This page is part of the FHIR Specification (v1.2.0: STU 3 Draft). The current version which supercedes this version is 5.0.0. For a full list of available versions, see the Directory of published versions 

Definitions for the argonaut-provider Profile.
| Practitioner | |
| Definition | A person who is directly or indirectly involved in the provisioning of healthcare. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Practitioner |
| Must Support | true |
| Comments | Note that a cab driver no longer fits the bill. You probably would be interested in the organization rather than the individual? |
| Practitioner.id | |
| Definition | The logical id of the resource, as used in the URL for the resource. Once assigned, this value never changes. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | id |
| Comments | The only time that a resource does not have an id is when it is being submitted to the server using a create operation. Bundles always have an id, though it is usually a generated UUID. |
| Practitioner.meta | |
| Definition | The metadata about the resource. This is content that is maintained by the infrastructure. Changes to the content may not always be associated with version changes to the resource. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | Meta |
| Practitioner.implicitRules | |
| Definition | A reference to a set of rules that were followed when the resource was constructed, and which must be understood when processing the content. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | uri |
| Is Modifier | true |
| Comments | Asserting this rule set restricts the content to be only understood by a limited set of trading partners. This inherently limits the usefulness of the data in the long term. However, the existing health eco-system is highly fractured, and not yet ready to define, collect, and exchange data in a generally computable sense. Wherever possible, implementers and/or specification writers should avoid using this element as much as possible. |
| Practitioner.language | |
| Definition | The base language in which the resource is written. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Binding | A human language. The codes SHALL be taken from http://tools.ietf.org/html/bcp47 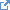 |
| Type | code |
| Comments | Language is provided to support indexing and accessibility (typically, services such as text to speech use the language tag). The html language tag in the narrative applies to the narrative. The language tag on the resource may be used to specify the language of other presentations generated from the data in the resource Not all the content has to be in the base language. The Resource.language should not be assumed to apply to the narrative automatically. If a language is specified, it should it also be specified on the div element in the html (see rules in HTML5 for information about the relationship between xml:lang and the html lang attribute). |
| Practitioner.text | |
| Definition | A human-readable narrative that contains a summary of the resource, and may be used to represent the content of the resource to a human. The narrative need not encode all the structured data, but is required to contain sufficient detail to make it "clinically safe" for a human to just read the narrative. Resource definitions may define what content should be represented in the narrative to ensure clinical safety. |
| Control | 0..1 This element is affected by the following invariants: dom-1 |
| Type | Narrative |
| Alternate Names | narrative, html, xhtml, display |
| Comments | Contained resources do not have narrative. Resources that are not contained SHOULD have a narrative. |
| Practitioner.contained | |
| Definition | These resources do not have an independent existence apart from the resource that contains them - they cannot be identified independently, and nor can they have their own independent transaction scope. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Resource |
| Alternate Names | inline resources, anonymous resources, contained resources |
| Comments | This should never be done when the content can be identified properly, as once identification is lost, it is extremely difficult (and context dependent) to restore it again. |
| Practitioner.extension | |
| Definition | May be used to represent additional information that is not part of the basic definition of the resource. In order to make the use of extensions safe and manageable, there is a strict set of governance applied to the definition and use of extensions. Though any implementer is allowed to define an extension, there is a set of requirements that SHALL be met as part of the definition of the extension. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Extension |
| Alternate Names | extensions, user content |
| Comments | There can be no stigma associated with the use of extensions by any application, project, or standard - regardless of the institution or jurisdiction that uses or defines the extensions. The use of extensions is what allows the FHIR specification to retain a core level of simplicity for everyone. |
| Practitioner.modifierExtension | |
| Definition | May be used to represent additional information that is not part of the basic definition of the resource, and that modifies the understanding of the element that contains it. Usually modifier elements provide negation or qualification. In order to make the use of extensions safe and manageable, there is a strict set of governance applied to the definition and use of extensions. Though any implementer is allowed to define an extension, there is a set of requirements that SHALL be met as part of the definition of the extension. Applications processing a resource are required to check for modifier extensions. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Extension |
| Is Modifier | true |
| Alternate Names | extensions, user content |
| Comments | There can be no stigma associated with the use of extensions by any application, project, or standard - regardless of the institution or jurisdiction that uses or defines the extensions. The use of extensions is what allows the FHIR specification to retain a core level of simplicity for everyone. |
| Practitioner.identifier | |
| Definition | An identifier that applies to this person in this role. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Identifier |
| Requirements | Often, specific identities are assigned for the agent. |
| Slicing | This element introduces a set of slices. The slicing rules are:
|
| Practitioner.identifier(DEA Number) | |
| Definition | An identifier that applies to this person in this role. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Identifier |
| Requirements | Often, specific identities are assigned for the agent. |
| Practitioner.identifier.id | |
| Definition | unique id for the element within a resource (for internal references). |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | id |
| Practitioner.identifier.extension | |
| Definition | May be used to represent additional information that is not part of the basic definition of the element. In order to make the use of extensions safe and manageable, there is a strict set of governance applied to the definition and use of extensions. Though any implementer is allowed to define an extension, there is a set of requirements that SHALL be met as part of the definition of the extension. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Extension |
| Alternate Names | extensions, user content |
| Comments | There can be no stigma associated with the use of extensions by any application, project, or standard - regardless of the institution or jurisdiction that uses or defines the extensions. The use of extensions is what allows the FHIR specification to retain a core level of simplicity for everyone. |
| Practitioner.identifier.use | |
| Definition | The purpose of this identifier. |
| Control | 0..0 |
| Binding | Identifies the purpose for this identifier, if known . The codes SHALL be taken from IdentifierUse |
| Type | code |
| Is Modifier | true |
| Requirements | Allows the appropriate identifier for a particular context of use to be selected from among a set of identifiers. |
| Comments | This is labeled as "Is Modifier" because applications should not mistake a temporary id for a permanent one. Applications can assume that an identifier is permanent unless it explicitly says that it is temporary. |
| Practitioner.identifier.type | |
| Definition | A coded type for the identifier that can be used to determine which identifier to use for a specific purpose. |
| Control | 0..0 |
| Binding | A coded type for an identifier that can be used to determine which identifier to use for a specific purpose. The codes SHALL be taken from Identifier Type Codes; other codes may be used where these codes are not suitable |
| Type | CodeableConcept |
| Requirements | Allows users to make use of identifiers when the identifier system is not known. |
| Comments | This element deals only with general categories of identifiers. It SHOULD not be used for codes that correspond 1..1 with the Identifier.system. Some identifiers may fall into multiple categories due to common usage. Where the system is known, a type is unnecessary because the type is always part of the system definition. However systems often need to handle identifiers where the system is not known. There is not a 1:1 relationship between type and system, since many different systems have the same type. |
| Practitioner.identifier.system | |
| Definition | Establishes the namespace in which set of possible id values is unique. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | uri |
| Must Support | true |
| Requirements | There are many sequences of identifiers. To perform matching, we need to know what sequence we're dealing with. The system identifies a particular sequence or set of unique identifiers. |
| Fixed Value | http://www.dea.gov/ |
| Example | http://www.acme.com/identifiers/patient or urn:ietf:rfc:3986 if the Identifier.value itself is a full uri |
| Practitioner.identifier.value | |
| Definition | The portion of the identifier typically displayed to the user and which is unique within the context of the system. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | string |
| Must Support | true |
| Comments | If the value is a full URI, then the system SHALL be urn:ietf:rfc:3986. |
| Example | AB2345690 |
| Practitioner.identifier.period | |
| Definition | Time period during which identifier is/was valid for use. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | Period |
| Practitioner.identifier.assigner | |
| Definition | Organization that issued/manages the identifier. |
| Control | 0..0 |
| Type | Reference(Organization) |
| Comments | The reference may be just a text description of the assigner. |
| Practitioner.identifier(Dentist License Number) | |
| Definition | An identifier that applies to this person in this role. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Identifier |
| Requirements | Often, specific identities are assigned for the agent. |
| Practitioner.identifier.id | |
| Definition | unique id for the element within a resource (for internal references). |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | id |
| Practitioner.identifier.extension | |
