their role, particularly in draft plans. |
| CarePlan.goal | |
| Definition | Describes the intended objective(s) of carrying out the care plan. |
| Control | 0..0 |
| Type | Reference(Goal) |
| Requirements | Provides context for plan. Allows plan effectiveness to be evaluated by clinicians. |
| Comments | Goal can be achieving a particular change or merely maintaining a current state or even slowing a decline. |
| CarePlan.activity | |
| Definition | Identifies a planned action to occur as part of the plan. For example, a medication to be used, lab tests to perform, self-monitoring, education, etc. |
| Control | 0..0 |
| Type | BackboneElement |
| Requirements | Allows systems to prompt for performance of planned activities, and validate plans against best practice. |
| Invariants | Defined on this element ctm-3: Provide a reference or detail, not both (xpath: not(exists(f:detail)) or not(exists(f:reference))) |
| CarePlan.activity.id | |
| Definition | unique id for the element within a resource (for internal references). |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | id |
| CarePlan.activity.extension | |
| Definition | May be used to represent additional information that is not part of the basic definition of the element. In order to make the use of extensions safe and manageable, there is a strict set of governance applied to the definition and use of extensions. Though any implementer is allowed to define an extension, there is a set of requirements that SHALL be met as part of the definition of the extension. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Extension |
| Alternate Names | extensions, user content |
| Comments | There can be no stigma associated with the use of extensions by any application, project, or standard - regardless of the institution or jurisdiction that uses or defines the extensions. The use of extensions is what allows the FHIR specification to retain a core level of simplicity for everyone. |
| CarePlan.activity.modifierExtension | |
| Definition | May be used to represent additional information that is not part of the basic definition of the element, and that modifies the understanding of the element that contains it. Usually modifier elements provide negation or qualification. In order to make the use of extensions safe and manageable, there is a strict set of governance applied to the definition and use of extensions. Though any implementer is allowed to define an extension, there is a set of requirements that SHALL be met as part of the definition of the extension. Applications processing a resource are required to check for modifier extensions. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Extension |
| Is Modifier | true |
| Alternate Names | extensions, user content, modifiers |
| Comments | There can be no stigma associated with the use of extensions by any application, project, or standard - regardless of the institution or jurisdiction that uses or defines the extensions. The use of extensions is what allows the FHIR specification to retain a core level of simplicity for everyone. |
| CarePlan.activity.actionResulting | |
| Definition | Resources that describe follow-on actions resulting from the plan, such as drug prescriptions, encounter records, appointments, etc. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Reference(Resource) |
| Requirements | Links plan to resulting actions. |
| CarePlan.activity.progress | |
| Definition | Notes about the adherence/status/progress of the activity. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Annotation |
| Requirements | Can be used to capture information about adherence, progress, concerns, etc. |
| Comments | This element should NOT be used to describe the activity to be performed - that occurs either within the resource pointed to by activity.detail.reference or in activity.detail.description. |
| CarePlan.activity.reference | |
| Definition | The details of the proposed activity represented in a specific resource. |
| Control | 0..1 This element is affected by the following invariants: ctm-3 |
| Type | Choice of: Reference(Appointment), Reference(CommunicationRequest), Reference(DeviceUseRequest), Reference(DiagnosticOrder), Reference(MedicationOrder), Reference(NutritionOrder), Reference(Order), Reference(ProcedureRequest), Reference(ProcessRequest), Reference(ReferralRequest), Reference(SupplyRequest), Reference(VisionPrescription) |
| Requirements | Details in a form consistent with other applications and contexts of use. |
| CarePlan.activity.detail | |
| Definition | A simple summary of a planned activity suitable for a general care plan system (e.g. form driven) that doesn't know about specific resources such as procedure etc. |
| Control | 0..1 This element is affected by the following invariants: ctm-3 |
| Type | BackboneElement |
| Requirements | Details in a simple form for generic care plan systems. |
| CarePlan.activity.detail.id | |
| Definition | unique id for the element within a resource (for internal references). |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | id |
| CarePlan.activity.detail.extension | |
| Definition | May be used to represent additional information that is not part of the basic definition of the element. In order to make the use of extensions safe and manageable, there is a strict set of governance applied to the definition and use of extensions. Though any implementer is allowed to define an extension, there is a set of requirements that SHALL be met as part of the definition of the extension. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Extension |
| Alternate Names | extensions, user content |
| Comments | There can be no stigma associated with the use of extensions by any application, project, or standard - regardless of the institution or jurisdiction that uses or defines the extensions. The use of extensions is what allows the FHIR specification to retain a core level of simplicity for everyone. |
| CarePlan.activity.detail.modifierExtension | |
| Definition | May be used to represent additional information that is not part of the basic definition of the element, and that modifies the understanding of the element that contains it. Usually modifier elements provide negation or qualification. In order to make the use of extensions safe and manageable, there is a strict set of governance applied to the definition and use of extensions. Though any implementer is allowed to define an extension, there is a set of requirements that SHALL be met as part of the definition of the extension. Applications processing a resource are required to check for modifier extensions. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Extension |
| Is Modifier | true |
| Alternate Names | extensions, user content, modifiers |
