 . Page versions: R5 R4B R4 R3 R2
. Page versions: R5 R4B R4 R3 R2This page is part of the FHIR Specification (v0.0.82: DSTU 1). The current version which supercedes this version is 5.0.0. For a full list of available versions, see the Directory of published versions  . Page versions: R5 R4B R4 R3 R2
. Page versions: R5 R4B R4 R3 R2
A domain resource is an resource that:
As an abstract resource, this resource never exists directly, only one of its descendent resources (list).
This resource is extends resource. All of the listed resources except Bundle and Binary extend this resource.
Structure
| Name | Flags | Card. | Type | Description & Constraints |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 | I | Resource | A resource with narrative, extensions, and contained resources If a resource is contained in another resource, it SHALL not have a meta.versionId or a meta.lastUpdated If the resource is contained in another resource, it SHALL be referred to from elsewhere in the resource If the resource is contained in another resource, it SHALL not contain nested Resources If the resource is contained in another resource, it SHALL not contain any narrative | |
 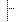 | I | 0..1 | Narrative | Text summary of the resource, for human interpretation |
 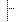 | 0..* | Resource | Contained, inline Resources | |
 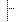 | 0..* | Extension | Additional Content defined by implementations | |
 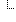 | 0..* | Extension | Extensions that cannot be ignored |
UML Diagram
XML Template
<[name] xmlns="http://hl7.org/fhir"><!-- from Element: extension --> <text><!--
0..1 Narrative Text summary of the resource, for human interpretation --></text> <contained><!-- 0..* Resource Contained, inline Resources --></contained> <extension><!-- 0..* Extension Additional Content defined by implementations --></extension> <modifierExtension><!-- 0..* Extension Extensions that cannot be ignored --></modifierExtension> </[name]>
JSON Template
{ "resourceType" : "[name]",
// from Resource: id, meta, implicitRules, and language
"text" : { Narrative }, // C? Text summary of the resource, for human interpretation
"contained" : [{ Resource }], // Contained, inline Resources
(Extensions - see JSON page)
(Modifier Extensions - see JSON page)
}
"resourceType" : "[name]",
// from Resource: id, meta, implicitRules, and language
"text" : { Narrative }, // C? Text summary of the resource, for human interpretation
"contained" : [{ Resource }], // Contained, inline Resources
(Extensions - see JSON page)
(Modifier Extensions - see JSON page)
}
Structure
| Name | Flags | Card. | Type | Description & Constraints |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 | I | Resource | A resource with narrative, extensions, and contained resources If a resource is contained in another resource, it SHALL not have a meta.versionId or a meta.lastUpdated If the resource is contained in another resource, it SHALL be referred to from elsewhere in the resource If the resource is contained in another resource, it SHALL not contain nested Resources If the resource is contained in another resource, it SHALL not contain any narrative | |
  | I | 0..1 | Narrative | Text summary of the resource, for human interpretation |
  | 0..* | Resource | Contained, inline Resources | |
  | 0..* | Extension | Additional Content defined by implementations | |
  | 0..* | Extension | Extensions that cannot be ignored |
XML Template
<[name] xmlns="http://hl7.org/fhir"><!-- from Element: extension --> <text><!--
0..1 Narrative Text summary of the resource, for human interpretation --></text> <contained><!-- 0..* Resource Contained, inline Resources --></contained> <extension><!-- 0..* Extension Additional Content defined by implementations --></extension> <modifierExtension><!-- 0..* Extension Extensions that cannot be ignored --></modifierExtension> </[name]>
JSON Template
{ "resourceType" : "[name]",
// from Resource: id, meta, implicitRules, and language
"text" : { Narrative }, // C? Text summary of the resource, for human interpretation
"contained" : [{ Resource }], // Contained, inline Resources
(Extensions - see JSON page)
(Modifier Extensions - see JSON page)
}
"resourceType" : "[name]",
// from Resource: id, meta, implicitRules, and language
"text" : { Narrative }, // C? Text summary of the resource, for human interpretation
"contained" : [{ Resource }], // Contained, inline Resources
(Extensions - see JSON page)
(Modifier Extensions - see JSON page)
}
This resource doesn't define any common Search parameters
To search for extensions, define a search parameter for the extension. All other search parameters are named aliases for existing content in the resource. In some cases, though not all, the search parameter name is the same as the element that it searches, but this is not required. Searching for extensions is the same - define a name that identifies the value extension by its URL, and then searches can filter based on the value of the extension.