| Definition | May be used to represent additional information that is not part of the basic definition of the element. In order to make the use of extensions safe and manageable, there is a strict set of governance applied to the definition and use of extensions. Though any implementer is allowed to define an extension, there is a set of requirements that SHALL be met as part of the definition of the extension. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Extension |
| Alternate Names | extensions, user content |
| Comments | There can be no stigma associated with the use of extensions by any application, project, or standard - regardless of the institution or jurisdiction that uses or defines the extensions. The use of extensions is what allows the FHIR specification to retain a core level of simplicity for everyone. |
| Practitioner.identifier.use | |
| Definition | The purpose of this identifier. |
| Control | 0..0 |
| Binding | Identifies the purpose for this identifier, if known . The codes SHALL be taken from IdentifierUse |
| Type | code |
| Is Modifier | true |
| Requirements | Allows the appropriate identifier for a particular context of use to be selected from among a set of identifiers. |
| Comments | This is labeled as "Is Modifier" because applications should not mistake a temporary id for a permanent one. Applications can assume that an identifier is permanent unless it explicitly says that it is temporary. |
| Practitioner.identifier.type | |
| Definition | A coded type for the identifier that can be used to determine which identifier to use for a specific purpose. |
| Control | 0..0 |
| Binding | A coded type for an identifier that can be used to determine which identifier to use for a specific purpose. The codes SHALL be taken from Identifier Type Codes; other codes may be used where these codes are not suitable |
| Type | CodeableConcept |
| Requirements | Allows users to make use of identifiers when the identifier system is not known. |
| Comments | This element deals only with general categories of identifiers. It SHOULD not be used for codes that correspond 1..1 with the Identifier.system. Some identifiers may fall into multiple categories due to common usage. Where the system is known, a type is unnecessary because the type is always part of the system definition. However systems often need to handle identifiers where the system is not known. There is not a 1:1 relationship between type and system, since many different systems have the same type. |
| Practitioner.identifier.system | |
| Definition | Establishes the namespace in which set of possible id values is unique. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | uri |
| Must Support | true |
| Requirements | There are many sequences of identifiers. To perform matching, we need to know what sequence we're dealing with. The system identifies a particular sequence or set of unique identifiers. |
| Fixed Value | http://example.org/DentistLicenseNumber |
| Example | http://www.acme.com/identifiers/patient or urn:ietf:rfc:3986 if the Identifier.value itself is a full uri |
| Practitioner.identifier.value | |
| Definition | The portion of the identifier typically displayed to the user and which is unique within the context of the system. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | string |
| Must Support | true |
| Comments | If the value is a full URI, then the system SHALL be urn:ietf:rfc:3986. |
| Example | 123 |
| Practitioner.identifier.period | |
| Definition | Time period during which identifier is/was valid for use. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | Period |
| Practitioner.identifier.assigner | |
| Definition | Organization that issued/manages the identifier. |
| Control | 0..0 |
| Type | Reference(Organization) |
| Comments | The reference may be just a text description of the assigner. |
| Practitioner.identifier(Medicaid Number) | |
| Definition | An identifier that applies to this person in this role. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Identifier |
| Requirements | Often, specific identities are assigned for the agent. |
| Practitioner.identifier.id | |
| Definition | unique id for the element within a resource (for internal references). |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | id |
| Practitioner.identifier.extension | |
| Definition | May be used to represent additional information that is not part of the basic definition of the element. In order to make the use of extensions safe and manageable, there is a strict set of governance applied to the definition and use of extensions. Though any implementer is allowed to define an extension, there is a set of requirements that SHALL be met as part of the definition of the extension. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Extension |
| Alternate Names | extensions, user content |
| Comments | There can be no stigma associated with the use of extensions by any application, project, or standard - regardless of the institution or jurisdiction that uses or defines the extensions. The use of extensions is what allows the FHIR specification to retain a core level of simplicity for everyone. |
| Practitioner.identifier.use | |
| Definition | The purpose of this identifier. |
| Control | 0..0 |
| Binding | Identifies the purpose for this identifier, if known . The codes SHALL be taken from IdentifierUse |
| Type | code |
| Is Modifier | true |
| Requirements | Allows the appropriate identifier for a particular context of use to be selected from among a set of identifiers. |
| Comments | This is labeled as "Is Modifier" because applications should not mistake a temporary id for a permanent one. Applications can assume that an identifier is permanent unless it explicitly says that it is temporary. |
| Practitioner.identifier.type | |
| Definition | A coded type for the identifier that can be used to determine which identifier to use for a specific purpose. |
| Control | 0..0 |
| Binding | A coded type for an identifier that can be used to determine which identifier to use for a specific purpose. The codes SHALL be taken from Identifier Type Codes; other codes may be used where these codes are not suitable |
| Type | CodeableConcept |
| Requirements | Allows users to make use of identifiers when the identifier system is not known. |
| Comments | This element deals only with general categories of identifiers. It SHOULD not be used for codes that correspond 1..1 with the Identifier.system. Some identifiers may fall into multiple categories due to common usage. Where the system is known, a type is unnecessary because the type is always part of the system definition. However systems often need to handle identifiers where the system is not known. There is not a 1:1 relationship between type and system, since many different systems have the same type. |
| Practitioner.identifier.system | |
| Definition | Establishes the namespace in which set of possible id values is unique. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | uri |
| Must Support | true |
| Requirements | There are many sequences of identifiers. To perform matching, we need to know what sequence we're dealing with. The system identifies a particular sequence or set of unique identifiers. |
| Fixed Value | http://www.medicaid.gov |
| Example | http://www.acme.com/identifiers/patient or urn:ietf:rfc:3986 if the Identifier.value itself is a full uri |
| Practitioner.identifier.value | |
| Definition | The portion of the identifier typically displayed to the user and which is unique within the context of the system. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | string |
| Must Support | true |
| Comments | If the value is a full URI, then the system SHALL be urn:ietf:rfc:3986. |
| Example | 21123 |
| Practitioner.identifier.period | |
| Definition | Time period during which identifier is/was valid for use. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | Period |
| Practitioner.identifier.assigner | |
| Definition | Organization that issued/manages the identifier. |
| Control | 0..0 |
| Type | Reference(Organization) |
| Comments | The reference may be just a text description of the assigner. |
| Practitioner.identifier(Medicare Number) | |
| Definition | An identifier that applies to this person in this role. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Identifier |
| Requirements | Often, specific identities are assigned for the agent. |
| Practitioner.identifier.id | |
| Definition | unique id for the element within a resource (for internal references). |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | id |
| Practitioner.identifier.extension | |
| Definition | May be used to represent additional information that is not part of the basic definition of the element. In order to make the use of extensions safe and manageable, there is a strict set of governance applied to the definition and use of extensions. Though any implementer is allowed to define an extension, there is a set of requirements that SHALL be met as part of the definition of the extension. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Extension |
| Alternate Names | extensions, user content |
| Comments | There can be no stigma associated with the use of extensions by any application, project, or standard - regardless of the institution or jurisdiction that uses or defines the extensions. The use of extensions is what allows the FHIR specification to retain a core level of simplicity for everyone. |
| Practitioner.identifier.use | |
| Definition | The purpose of this identifier. |
| Control | 0..0 |
| Binding | Identifies the purpose for this identifier, if known . The codes SHALL be taken from IdentifierUse |
| Type | code |
| Is Modifier | true |
| Requirements | Allows the appropriate identifier for a particular context of use to be selected from among a set of identifiers. |
| Comments | This is labeled as "Is Modifier" because applications should not mistake a temporary id for a permanent one. Applications can assume that an identifier is permanent unless it explicitly says that it is temporary. |
| Practitioner.identifier.type | |
| Definition | A coded type for the identifier that can be used to determine which identifier to use for a specific purpose. |
| Control | 0..0 |
| Binding | A coded type for an identifier that can be used to determine which identifier to use for a specific purpose. The codes SHALL be taken from Identifier Type Codes; other codes may be used where these codes are not suitable |
| Type | CodeableConcept |
| Requirements | Allows users to make use of identifiers when the identifier system is not known. |
| Comments | This element deals only with general categories of identifiers. It SHOULD not be used for codes that correspond 1..1 with the Identifier.system. Some identifiers may fall into multiple categories due to common usage. Where the system is known, a type is unnecessary because the type is always part of the system definition. However systems often need to handle identifiers where the system is not known. There is not a 1:1 relationship between type and system, since many different systems have the same type. |
| Practitioner.identifier.system | |
| Definition | Establishes the namespace in which set of possible id values is unique. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | uri |
| Must Support | true |
| Requirements | There are many sequences of identifiers. To perform matching, we need to know what sequence we're dealing with. The system identifies a particular sequence or set of unique identifiers. |
