This page is part of the Clinical Guidelines (v2.0.0: STU2) based on FHIR (HL7® FHIR® Standard) R4. This is the current published version in its permanent home (it will always be available at this URL). For a full list of available versions, see the Directory of published versions
This section discusses methods of implementation, as well as conceptual execution semantics for computable artifacts described by this implementation guide.
Once computable representations and expressions of any clinical practice guideline have been developed (as a CPG-IG) they must be implemented and integrated with various clinical and operational information systems (e.g., EHRs, Workflow Apps, Quality and Practice Analytics tools, Quality and Registry Reporting tools, etc.) Three main factors come into play. The first consideration is where and how these computable expressions and artifacts will be executed- natively withing systems of record, in an external reasoning engine, or translated and reimplemented in target system native logic languages (e.g. rules engines). The second consideration, which is related to the first, Is how the inferences or insights (e.g. CaseFeatures, Recommendations/Proposals, Metrics) are to be integrated into existing clinical application ecosystems and/or the same or similar workflows supported by these applications. The third consideration, which further relates to the first two, Is where and how these insights will be manifested in such a way to enable guideline-informed clinical workflows and related healthcare activities. Partially orthogonal to, but just as important as these three considerations, is the ability to assess and ensure conformance of specific implementations of computable clinical practice guidelines using the specifications and requirements outlined in this implementation guide.
While all of these factors Have implications for the overall level of effort, the methods of implementing knowledge and mechanisms of integration are directly reflected in the overall selection of workflow enablements in a given setting. The last two sections further discuss trade-offs between effort, time to develop, and capabilities enabled (and value that can be derived) when developing a CPG. From very basic context for narrative snippets searchable in a library (or Infobutton from EHR) to full clinical workflow enablement, cognitive support, and pathway tracking (likely via SMART-on-FHIR App or deep EHR integration). CPGs also enable feedback loops with real-world evidence of actual guideline usage and outcomes, and provide a substrate for the evidence ecosystem and a feedforward loop for evidence updates. To support description of, and allow declaration of conformance to, these various capabilities enabled by CPGs, the CPG-IG defines levels of enablement that correlate to work effort, time to delivery, and capabilities enabled.
Methods of implementation refers to three (3) broad approaches to moving from the computable, structured representation (L3) of guideline content to the executable representation (L4):
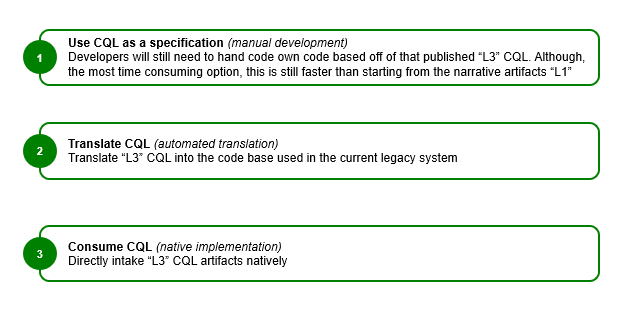
Note that there are numerous factors that must be considered as part of the local implementation of guideline content. The intent of the L3 artifacts described in this implementation guide is to ensure that these factors can be appropriately considered and addressed as part of implementation while still providing useful content that can accelerate the process.
Manual implementation involves development of clinical guideline functionality using the computable (L3) content as a set of rigorously specified requirements for the implementation. In the absence of computable (L3) content, this is the only method.
Automatic implementation involves programmatic translation of the L3 content into an appropriate L4 format. For example, a CQL query may be translated into an equivalent SQL query for execution, or a PlanDefinition may be transformed into a production rule. This approach involves potentially significant effort to build the appropriate tooling but can pay dividends at scale once the tooling is in place.
Native implementation involves direct execution of L3 content. For example, a CQL query may be run directly on a native CQL engine. As with the automatic approach, this approach may involve significant initial tooling effort but can dramatically reduce implementation time thereafter. In addition, there are open source reference implementations that support the use of the FHIR Clinical Reasoning module resources. In particular:
The knowledge architecture described here builds on the overall workflow patterns established by the base FHIR specification. In particular, activities are modeled as requests and events: requests for proposed or planned actions that have not yet occurred, but are intended to be taken, and events for actions that are in progress, or have completed. The following sections detail these activity processing semantics, and how the knowledge architecture described here relies on these semantics to enable effective modeling of clinical reasoning logic.
In general, activities within a computable practice guideline are modeled as requests that either have not yet occurred, but are proposed or planned, or events that have occurred. Requests have a status, typically indicating the level of completeness of the request; an intent, representing the level of authorization or certainty with which the request should be taken; and a doNotPerform, indicating whether the request is to perform or not to perform the action.