| Comments | There can be no stigma associated with the use of extensions by any application, project, or standard - regardless of the institution or jurisdiction that uses or defines the extensions. The use of extensions is what allows the FHIR specification to retain a core level of simplicity for everyone. |
| CarePlan.activity.detail.category | |
| Definition | High-level categorization of the type of activity in a care plan. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Binding | High-level categorization of the type of activity in a care plan. For example codes, see CarePlanActivityCategory |
| Type | CodeableConcept |
| Requirements | May determine what types of extensions are permitted. |
| CarePlan.activity.detail.code | |
| Definition | Detailed description of the type of planned activity; e.g. What lab test, what procedure, what kind of encounter. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Binding | Detailed description of the type of activity; e.g. What lab test, what procedure, what kind of encounter. For example codes, see Care Plan Activity |
| Type | CodeableConcept |
| Requirements | Allows matching performed to planned as well as validation against protocols. |
| Comments | Tends to be less relevant for activities involving particular products. Codes should not convey negation - use "prohibited" instead. |
| CarePlan.activity.detail.reasonCode | |
| Definition | Provides the rationale that drove the inclusion of this particular activity as part of the plan. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Binding | Identifies why a care plan activity is needed. Can include any health condition codes as well as such concepts as "general wellness", prophylaxis, surgical preparation, etc. For example codes, see Activity Reason |
| Type | CodeableConcept |
| Comments | This could be a diagnosis code. If a full condition record exists or additional detail is needed, use reasonCondition instead. |
| CarePlan.activity.detail.reasonReference | |
| Definition | Provides the health condition(s) that drove the inclusion of this particular activity as part of the plan. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Reference(Condition) |
| Comments | Conditions can be identified at the activity level that are not identified as reasons for the overall plan. |
| CarePlan.activity.detail.goal | |
| Definition | Internal reference that identifies the goals that this activity is intended to contribute towards meeting. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Reference(Goal) |
| Requirements | So that participants know the link explicitly. |
| CarePlan.activity.detail.status | |
| Definition | Identifies what progress is being made for the specific activity. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Binding | Indicates where the activity is at in its overall life cycle. The codes SHALL be taken from CarePlanActivityStatus |
| Type | code |
| Is Modifier | true |
| Requirements | Indicates progress against the plan, whether the activity is still relevant for the plan. |
| Comments | Some aspects of status can be inferred based on the resources linked in actionTaken. Note that "status" is only as current as the plan was most recently updated. |
| CarePlan.activity.detail.statusReason | |
| Definition | Provides reason why the activity isn't yet started, is on hold, was cancelled, etc. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Binding | Describes why the current activity has the status it does; e.g. "Recovering from injury" as a reason for non-started or on-hold, "Patient does not enjoy activity" as a reason for cancelling a planned activity. For example codes, see GoalStatusReason |
| Type | CodeableConcept |
| Comments | Will generally not be present if status is "complete". Be sure to prompt to update this (or at least remove the existing value) if the status is changed. |
| CarePlan.activity.detail.prohibited | |
| Definition | If true, indicates that the described activity is one that must NOT be engaged in when following the plan. |
| Control | 1..1 |
| Type | boolean |
| Is Modifier | true |
| Requirements | Captures intention to not do something that may have been previously typical. |
| CarePlan.activity.detail.scheduled[x] | |
| Definition | The period, timing or frequency upon which the described activity is to occur. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | Choice of: Timing, Period, string |
| [x] Note | See Choice of Data Types for further information about how to use [x] |
| Requirements | Allows prompting for activities and detection of missed planned activities. |
| CarePlan.activity.detail.location | |
| Definition | Identifies the facility where the activity will occur; e.g. home, hospital, specific clinic, etc. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | Reference(Location) |
| Requirements | Helps in planning of activity. |
| Comments | May reference a specific clinical location or may identify a type of location. |
| CarePlan.activity.detail.performer | |
| Definition | Identifies who's expected to be involved in the activity. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Choice of: Reference(Practitioner), Reference(Organization), Reference(RelatedPerson), Reference(Patient) |
| Requirements | Helps in planning of activity. |
| Comments | A performer MAY also be a participant in the care plan. |
| CarePlan.activity.detail.product[x] | |
| Definition | Identifies the food, drug or other product to be consumed or supplied in the activity. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Binding | A product supplied or administered as part of a care plan activity. For example codes, see SNOMED CT Medication Codes |
| Type | Choice of: CodeableConcept, Reference(Medication), Reference(Substance) |
| [x] Note | See Choice of Data Types for further information about how to use [x] |
| CarePlan.activity.detail.dailyAmount | |
| Definition | Identifies the quantity expected to be consumed in a given day. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | Quantity(SimpleQuantity) |
| Requirements | Allows rough dose checking. |
| Alternate Names | daily dose |
| CarePlan.activity.detail.quantity | |
| Definition | Identifies the quantity expected to be supplied, administered or consumed by the subject. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | Quantity(SimpleQuantity) |
| CarePlan.activity.detail.description | |
| Definition | This provides a textual description of constraints on the intended activity occurrence, including relation to other activities. It may also include objectives, pre-conditions and end-conditions. Finally, it may convey specifics about the activity such as body site, method, route, etc. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | string |
| CarePlan.note | |
| Definition | General notes about the care plan not covered elsewhere. |
| Control | 0..0 |
| Type | Annotation |
| Requirements | Used to capture information that applies to the plan as a whole that doesn't fit into discrete elements. |