| Fixed Value | http://www.medicare.gov |
| Example | http://www.acme.com/identifiers/patient or urn:ietf:rfc:3986 if the Identifier.value itself is a full uri |
| Practitioner.identifier.value | |
| Definition | The portion of the identifier typically displayed to the user and which is unique within the context of the system. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | string |
| Must Support | true |
| Comments | If the value is a full URI, then the system SHALL be urn:ietf:rfc:3986. |
| Example | 23432 |
| Practitioner.identifier.period | |
| Definition | Time period during which identifier is/was valid for use. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | Period |
| Practitioner.identifier.assigner | |
| Definition | Organization that issued/manages the identifier. |
| Control | 0..0 |
| Type | Reference(Organization) |
| Comments | The reference may be just a text description of the assigner. |
| Practitioner.identifier(NPI) | |
| Definition | An identifier that applies to this person in this role. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Identifier |
| Requirements | Often, specific identities are assigned for the agent. |
| Practitioner.identifier.id | |
| Definition | unique id for the element within a resource (for internal references). |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | id |
| Practitioner.identifier.extension | |
| Definition | May be used to represent additional information that is not part of the basic definition of the element. In order to make the use of extensions safe and manageable, there is a strict set of governance applied to the definition and use of extensions. Though any implementer is allowed to define an extension, there is a set of requirements that SHALL be met as part of the definition of the extension. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Extension |
| Alternate Names | extensions, user content |
| Comments | There can be no stigma associated with the use of extensions by any application, project, or standard - regardless of the institution or jurisdiction that uses or defines the extensions. The use of extensions is what allows the FHIR specification to retain a core level of simplicity for everyone. |
| Practitioner.identifier.use | |
| Definition | The purpose of this identifier. |
| Control | 0..0 |
| Binding | Identifies the purpose for this identifier, if known . The codes SHALL be taken from IdentifierUse |
| Type | code |
| Is Modifier | true |
| Requirements | Allows the appropriate identifier for a particular context of use to be selected from among a set of identifiers. |
| Comments | This is labeled as "Is Modifier" because applications should not mistake a temporary id for a permanent one. Applications can assume that an identifier is permanent unless it explicitly says that it is temporary. |
| Practitioner.identifier.type | |
| Definition | A coded type for the identifier that can be used to determine which identifier to use for a specific purpose. |
| Control | 0..0 |
| Binding | A coded type for an identifier that can be used to determine which identifier to use for a specific purpose. The codes SHALL be taken from Identifier Type Codes; other codes may be used where these codes are not suitable |
| Type | CodeableConcept |
| Requirements | Allows users to make use of identifiers when the identifier system is not known. |
| Comments | This element deals only with general categories of identifiers. It SHOULD not be used for codes that correspond 1..1 with the Identifier.system. Some identifiers may fall into multiple categories due to common usage. Where the system is known, a type is unnecessary because the type is always part of the system definition. However systems often need to handle identifiers where the system is not known. There is not a 1:1 relationship between type and system, since many different systems have the same type. |
| Practitioner.identifier.system | |
| Definition | Establishes the namespace in which set of possible id values is unique. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | uri |
| Must Support | true |
| Requirements | There are many sequences of identifiers. To perform matching, we need to know what sequence we're dealing with. The system identifies a particular sequence or set of unique identifiers. |
| Fixed Value | http://hl7.org/fhir/sid/us-npi |
| Example | http://www.acme.com/identifiers/patient or urn:ietf:rfc:3986 if the Identifier.value itself is a full uri |
| Practitioner.identifier.value | |
| Definition | The portion of the identifier typically displayed to the user and which is unique within the context of the system. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | string |
| Must Support | true |
| Comments | If the value is a full URI, then the system SHALL be urn:ietf:rfc:3986. |
| Example | 1369569128 |
| Practitioner.identifier.period | |
| Definition | Time period during which identifier is/was valid for use. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | Period |
| Practitioner.identifier.assigner | |
| Definition | Organization that issued/manages the identifier. |
| Control | 0..0 |
| Type | Reference(Organization) |
| Comments | The reference may be just a text description of the assigner. |
| Practitioner.identifier(SSN) | |
| Definition | An identifier that applies to this person in this role. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Identifier |
| Requirements | Often, specific identities are assigned for the agent. |
| Practitioner.identifier.id | |
| Definition | unique id for the element within a resource (for internal references). |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | id |
| Practitioner.identifier.extension | |
| Definition | May be used to represent additional information that is not part of the basic definition of the element. In order to make the use of extensions safe and manageable, there is a strict set of governance applied to the definition and use of extensions. Though any implementer is allowed to define an extension, there is a set of requirements that SHALL be met as part of the definition of the extension. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Extension |
| Alternate Names | extensions, user content |
| Comments | There can be no stigma associated with the use of extensions by any application, project, or standard - regardless of the institution or jurisdiction that uses or defines the extensions. The use of extensions is what allows the FHIR specification to retain a core level of simplicity for everyone. |
| Practitioner.identifier.use | |
| Definition | The purpose of this identifier. |
| Control | 0..0 |
| Binding | Identifies the purpose for this identifier, if known . The codes SHALL be taken from IdentifierUse |
| Type | code |
| Is Modifier | true |
| Requirements | Allows the appropriate identifier for a particular context of use to be selected from among a set of identifiers. |
| Comments | This is labeled as "Is Modifier" because applications should not mistake a temporary id for a permanent one. Applications can assume that an identifier is permanent unless it explicitly says that it is temporary. |
| Practitioner.identifier.type | |
| Definition | A coded type for the identifier that can be used to determine which identifier to use for a specific purpose. |
| Control | 0..0 |
| Binding | A coded type for an identifier that can be used to determine which identifier to use for a specific purpose. The codes SHALL be taken from Identifier Type Codes; other codes may be used where these codes are not suitable |
| Type | CodeableConcept |
| Requirements | Allows users to make use of identifiers when the identifier system is not known. |
| Comments | This element deals only with general categories of identifiers. It SHOULD not be used for codes that correspond 1..1 with the Identifier.system. Some identifiers may fall into multiple categories due to common usage. Where the system is known, a type is unnecessary because the type is always part of the system definition. However systems often need to handle identifiers where the system is not known. There is not a 1:1 relationship between type and system, since many different systems have the same type. |
| Practitioner.identifier.system | |
| Definition | Establishes the namespace in which set of possible id values is unique. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | uri |
| Must Support | true |
| Requirements | There are many sequences of identifiers. To perform matching, we need to know what sequence we're dealing with. The system identifies a particular sequence or set of unique identifiers. |
| Fixed Value | http://hl7.org/fhir/sid/us-ssn |
| Example | http://www.acme.com/identifiers/patient or urn:ietf:rfc:3986 if the Identifier.value itself is a full uri |
| Practitioner.identifier.value | |
| Definition | The portion of the identifier typically displayed to the user and which is unique within the context of the system. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | string |
| Must Support | true |
| Comments | If the value is a full URI, then the system SHALL be urn:ietf:rfc:3986. |
| Example | 983232323 |
| Practitioner.identifier.period | |
| Definition | Time period during which identifier is/was valid for use. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | Period |
| Practitioner.identifier.assigner | |
| Definition | Organization that issued/manages the identifier. |
| Control | 0..0 |
| Type | Reference(Organization) |
| Comments | The reference may be just a text description of the assigner. |
| Practitioner.active | |
| Definition | Whether this practitioner's record is in active use. |
| Control | 0..0 |
| Type | boolean |
| Must Support | true |
| Requirements | Only active records to be exposed |
| Comments | Default is true |
| Default Value | true |
| Practitioner.name | |
| Definition | A name associated with the person. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | HumanName |
| Must Support | true |
| Requirements | Contact persons need to be identified by name, but it is uncommon to need details about multiple other names for that person. |
| Practitioner.name.id | |
| Definition | unique id for the element within a resource (for internal references). |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | id |
| Practitioner.name.extension | |
| Definition | May be used to represent additional information that is not part of the basic definition of the element. In order to make the use of extensions safe and manageable, there is a strict set of governance applied to the definition and use of extensions. Though any implementer is allowed to define an extension, there is a set of requirements that SHALL be met as part of the definition of the extension. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Extension |
| Alternate Names | extensions, user content |
| Comments | There can be no stigma associated with the use of extensions by any application, project, or standard - regardless of the institution or jurisdiction that uses or defines the extensions. The use of extensions is what allows the FHIR specification to retain a core level of simplicity for everyone. |
| Practitioner.name.use | |
| Definition | Identifies the purpose for this name. |
| Control | 0..0 |
| Binding | The use of a human name The codes SHALL be taken from NameUse |
| Type | code |
| Is Modifier | true |
