This page is part of the Specialty Medication Enrollment (v1.0.0: STU1) based on FHIR (HL7® FHIR® Standard) R4. The current version which supersedes this version is 2.0.0. For a full list of available versions, see the Directory of published versions
Pharmacies and other stakeholders (referred to as “information requester” below) sometimes need information that isn’t available through systematic querying of the prescriber’s EHR (using the RESTful searches or Specialty Rx Query messages as described in the Systematic Query Workflows section).
For example, the information requester may need to:
This implementation guide describes a method to support these situations by enabling the prescriber or staff to provide information through a SMART application launched from the EHR–prompted by a request from a Data Consumer system used by the pharmacy or other information requester.
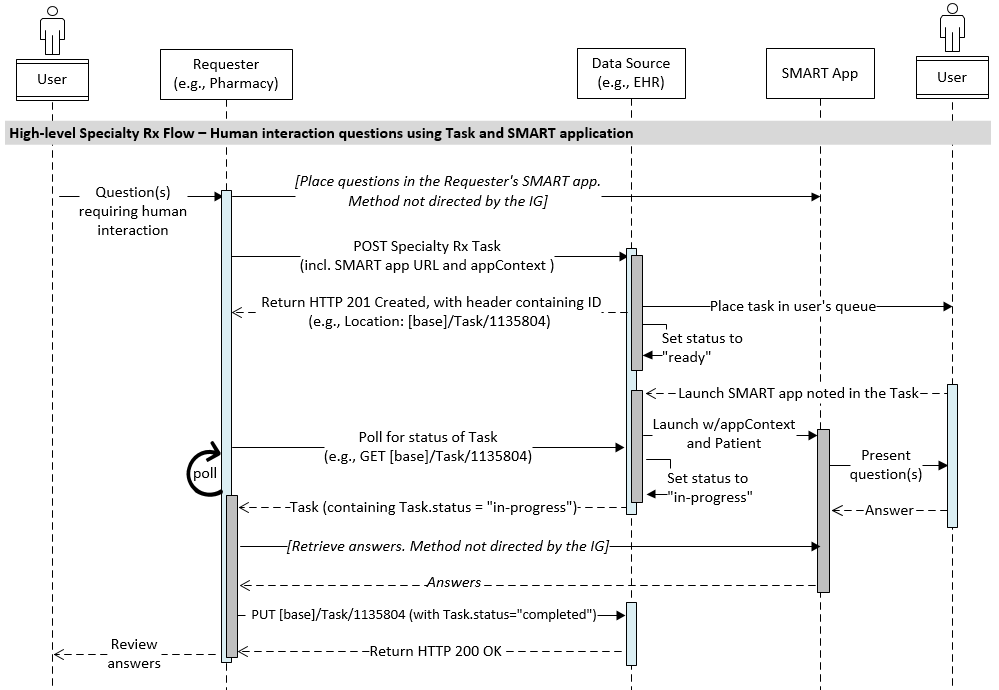
An information requester may host a SMART application that the prescriber or staff can launch from the EHR to view and respond to questions. Below is a scenario illustrating this approach for (a) communicating the need for information to the EHR and (b) enabling an EHR user to launch the application and complete the task.
ready. The EHR returns a 201 CREATED responselaunches the information requester’s SMART App, sending a launch context parameter reflecting:
.id of the Patient it received in the .for element of the Task resource–which references the Data Source system’s Patient resourceTask.identifier value–which the SMART app will use to present the right questions for the patient and medication. This value is later returned to the app in the access token response from the EHR authorization serverFor example, the EHR redirects to:
https://my-pharmacy-smart-app.com?
launch=123&
iss=htttp://my-ehr.com/fhir
responds to the app’s authorization request in the launch sequence with an OAuth 2.0 access token response that includes the Patient.id and appContext values. For example:
{
access_token:"secret-token-xyz",
expires-in:"3600",
patient:"specialty-rx-patient-1",
appContext:"launch-context-id-01345005",
...
}
sets the Task status to in-progress
status to monitor its progress. E.g., GET [base]/Task/1135804completed. The EHR updates the status and returns a 200 OK response
Note: If an event occurs within the Data Source system that prevents the Task from being performed, it SHOULD indicate that the request will not completed by updating Task.status to failed and, optionally, indicating why in Task.statusReason.
The Task resource contains the following information needed to reference related information in the EHR and launch the SMART application:
Task.identifier - This is a unique identifier representing the context of this task within the SMART application (e.g., the specific set of questions that need to be answered). It is to be conveyed during launch of the referenced SMART application in the appContext parameter and used by that application to direct the user to information and functions necessary to complete this taskTask.code - A code that characterizes the requested user action
complete-app-questionnaire (display: “Complete Questionnaire in SMART App”)Task.description - Human-readable description of the task to be performed by the user. This description SHALL include the user-recognizable name of the SMART application to launch to perform the task, and SHALL state the action to be performed in the app once it’s been launched.
Task.for - A reference to the patientTask.requester - The organization submitting the TaskTask.owner - The prescriberTask.reasonReference - The prescription to which the task pertains. A human-readable description is included in Task.display, and specific identification is conveyed through either…
Task.reasonReference.reference - A reference to a MedicationRequest resource, orTask.reasonReference.identifier - The prescription identifier set by the prescribing system. (Referred to as the Placer Order Number in HL7 v2 and Prescriber Order Number in NCPDP SCRIPT)Task.input - Identifies the SMART app to be launched.
Task.input.type contains the code, smart-app-client-id and Task.input.valueIdentifier contains the SMART app’s client ID.Task.input.type contains the code, smart-app-launch-url and Task.input.valueUrl contains the actual endpoint URL to launch the SMART app.See this example of a populated Task.
The appContext parameter is sent to the SMART app as part of the OAuth 2.0 access token response, alongside other SMART launch parameters when the SMART app is launched. The appContext contains the value received in the Task.identifier value.
Example:
"appContext": "launch-context-id-01345005"
SMART App Launch Implementation Guide
An information requester may potentially partner with an intermediary or other party to host the SMART application and perform the above process on its behalf.