Note that although these elements are described by the base request pattern within FHIR, the request resources do not necessarily follow these patterns exactly. Variability in use cases and scope of the request resources results in variability in how the request pattern is applied. This results in differences in the way the pattern is implemented, but in general, activities in the CPG move through the following basic steps:
active and an intent of proposalactive and an intent of planfocus that references the rejected proposal and a status of rejectedordercompleted, and result in the creation of a corresponding event resourcepreparation or in-progress, and the basedOn element is used to indicate the request the event is fulfillingcompletedsuspended or abortedNote that although this is the general pattern, because of the variability in request resources, the specific pattern for each activity varies slightly, depending on the actual status and intent values defined for use with each specific resource type.
Note also that an event may be documented directly without a corresponding request, and that with or without a request, the event may be documented as not-done, meaning explicitly that the event was not performed for some reason, typically provided via the statusReason element.
Following this pattern for a positive recommendation (i.e. a recommendation to perform some activity), we can state the applicability logic generally as:
If the activity has not been performed (nor documented as not having been performed), and is not proposed, planned, or ordered, then propose the activity
And similarly, for a negative recommendation (i.e. a recommendation not to perform some activity), we can state the applicability logic generally as:
If the activity is proposed, planned, ordered, or in-progress (and not documented as not having been performed), and there is no proposal (planned or rejected) to stop or not to perform the activity, then propose stopping and/or not performing the activity
The Activity Flow topic provides a detailed description of the above process, including how each activity is realized in each FHIR resource.
The knowledge architecture presented here uses the PlanDefinition in various ways to represent recommendations, strategies, and pathways. Recommendations are represented with a PlanDefinition playing the role of an event-condition-action rule, while strategies and pathways are represented with a PlanDefinition playing the role of a workflow-definition or clinical-protocol. In all these cases, the following execution semantics are used to ensure consistent and meaningful interpretation of knowledge artifacts.
before-start relationship, with or without an offset to allow for delaystrigger, all other action execution occurs through either child or related actionsIn addition, when a request is referenced by a RequestGroup, then its intent must be option, and it is treated as part of the overall RequestGroup, implying that the intent of the request is established by the intent of the RequestGroup. For PlanDefinition apply processing, this means the returned RequestGroup will have an intent of proposal, while all the referenced requests will have an intent of option, and when the "options" are selected by the user or application for processing into a Plan, Order, or Event, they will no longer be part of the RequestGroup, will have an intent of Plan or Order as appropriate, and will be independent requests at that point.
When used as a knowledge artifact, a PlanDefinition only describes a specific expected process. The cpg-enabled extension is used to indicate that the PlanDefinition is not only registered (or known) but is active in the sense that its behavior is active and will be applied by the system.
Initiation of a PlanDefinition can only occur by trigger, as in the conditions defined by the triggering conditions of any action within the PlanDefinition are met, or by call, as in the PlanDefinition is invoked directly, or called directly by reference from another PlanDefinition.
Recommendations are represented as event-condition-action PlanDefinitions, meaning in particular that they can have at most one triggering action, and that they cannot reference other PlanDefinitions.
Strategies are represented as workflow-definition PlanDefinitions, meaning in particular that they can have at most one triggering action (the start action), and that they can reference other PlanDefinitions, but typically do not reference ActivityDefinitions directly.
And finally, Pathways are represented as clinical-protocol PlanDefinitions, meaning that they may have multiple triggering actions, and that they can reference other PlanDefinitions (typically other pathways, strategies, and, less often, recommendations), and they typically do not reference ActivityDefinitions directly.
In addition, pathways (and to a lesser extent, strategies) may have eligibility and enrollment. When a pathway or strategy is invoked, enrollment is checked.
partOf PlanDefinition (an extension on PlanDefinitions to indicate that the Pathway or Strategy is part of another, higher-level Strategy or Pathway).Note that for Recommendations, "eligibility criteria" is typically expressed as part of the recommendation logic, as inclusion criteria directly.
These capabilities support the description of enrollment in various ways, including:
By applying these execution semantics to the creation of recommendations, strategies, and pathways, orchestration of complex guideline-directed care can be represented. In the most straight-forward case, a guideline consists of:
The Pathway specifies eligibility and enrollment, the Strategy specifies the triggering event, and incorporates all the Recommendation artifacts as children.
This pattern allows for a straightforward implementation that only needs to integrate with well-known triggers such as encounter-start. Initiation always occurs from that event, and enrollment is checked for any PlanDefinition that is a Pathway or Strategy, or that has a partOf that references a Pathway or Strategy.
Applications can then implement the guideline by tracking and invoking known (and enabled) PlanDefinitions directly. The result of these calls are a set of proposals for actions that should be considered or taken.
The Care Planning topic describes expectations for the use of dynamic care planning with computable guideline content.