| Requirements | Allows the appropriate name for a particular context of use to be selected from among a set of names. |
| Comments | This is labeled as "Is Modifier" because applications should not mistake a temporary or old name etc.for a current/permanent one. Applications can assume that a name is current unless it explicitly says that it is temporary or old. |
| Practitioner.name.text | |
| Definition | A full text representation of the name. |
| Control | 0..0 |
| Type | string |
| Requirements | A renderable, unencoded form. |
| Comments | Structured names only |
| Practitioner.name.family(Last Name) | |
| Definition | The part of a name that links to the genealogy. In some cultures (e.g. Eritrea) the family name of a son is the first name of his father. |
| Control | 1..1 |
| Type | string |
| Must Support | true |
| Alternate Names | surname |
| Comments | Only one family name in US usage |
| Example | Jones |
| Practitioner.name.given | |
| Definition | Given name. |
| Control | 1..2 |
| Type | string |
| Alternate Names | first name, middle name |
| Comments | If only initials are recorded, they may be used in place of the full name. Not called "first name" since given names do not always come first. |
| Slicing | This element introduces a set of slices. The slicing rules are:
|
| Practitioner.name.given(first name) | |
| Definition | Given name. |
| Control | 1..1 |
| Type | string |
| Must Support | true |
| Alternate Names | first name, middle name |
| Comments | If only initials are recorded, they may be used in place of the full name. Not called "first name" since given names do not always come first. |
| Example | Bob |
| Practitioner.name.given(middle name) | |
| Definition | Given name. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | string |
| Must Support | true |
| Alternate Names | first name, middle name |
| Comments | Is often just an initial |
| Example | M |
| Practitioner.name.prefix | |
| Definition | Part of the name that is acquired as a title due to academic, legal, employment or nobility status, etc. and that appears at the start of the name. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | string |
| Must Support | true |
| Example | Dr |
| Practitioner.name.suffix | |
| Definition | Part of the name that is acquired as a title due to academic, legal, employment or nobility status, etc. and that appears at the end of the name. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | string |
| Must Support | true |
| Example | MD |
| Practitioner.name.period | |
| Definition | Indicates the period of time when this name was valid for the named person. |
| Control | 0..0 |
| Type | Period |
| Requirements | Allows names to be placed in historical context. |
| Practitioner.telecom | |
| Definition | A contact detail for the practitioner, e.g. a telephone number or an email address. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | ContactPoint |
| Requirements | Need to know how to reach a practitioner. |
| Comments | Person may have multiple ways to be contacted with different uses or applicable periods. May need to have options for contacting the person urgently, and also to help with identification. |
| Slicing | This element introduces a set of slices. The slicing rules are:
|
| Practitioner.telecom(email) | |
| Definition | A contact detail for the practitioner, e.g. a telephone number or an email address. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | ContactPoint |
| Must Support | true |
| Requirements | Need to know how to reach a practitioner. |
| Comments | Person may have multiple ways to be contacted with different uses or applicable periods. May need to have options for contacting the person urgently, and also to help with identification. |
| Practitioner.telecom.id | |
| Definition | unique id for the element within a resource (for internal references). |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | id |
| Practitioner.telecom.extension | |
| Definition | An Extension |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Extension |
| Slicing | This element introduces a set of slices. The slicing rules are:
|
| Practitioner.telecom.extension (http://hl7.org/fhir/StructureDefinition/us-core-direct) | |
| Definition | This email address is associated with a "direct" service - e.g. http://wiki.directproject.org/Addressing+Specification. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | Extension (Extension Type: boolean) |
| Comments | This extension can only be used on contact points where the system = 'email'. |
| Practitioner.telecom.system | |
| Definition | Telecommunications form for contact point - what communications system is required to make use of the contact. |
| Control | 1..1 This element is affected by the following invariants: cpt-2 |
| Binding | Telecommunications form for contact point The codes SHALL be taken from ContactPointSystem |
| Type | code |
| Must Support | true |
| Fixed Value | |
| Practitioner.telecom.value | |
| Definition | The actual contact point details, in a form that is meaningful to the designated communication system (i.e. phone number or email address). |
| Control | 1..1 |
| Type | string |
| Requirements | Need to support legacy numbers that are not in a tightly controlled format. |
| Comments | Additional text data such as phone extension numbers, or notes about use of the contact are sometimes included in the value. |
| Example | example@surescripts.com |
| Practitioner.telecom.use | |
| Definition | Identifies the purpose for the contact point. |
| Control | 0..0 |
| Binding | Use of contact point The codes SHALL be taken from ContactPointUse |
| Type | code |
| Is Modifier | true |
| Requirements | Need to track the way a person uses this contact, so a user can choose which is appropriate for their purpose. |
| Comments | This is labeled as "Is Modifier" because applications should not mistake a temporary or old contact etc.for a current/permanent one. Applications can assume that a contact is current unless it explicitly says that it is temporary or old. |
| Practitioner.telecom.rank | |
| Definition | Specifies a preferred order in which to use a set of contacts. Contacts are ranked with lower values coming before higher values. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | positiveInt |
| Comments | Note that rank does not necessarily follow the order in which the contacts are represented in the instance. |
| Practitioner.telecom.period | |
| Definition | Time period when the contact point was/is in use. |
| Control | 0..0 |
| Type | Period |
| Practitioner.telecom(fax) | |
| Definition | A contact detail for the practitioner, e.g. a telephone number or an email address. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | ContactPoint |
| Must Support | true |
| Requirements | Need to know how to reach a practitioner. |
| Comments | Person may have multiple ways to be contacted with different uses or applicable periods. May need to have options for contacting the person urgently, and also to help with identification. |
| Practitioner.telecom.id | |
| Definition | unique id for the element within a resource (for internal references). |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | id |
| Practitioner.telecom.extension | |
| Definition | May be used to represent additional information that is not part of the basic definition of the element. In order to make the use of extensions safe and manageable, there is a strict set of governance applied to the definition and use of extensions. Though any implementer is allowed to define an extension, there is a set of requirements that SHALL be met as part of the definition of the extension. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Extension |
| Alternate Names | extensions, user content |
| Comments | There can be no stigma associated with the use of extensions by any application, project, or standard - regardless of the institution or jurisdiction that uses or defines the extensions. The use of extensions is what allows the FHIR specification to retain a core level of simplicity for everyone. |
| Practitioner.telecom.system | |
| Definition | Telecommunications form for contact point - what communications system is required to make use of the contact. |
| Control | 1..1 This element is affected by the following invariants: cpt-2 |
| Binding | Telecommunications form for contact point The codes SHALL be taken from ContactPointSystem |
| Type | code |
| Must Support | true |
| Fixed Value | fax |
| Practitioner.telecom.value | |
| Definition | The actual contact point details, in a form that is meaningful to the designated communication system (i.e. phone number or email address). |
| Control | 1..1 |
| Type | string |
| Must Support | true |
| Requirements | Need to support legacy numbers that are not in a tightly controlled format. |
| Comments | Additional text data such as phone extension numbers, or notes about use of the contact are sometimes included in the value. |
| Example | 6518553001 |
| Practitioner.telecom.use | |
| Definition | Identifies the purpose for the contact point. |
| Control | 0..0 |
| Binding | Use of contact point The codes SHALL be taken from ContactPointUse |
| Type | code |
| Is Modifier | true |
| Requirements | Need to track the way a person uses this contact, so a user can choose which is appropriate for their purpose. |
| Comments | This is labeled as "Is Modifier" because applications should not mistake a temporary or old contact etc.for a current/permanent one. Applications can assume that a contact is current unless it explicitly says that it is temporary or old. |
| Practitioner.telecom.rank | |
| Definition | Specifies a preferred order in which to use a set of contacts. Contacts are ranked with lower values coming before higher values. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | positiveInt |
| Comments | Note that rank does not necessarily follow the order in which the contacts are represented in the instance. |
| Practitioner.telecom.period | |
| Definition | Time period when the contact point was/is in use. |
| Control | 0..0 |
| Type | Period |
| Practitioner.telecom(home phone) | |
| Definition | A contact detail for the practitioner, e.g. a telephone number or an email address. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | ContactPoint |
| Requirements | Need to know how to reach a practitioner. |
| Comments | Person may have multiple ways to be contacted with different uses or applicable periods. May need to have options for contacting the person urgently, and also to help with identification. |
| Practitioner.telecom.id | |
| Definition | unique id for the element within a resource (for internal references). |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | id |
| Practitioner.telecom.extension | |
| Definition | May be used to represent additional information that is not part of the basic definition of the element. In order to make the use of extensions safe and manageable, there is a strict set of governance applied to the definition and use of extensions. Though any implementer is allowed to define an extension, there is a set of requirements that SHALL be met as part of the definition of the extension. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Extension |
| Alternate Names | extensions, user content |
| Comments | There can be no stigma associated with the use of extensions by any application, project, or standard - regardless of the institution or jurisdiction that uses or defines the extensions. The use of extensions is what allows the FHIR specification to retain a core level of simplicity for everyone. |
| Practitioner.telecom.system | |
| Definition | Telecommunications form for contact point - what communications system is required to make use of the contact. |
| Control | 1..1 This element is affected by the following invariants: cpt-2 |
| Binding | Telecommunications form for contact point The codes SHALL be taken from ContactPointSystem |
| Type | code |
| Fixed Value | phone |
| Practitioner.telecom.value | |
| Definition | The actual contact point details, in a form that is meaningful to the designated communication system (i.e. phone number or email address). |
| Control | 1..1 |
| Type | string |
| Requirements | Need to support legacy numbers that are not in a tightly controlled format. |
| Comments | Additional text data such as phone extension numbers, or notes about use of the contact are sometimes included in the value. |
| Example | 6122765459 |
| Practitioner.telecom.use | |
| Definition | Identifies the purpose for the contact point. |
| Control | 1..1 |
| Binding | Use of contact point The codes SHALL be taken from ContactPointUse |
| Type | code |
| Is Modifier | true |
| Requirements | Need to track the way a person uses this contact, so a user can choose which is appropriate for their purpose. |
| Comments | This is labeled as "Is Modifier" because applications should not mistake a temporary or old contact etc.for a current/permanent one. Applications can assume that a contact is current unless it explicitly says that it is temporary or old. |
| Fixed Value | home |
| Practitioner.telecom.rank | |
| Definition | Specifies a preferred order in which to use a set of contacts. Contacts are ranked with lower values coming before higher values. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | positiveInt |
| Comments | Note that rank does not necessarily follow the order in which the contacts are represented in the instance. |
| Practitioner.telecom.period | |
| Definition | Time period when the contact point was/is in use. |
| Control | 0..0 |
| Type | Period |
| Practitioner.telecom(mobile phone) | |
| Definition | A contact detail for the practitioner, e.g. a telephone number or an email address. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | ContactPoint |
| Must Support | true |
| Requirements | Need to know how to reach a practitioner. |
| Comments | Person may have multiple ways to be contacted with different uses or applicable periods. May need to have options for contacting the person urgently, and also to help with identification. |
| Practitioner.telecom.id | |
| Definition | unique id for the element within a resource (for internal references). |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | id |
| Practitioner.telecom.extension | |
| Definition | May be used to represent additional information that is not part of the basic definition of the element. In order to make the use of extensions safe and manageable, there is a strict set of governance applied to the definition and use of extensions. Though any implementer is allowed to define an extension, there is a set of requirements that SHALL be met as part of the definition of the extension. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Extension |
| Alternate Names | extensions, user content |
| Comments | There can be no stigma associated with the use of extensions by any application, project, or standard - regardless of the institution or jurisdiction that uses or defines the extensions. The use of extensions is what allows the FHIR specification to retain a core level of simplicity for everyone. |
| Practitioner.telecom.system | |
| Definition | Telecommunications form for contact point - what communications system is required to make use of the contact. |
| Control | 1..1 This element is affected by the following invariants: cpt-2 |
| Binding | Telecommunications form for contact point The codes SHALL be taken from ContactPointSystem |
| Type | code |
| Must Support | true |
| Fixed Value | phone |
| Practitioner.telecom.value | |
| Definition | The actual contact point details, in a form that is meaningful to the designated communication system (i.e. phone number or email address). |
| Control | 1..1 |
| Type | string |
| Must Support | true |
| Requirements | Need to support legacy numbers that are not in a tightly controlled format. |
| Comments | Additional text data such as phone extension numbers, or notes about use of the contact are sometimes included in the value. |
| Example | 6122765459 |
| Practitioner.telecom.use | |
| Definition | Identifies the purpose for the contact point. |
| Control | 1..1 |
| Binding | Use of contact point The codes SHALL be taken from ContactPointUse |
| Type | code |
| Is Modifier | true |
| Must Support | true |
| Requirements | Need to track the way a person uses this contact, so a user can choose which is appropriate for their purpose. |
| Comments | This is labeled as "Is Modifier" because applications should not mistake a temporary or old contact etc.for a current/permanent one. Applications can assume that a contact is current unless it explicitly says that it is temporary or old. |
| Fixed Value | mobile |
| Practitioner.telecom.rank | |
| Definition | Specifies a preferred order in which to use a set of contacts. Contacts are ranked with lower values coming before higher values. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | positiveInt |
| Comments | Note that rank does not necessarily follow the order in which the contacts are represented in the instance. |
| Practitioner.telecom.period | |
| Definition | Time period when the contact point was/is in use. |
| Control | 0..0 |
| Type | Period |
| Practitioner.telecom(work phone) | |
| Definition | A contact detail for the practitioner, e.g. a telephone number or an email address. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | ContactPoint |
| Must Support | true |
| Requirements | Need to know how to reach a practitioner. |
| Comments | Person may have multiple ways to be contacted with different uses or applicable periods. May need to have options for contacting the person urgently, and also to help with identification. |
| Practitioner.telecom.id | |
| Definition | unique id for the element within a resource (for internal references). |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | id |
| Practitioner.telecom.extension | |
| Definition | May be used to represent additional information that is not part of the basic definition of the element. In order to make the use of extensions safe and manageable, there is a strict set of governance applied to the definition and use of extensions. Though any implementer is allowed to define an extension, there is a set of requirements that SHALL be met as part of the definition of the extension. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Extension |
| Alternate Names | extensions, user content |
| Comments | There can be no stigma associated with the use of extensions by any application, project, or standard - regardless of the institution or jurisdiction that uses or defines the extensions. The use of extensions is what allows the FHIR specification to retain a core level of simplicity for everyone. |
| Practitioner.telecom.system | |
| Definition | Telecommunications form for contact point - what communications system is required to make use of the contact. |
| Control | 1..1 This element is affected by the following invariants: cpt-2 |
| Binding | Telecommunications form for contact point The codes SHALL be taken from ContactPointSystem |
| Type | code |
| Must Support | true |
| Fixed Value | phone |
| Practitioner.telecom.value | |
| Definition | The actual contact point details, in a form that is meaningful to the designated communication system (i.e. phone number or email address). |
| Control | 1..1 |
| Type | string |
| Must Support | true |
| Requirements | Need to support legacy numbers that are not in a tightly controlled format. |
| Comments | Additional text data such as phone extension numbers, or notes about use of the contact are sometimes included in the value. |
| Example | 6122765459 |
| Practitioner.telecom.use | |
| Definition | Identifies the purpose for the contact point. |
| Control | 1..1 |
| Binding | Use of contact point The codes SHALL be taken from ContactPointUse |
| Type | code |
| Is Modifier | true |
| Must Support | true |
| Requirements | Need to track the way a person uses this contact, so a user can choose which is appropriate for their purpose. |
| Comments | This is labeled as "Is Modifier" because applications should not mistake a temporary or old contact etc.for a current/permanent one. Applications can assume that a contact is current unless it explicitly says that it is temporary or old. |
| Fixed Value | work |
| Practitioner.telecom.rank | |
| Definition | Specifies a preferred order in which to use a set of contacts. Contacts are ranked with lower values coming before higher values. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | positiveInt |
| Comments | Note that rank does not necessarily follow the order in which the contacts are represented in the instance. |
| Practitioner.telecom.period | |
| Definition | Time period when the contact point was/is in use. |
| Control | 0..0 |
| Type | Period |
| Practitioner.telecom(pager) | |
| Definition | A contact detail for the practitioner, e.g. a telephone number or an email address. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | ContactPoint |
| Must Support | true |
| Requirements | Need to know how to reach a practitioner. |
| Comments | Person may have multiple ways to be contacted with different uses or applicable periods. May need to have options for contacting the person urgently, and also to help with identification. |
| Practitioner.telecom.id | |
| Definition | unique id for the element within a resource (for internal references). |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | id |
| Practitioner.telecom.extension | |
| Definition | May be used to represent additional information that is not part of the basic definition of the element. In order to make the use of extensions safe and manageable, there is a strict set of governance applied to the definition and use of extensions. Though any implementer is allowed to define an extension, there is a set of requirements that SHALL be met as part of the definition of the extension. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Extension |
| Alternate Names | extensions, user content |
| Comments | There can be no stigma associated with the use of extensions by any application, project, or standard - regardless of the institution or jurisdiction that uses or defines the extensions. The use of extensions is what allows the FHIR specification to retain a core level of simplicity for everyone. |
| Practitioner.telecom.system | |
| Definition | Telecommunications form for contact point - what communications system is required to make use of the contact. |
| Control | 0..1 This element is affected by the following invariants: cpt-2 |
| Binding | Telecommunications form for contact point The codes SHALL be taken from ContactPointSystem |
| Type | code |
| Must Support | true |
| Fixed Value | pager |
| Practitioner.telecom.value | |
| Definition | The actual contact point details, in a form that is meaningful to the designated communication system (i.e. phone number or email address). |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | string |
| Must Support | true |
| Requirements | Need to support legacy numbers that are not in a tightly controlled format. |
| Comments | Additional text data such as phone extension numbers, or notes about use of the contact are sometimes included in the value. |
| Example | 6122765459 |
| Practitioner.telecom.use | |
| Definition | Identifies the purpose for the contact point. |
| Control | 0..0 |
| Binding | Use of contact point The codes SHALL be taken from ContactPointUse |
| Type | code |
| Is Modifier | true |
| Requirements | Need to track the way a person uses this contact, so a user can choose which is appropriate for their purpose. |
| Comments | This is labeled as "Is Modifier" because applications should not mistake a temporary or old contact etc.for a current/permanent one. Applications can assume that a contact is current unless it explicitly says that it is temporary or old. |
| Practitioner.telecom.rank | |
| Definition | Specifies a preferred order in which to use a set of contacts. Contacts are ranked with lower values coming before higher values. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | positiveInt |
| Comments | Note that rank does not necessarily follow the order in which the contacts are represented in the instance. |
| Practitioner.telecom.period | |
| Definition | Time period when the contact point was/is in use. |
| Control | 0..0 |
| Type | Period |
| Practitioner.address | |
| Definition | The postal address where the practitioner can be found or visited or to which mail can be delivered. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | Address |
| Requirements | Need to keep track where the practitioner can found during work or for directing mail. |
| Practitioner.address.id | |
| Definition | unique id for the element within a resource (for internal references). |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | id |
| Practitioner.address.extension | |
| Definition | May be used to represent additional information that is not part of the basic definition of the element. In order to make the use of extensions safe and manageable, there is a strict set of governance applied to the definition and use of extensions. Though any implementer is allowed to define an extension, there is a set of requirements that SHALL be met as part of the definition of the extension. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Extension |
| Alternate Names | extensions, user content |
| Comments | There can be no stigma associated with the use of extensions by any application, project, or standard - regardless of the institution or jurisdiction that uses or defines the extensions. The use of extensions is what allows the FHIR specification to retain a core level of simplicity for everyone. |
| Practitioner.address.use | |
| Definition | The purpose of this address. |
| Control | 1..1 |
| Binding | The use of an address The codes SHALL be taken from AddressUse |
| Type | code |
| Is Modifier | true |
| Requirements | Allows an appropriate address to be chosen from a list of many. |
| Comments | This is labeled as "Is Modifier" because applications should not mistake a temporary or old address etc.for a current/permanent one. Applications can assume that an address is current unless it explicitly says that it is temporary or old. |
| Fixed Value | work |
| Example | work |
| Practitioner.address.type | |
| Definition | Distinguishes between physical addresses (those you can visit) and mailing addresses (e.g. PO Boxes and care-of addresses). Most addresses are both. |
| Control | 1..1 |
| Binding | The type of an address (physical / postal) The codes SHALL be taken from AddressType |
| Type | code |
| Fixed Value | physical |
| Example | physical |
| Practitioner.address.text | |
| Definition | A full text representation of the address. |
| Control | 0..0 |
| Type | string |
| Requirements | A renderable, unencoded form. |
| Comments | Structured Address values only |
| Example | 137 Nowhere Street, Erewhon 9132 |
| Practitioner.address.line | |
| Definition | This component contains the house number, apartment number, street name, street direction, P.O. Box number, delivery hints, and similar address information. |
| Control | 0..2 |
| Type | string |
| Requirements | home | work | temp | old - purpose of this address. |
| Example | 137 Nowhere Street |
| Slicing | This element introduces a set of slices. The slicing rules are:
|
| Practitioner.address.line(no name) | |
| Definition | This component contains the house number, apartment number, street name, street direction, P.O. Box number, delivery hints, and similar address information. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | string |
| Must Support | true |
| Requirements | home | work | temp | old - purpose of this address. |
| Example | 920 Second Ave S |
| Practitioner.address.line(no name) | |
| Definition | This component contains the house number, apartment number, street name, street direction, P.O. Box number, delivery hints, and similar address information. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | string |
| Must Support | true |
| Requirements | home | work | temp | old - purpose of this address. |
| Example | Suite 400 |
| Practitioner.address.city | |
| Definition | The name of the city, town, village or other community or delivery center. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | string |
| Alternate Names | Municpality |
| Example | Minneapolis |
| Practitioner.address.district | |
| Definition | The name of the administrative area (county). |
| Control | 0..0 |
| Type | string |
| Alternate Names | County |
| Comments | District is sometimes known as county, but in some regions 'county' in used in place of city (municipality), so county name should be conveyed in city instead. |
| Example | Madison |
| Practitioner.address.state | |
| Definition | Sub-unit of a country with limited sovereignty in a federally organized country. A code may be used if codes are in common use (i.e. US 2 letter state codes). |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | string |
| Must Support | true |
| Alternate Names | Province, Territory |
| Example | MN |
| Practitioner.address.postalCode | |
| Definition | A postal code designating a region defined by the postal service. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | string |
| Alternate Names | Zip |
| Example | 55402 |
| Practitioner.address.country | |
| Definition | Country - a nation as commonly understood or generally accepted. |
| Control | 0..0 |
| Type | string |
| Comments | Assumed to be USA |
| Practitioner.address.period | |
| Definition | Time period when address was/is in use. |
| Control | 0..0 |
| Type | Period |
| Requirements | Allows addresses to be placed in historical context. |
| Example | <valuePeriod xmlns="http://hl7.org/fhir"><br/> <start value="2010-03-23"/><br/> <end value="2010-07-01"/><br/></valuePeriod><br/> |
| Practitioner.gender | |
| Definition | Administrative Gender - the gender that the person is considered to have for administration and record keeping purposes. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Binding | The gender of a person used for administrative purposes. The codes SHALL be taken from AdministrativeGender |
| Type | code |
| Requirements | Needed to address the person correctly. |
| Practitioner.birthDate | |
| Definition | The date of birth for the practitioner. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | date |
| Requirements | Needed for identification. |
| Practitioner.photo | |
| Definition | Image of the person. |
| Control | 0..0 |
| Type | Attachment |
| Requirements | Many EHR systems have the capability to capture an image of patients and personnel. Fits with newer social media usage too. |
| Comments | Not supported in provider registries |
| Practitioner.practitionerRole | |
| Definition | The list of roles/organizations that the practitioner is associated with. |
| Control | 1..1 |
| Type | BackboneElement |
| Must Support | true |
| Practitioner.practitionerRole.id | |
| Definition | unique id for the element within a resource (for internal references). |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | id |
| Practitioner.practitionerRole.extension | |
| Definition | May be used to represent additional information that is not part of the basic definition of the element. In order to make the use of extensions safe and manageable, there is a strict set of governance applied to the definition and use of extensions. Though any implementer is allowed to define an extension, there is a set of requirements that SHALL be met as part of the definition of the extension. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Extension |
| Alternate Names | extensions, user content |
| Comments | There can be no stigma associated with the use of extensions by any application, project, or standard - regardless of the institution or jurisdiction that uses or defines the extensions. The use of extensions is what allows the FHIR specification to retain a core level of simplicity for everyone. |
| Practitioner.practitionerRole.modifierExtension | |
| Definition | May be used to represent additional information that is not part of the basic definition of the element, and that modifies the understanding of the element that contains it. Usually modifier elements provide negation or qualification. In order to make the use of extensions safe and manageable, there is a strict set of governance applied to the definition and use of extensions. Though any implementer is allowed to define an extension, there is a set of requirements that SHALL be met as part of the definition of the extension. Applications processing a resource are required to check for modifier extensions. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Extension |
| Is Modifier | true |
| Alternate Names | extensions, user content, modifiers |
| Comments | There can be no stigma associated with the use of extensions by any application, project, or standard - regardless of the institution or jurisdiction that uses or defines the extensions. The use of extensions is what allows the FHIR specification to retain a core level of simplicity for everyone. |
| Practitioner.practitionerRole.managingOrganization | |
| Definition | The organization where the Practitioner performs the roles associated. |
| Control | 1..1 |
| Type | Reference(Organization) |
| Must Support | true |
| Practitioner.practitionerRole.managingOrganization.id | |
| Definition | The logical id of the resource, as used in the URL for the resource. Once assigned, this value never changes. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | id |
| Comments | The only time that a resource does not have an id is when it is being submitted to the server using a create operation. Bundles always have an id, though it is usually a generated UUID. |
| Practitioner.practitionerRole.managingOrganization.meta | |
| Definition | The metadata about the resource. This is content that is maintained by the infrastructure. Changes to the content may not always be associated with version changes to the resource. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | Meta |
| Practitioner.practitionerRole.managingOrganization.implicitRules | |
| Definition | A reference to a set of rules that were followed when the resource was constructed, and which must be understood when processing the content. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | uri |
| Is Modifier | true |
| Comments | Asserting this rule set restricts the content to be only understood by a limited set of trading partners. This inherently limits the usefulness of the data in the long term. However, the existing health eco-system is highly fractured, and not yet ready to define, collect, and exchange data in a generally computable sense. Wherever possible, implementers and/or specification writers should avoid using this element as much as possible. |
| Practitioner.practitionerRole.managingOrganization.language | |
| Definition | The base language in which the resource is written. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Binding | A human language. The codes SHALL be taken from http://tools.ietf.org/html/bcp47  |
| Type | code |
| Comments | Language is provided to support indexing and accessibility (typically, services such as text to speech use the language tag). The html language tag in the narrative applies to the narrative. The language tag on the resource may be used to specify the language of other presentations generated from the data in the resource Not all the content has to be in the base language. The Resource.language should not be assumed to apply to the narrative automatically. If a language is specified, it should it also be specified on the div element in the html (see rules in HTML5 for information about the relationship between xml:lang and the html lang attribute). |
| Practitioner.practitionerRole.managingOrganization.text | |
| Definition | A human-readable narrative that contains a summary of the resource, and may be used to represent the content of the resource to a human. The narrative need not encode all the structured data, but is required to contain sufficient detail to make it "clinically safe" for a human to just read the narrative. Resource definitions may define what content should be represented in the narrative to ensure clinical safety. |
| Control | 0..1 This element is affected by the following invariants: dom-1 |
| Type | Narrative |
| Alternate Names | narrative, html, xhtml, display |
| Comments | Contained resources do not have narrative. Resources that are not contained SHOULD have a narrative. |
| Practitioner.practitionerRole.managingOrganization.contained | |
| Definition | These resources do not have an independent existence apart from the resource that contains them - they cannot be identified independently, and nor can they have their own independent transaction scope. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Resource |
| Alternate Names | inline resources, anonymous resources, contained resources |
| Comments | This should never be done when the content can be identified properly, as once identification is lost, it is extremely difficult (and context dependent) to restore it again. |
| Practitioner.practitionerRole.managingOrganization.extension | |
| Definition | May be used to represent additional information that is not part of the basic definition of the resource. In order to make the use of extensions safe and manageable, there is a strict set of governance applied to the definition and use of extensions. Though any implementer is allowed to define an extension, there is a set of requirements that SHALL be met as part of the definition of the extension. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Extension |
| Alternate Names | extensions, user content |
| Comments | There can be no stigma associated with the use of extensions by any application, project, or standard - regardless of the institution or jurisdiction that uses or defines the extensions. The use of extensions is what allows the FHIR specification to retain a core level of simplicity for everyone. |
| Practitioner.practitionerRole.managingOrganization.modifierExtension | |
| Definition | May be used to represent additional information that is not part of the basic definition of the resource, and that modifies the understanding of the element that contains it. Usually modifier elements provide negation or qualification. In order to make the use of extensions safe and manageable, there is a strict set of governance applied to the definition and use of extensions. Though any implementer is allowed to define an extension, there is a set of requirements that SHALL be met as part of the definition of the extension. Applications processing a resource are required to check for modifier extensions. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Extension |
| Is Modifier | true |
| Alternate Names | extensions, user content |
| Comments | There can be no stigma associated with the use of extensions by any application, project, or standard - regardless of the institution or jurisdiction that uses or defines the extensions. The use of extensions is what allows the FHIR specification to retain a core level of simplicity for everyone. |
| Practitioner.practitionerRole.managingOrganization.identifier | |
| Definition | Identifier for the organization that is used to identify the organization across multiple disparate systems. |
| Control | 0..* This element is affected by the following invariants: org-1 |
| Type | Identifier |
| Requirements | Organizations are known by a variety of ids. Some institutions maintain several, and most collect identifiers for exchange with other organizations concerning the organization. |
| Practitioner.practitionerRole.managingOrganization.active | |
| Definition | Whether the organization's record is still in active use. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | boolean |
| Is Modifier | true |
| Requirements | Need a flag to indicate a record is no longer to be used and should generally be hidden for the user in the UI. |
| Comments | Default is true. |
| Default Value | true |
| Practitioner.practitionerRole.managingOrganization.type | |
| Definition | The kind of organization that this is. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Binding | Used to categorize the organization For example codes, see OrganizationType |
| Type | CodeableConcept |
| Requirements | Need to be able to track the kind of organization that this is - different organization types have different uses. |
| Comments | Organizations can be corporations, wards, sections, clinical teams, government departments, etc. Note that code is generally a classifier of the type of organization; in many applications, codes are used to identity a particular organization (say, ward) as opposed to another of the same type - these are identifiers, not codes. |
| Practitioner.practitionerRole.managingOrganization.name | |
| Definition | A name associated with the organization. |
| Control | 0..1 This element is affected by the following invariants: org-1 |
| Type | string |
| Requirements | Need to use the name as the label of the organization. |
| Practitioner.practitionerRole.managingOrganization.telecom | |
| Definition | A contact detail for the organization. |
| Control | 0..* This element is affected by the following invariants: org-3 |
| Type | ContactPoint |
| Requirements | Human contact for the organization. |
| Comments | The use code home is not to be used. Note that these contacts are not the contact details of people who are employed by or represent the organization, but official contacts for the organization itself. |
| Invariants | Defined on this element org-3: The telecom of an organization can never be of use 'home' (xpath: count(f:use[@value='home']) = 0) |
| Practitioner.practitionerRole.managingOrganization.address | |
| Definition | An address for the organization. |
| Control | 0..* This element is affected by the following invariants: org-2 |
| Type | Address |
| Requirements | May need to keep track of the organization's addresses for contacting, billing or reporting requirements. |
| Comments | Organization may have multiple addresses with different uses or applicable periods. The use code home is not to be used. |
| Invariants | Defined on this element org-2: An address of an organization can never be of use 'home' (xpath: count(f:use[@value='home']) = 0) |
| Practitioner.practitionerRole.managingOrganization.partOf | |
| Definition | The organization of which this organization forms a part. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | Reference(Organization) |
| Requirements | Need to be able to track the hierarchy of organizations within an organization. |
| Practitioner.practitionerRole.managingOrganization.contact | |
| Definition | Contact for the organization for a certain purpose. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | BackboneElement |
| Requirements | Need to keep track of assigned contact points within bigger organization. |
| Comments | Where multiple contacts for the same purpose are provided there is a standard extension that can be used to determine which one is the preferred contact to use. |
| Practitioner.practitionerRole.managingOrganization.contact.id | |
| Definition | unique id for the element within a resource (for internal references). |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | id |
| Practitioner.practitionerRole.managingOrganization.contact.extension | |
| Definition | May be used to represent additional information that is not part of the basic definition of the element. In order to make the use of extensions safe and manageable, there is a strict set of governance applied to the definition and use of extensions. Though any implementer is allowed to define an extension, there is a set of requirements that SHALL be met as part of the definition of the extension. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Extension |
| Alternate Names | extensions, user content |
| Comments | There can be no stigma associated with the use of extensions by any application, project, or standard - regardless of the institution or jurisdiction that uses or defines the extensions. The use of extensions is what allows the FHIR specification to retain a core level of simplicity for everyone. |
| Practitioner.practitionerRole.managingOrganization.contact.modifierExtension | |
| Definition | May be used to represent additional information that is not part of the basic definition of the element, and that modifies the understanding of the element that contains it. Usually modifier elements provide negation or qualification. In order to make the use of extensions safe and manageable, there is a strict set of governance applied to the definition and use of extensions. Though any implementer is allowed to define an extension, there is a set of requirements that SHALL be met as part of the definition of the extension. Applications processing a resource are required to check for modifier extensions. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Extension |
| Is Modifier | true |
| Alternate Names | extensions, user content, modifiers |
| Comments | There can be no stigma associated with the use of extensions by any application, project, or standard - regardless of the institution or jurisdiction that uses or defines the extensions. The use of extensions is what allows the FHIR specification to retain a core level of simplicity for everyone. |
| Practitioner.practitionerRole.managingOrganization.contact.purpose | |
| Definition | Indicates a purpose for which the contact can be reached. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Binding | The purpose for which you would contact a contact party The codes SHALL be taken from ContactEntityType; other codes may be used where these codes are not suitable |
| Type | CodeableConcept |
| Requirements | Need to distinguish between multiple contact persons. |
| Practitioner.practitionerRole.managingOrganization.contact.name | |
| Definition | A name associated with the contact. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | HumanName |
| Requirements | Need to be able to track the person by name. |
| Practitioner.practitionerRole.managingOrganization.contact.telecom | |
| Definition | A contact detail (e.g. a telephone number or an email address) by which the party may be contacted. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | ContactPoint |
| Requirements | People have (primary) ways to contact them in some way such as phone, email. |
| Practitioner.practitionerRole.managingOrganization.contact.address | |
| Definition | Visiting or postal addresses for the contact. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | Address |
| Requirements | May need to keep track of a contact party's address for contacting, billing or reporting requirements. |
| Practitioner.practitionerRole.role | |
| Definition | Roles which this practitioner is authorized to perform for the organization. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Binding | The role a person plays representing an organization For example codes, see PractitionerRole |
| Type | CodeableConcept |
| Requirements | Need to know what authority the practitioner has - what can they do? |
| Comments | A person may have more than one role. At least one role is required. |
| Practitioner.practitionerRole.specialty | |
| Definition | Specific specialty of the practitioner. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Binding | Specific specialty associated with the agency For example codes, see PractitionerSpecialty |
| Type | CodeableConcept |
| Must Support | true |
| Comments | Specialty can be coded using AMA codes, or other codes as desired |
| Practitioner.practitionerRole.specialty.id | |
| Definition | unique id for the element within a resource (for internal references). |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | id |
| Practitioner.practitionerRole.specialty.extension | |
| Definition | May be used to represent additional information that is not part of the basic definition of the element. In order to make the use of extensions safe and manageable, there is a strict set of governance applied to the definition and use of extensions. Though any implementer is allowed to define an extension, there is a set of requirements that SHALL be met as part of the definition of the extension. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Extension |
| Alternate Names | extensions, user content |
| Comments | There can be no stigma associated with the use of extensions by any application, project, or standard - regardless of the institution or jurisdiction that uses or defines the extensions. The use of extensions is what allows the FHIR specification to retain a core level of simplicity for everyone. |
| Practitioner.practitionerRole.specialty.coding | |
| Definition | A reference to a code defined by a terminology system. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Coding |
| Requirements | Allows for translations and alternate encodings within a code system. Also supports communication of the same instance to systems requiring different encodings. |
| Comments | Codes may be defined very casually in enumerations, or code lists, up to very formal definitions such as SNOMED CT - see the HL7 v3 Core Principles for more information. Ordering of codings is undefined and SHALL NOT be used to infer meaning. Generally, at most only one of the coding values will be labelled as UserSelected = true. |
| Practitioner.practitionerRole.specialty.text | |
| Definition | A human language representation of the concept as seen/selected/uttered by the user who entered the data and/or which represents the intended meaning of the user. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | string |
| Must Support | true |
| Requirements | The codes from the terminologies do not always capture the correct meaning with all the nuances of the human using them, or sometimes there is no appropriate code at all. In these cases, the text is used to capture the full meaning of the source. |
| Comments | Very often the text is the same as a displayName of one of the codings. |
| Example | Doctor |
| Practitioner.practitionerRole.period | |
| Definition | The period during which the person is authorized to act as a practitioner in these role(s) for the organization. |
| Control | 0..0 |
| Type | Period |
| Requirements | Even after the agencies is revoked, the fact that it existed must still be recorded. |
| Practitioner.practitionerRole.period.id | |
| Definition | unique id for the element within a resource (for internal references). |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | id |
| Practitioner.practitionerRole.period.extension | |
| Definition | May be used to represent additional information that is not part of the basic definition of the element. In order to make the use of extensions safe and manageable, there is a strict set of governance applied to the definition and use of extensions. Though any implementer is allowed to define an extension, there is a set of requirements that SHALL be met as part of the definition of the extension. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Extension |
| Alternate Names | extensions, user content |
| Comments | There can be no stigma associated with the use of extensions by any application, project, or standard - regardless of the institution or jurisdiction that uses or defines the extensions. The use of extensions is what allows the FHIR specification to retain a core level of simplicity for everyone. |
| Practitioner.practitionerRole.period.start | |
| Definition | The start of the period. The boundary is inclusive. |
| Control | 0..1 This element is affected by the following invariants: per-1 |
| Type | dateTime |
| Must Support | true |
| Comments | If the low element is missing, the meaning is that the low boundary is not known. |
| Example | 2099-12-31T11:00:00+11:00 |
| Practitioner.practitionerRole.period.end | |
| Definition | The end of the period. If the end of the period is missing, it means that the period is ongoing. The start may be in the past, and the end date in the future, which means that period is expected/planned to end at that time. |
| Control | 0..1 This element is affected by the following invariants: per-1 |
| Type | dateTime |
| Must Support | true |
| Comments | The high value includes any matching date/time. i.e. 2012-02-03T10:00:00 is in a period that has a end value of 2012-02-03. |
| Meaning if Missing | If the end of the period is missing, it means that the period is ongoing |
| Example | 2013-02-22T04:25:00+11:00 |
| Practitioner.practitionerRole.location | |
| Definition | The location(s) at which this practitioner provides care. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Reference(Location) |
| Practitioner.practitionerRole.healthcareService | |
| Definition | The list of healthcare services that this worker provides for this role's Organization/Location(s). |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Reference(HealthcareService) |
| Practitioner.qualification | |
| Definition | Qualifications obtained by training and certification. |
| Control | 0..0 |
| Type | BackboneElement |
| Comments | not supported for Provider Registry |
| Practitioner.qualification.id | |
| Definition | unique id for the element within a resource (for internal references). |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | id |
| Practitioner.qualification.extension | |
| Definition | May be used to represent additional information that is not part of the basic definition of the element. In order to make the use of extensions safe and manageable, there is a strict set of governance applied to the definition and use of extensions. Though any implementer is allowed to define an extension, there is a set of requirements that SHALL be met as part of the definition of the extension. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Extension |
| Alternate Names | extensions, user content |
| Comments | There can be no stigma associated with the use of extensions by any application, project, or standard - regardless of the institution or jurisdiction that uses or defines the extensions. The use of extensions is what allows the FHIR specification to retain a core level of simplicity for everyone. |
| Practitioner.qualification.modifierExtension | |
| Definition | May be used to represent additional information that is not part of the basic definition of the element, and that modifies the understanding of the element that contains it. Usually modifier elements provide negation or qualification. In order to make the use of extensions safe and manageable, there is a strict set of governance applied to the definition and use of extensions. Though any implementer is allowed to define an extension, there is a set of requirements that SHALL be met as part of the definition of the extension. Applications processing a resource are required to check for modifier extensions. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Extension |
| Is Modifier | true |
| Alternate Names | extensions, user content, modifiers |
| Comments | There can be no stigma associated with the use of extensions by any application, project, or standard - regardless of the institution or jurisdiction that uses or defines the extensions. The use of extensions is what allows the FHIR specification to retain a core level of simplicity for everyone. |
| Practitioner.qualification.identifier | |
| Definition | An identifier that applies to this person's qualification in this role. |
| Control | 0..* |
| Type | Identifier |
| Requirements | Often, specific identities are assigned for the qualification. |
| Practitioner.qualification.code | |
| Definition | Coded representation of the qualification. |
| Control | 1..1 |
| Binding | Specific qualification the practitioner has to provide a service For example codes, see ANZSCO -- Australian and New Zealand Standard Classification of Occupations, 2013, Version 1.2 |
| Type | CodeableConcept |
| Practitioner.qualification.period | |
| Definition | Period during which the qualification is valid. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | Period |
| Requirements | Qualifications are often for a limited period of time, and can be revoked. |
| Practitioner.qualification.issuer | |
| Definition | Organization that regulates and issues the qualification. |
| Control | 0..1 |
| Type | Reference(Organization) |
| Practitioner.communication | |
| Definition | A language the practitioner is able to use in patient communication. |
| Control | 0..0 |
| Binding | A human language. The codes SHALL be taken from http://tools.ietf.org/html/bcp47  |
| Type | CodeableConcept |
| Requirements | Knowing which language a practitioner speaks can help in facilitating communication with patients. |
| Comments | The structure aa-BB with this exact casing is one the most widely used notations for locale. However not all systems actually code this but instead have it as free text. Hence CodeableConcept instead of code as the data type. |