This page is part of the FHIR Specification (v1.0.0: DSTU 2 Ballot 3). The current version which supercedes this version is 5.0.0. For a full list of available versions, see the Directory of published versions 

In September 2015, this FHIR Implementation Guide will undergo a comment-only ballot. The focus of the ballot is limited in scope to the IG, the profiles, operations, value sets, and conformance statements it defines. This implementation Guide will be balloted separately from the FHIR specification itself.


This Implementation Guide is prepared as a Universal Realm Specification with support from the Clinical Quality Framework (CQF) initiative  , which is a public-private partnership sponsored by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) and the U.S. Office of the National Coordinator (ONC) to harmonize standards for clinical decision support and electronic clinical quality measurement.
, which is a public-private partnership sponsored by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) and the U.S. Office of the National Coordinator (ONC) to harmonize standards for clinical decision support and electronic clinical quality measurement.
The CQIF Implementation Guide provides profiles and operation definitions to enable multiple quality-related use cases, including decision support request/response, quality measurement evaluation, as well as knowledge artifact representation and sharing.

The CQIF Implementation Guide is built by the Clinical Decision Support (CDS) and Clinical Quality Information (CQI) HL7 Work Groups, with input and coordination from the FHIR Infrastructure and Service Oriented Architecture HL7 Work Groups.
The Clinical Quality Framework initiative has focused on harmonizing the historically disjoint specifications used by the Clinical Quality Measurement and Clinical Decision Support communities. Specifically, the initiative has focused on the specifications used to represent knowledge artifacts within the two communities. The strategy employed has been to break the conceptual content of knowledge artifacts into three core components:
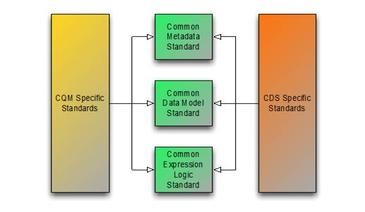
The first component has resulted in the Clinical Quality Common Metadata Conceptual Model  , an informative document harmonizing metadata requirements between Quality Measurement and Decision Support artifacts.
, an informative document harmonizing metadata requirements between Quality Measurement and Decision Support artifacts.
The second component has resulted in the QUICK Conceptual  and Logical Models, a harmonization of the Virtual Medical Record (vMR)
and Logical Models, a harmonization of the Virtual Medical Record (vMR)  used in Decision Support and the Quality Data Model (QDM)
used in Decision Support and the Quality Data Model (QDM)  used in Quality Measurement, and realized in FHIR as the QICore profiles.
used in Quality Measurement, and realized in FHIR as the QICore profiles.
And finally, the third component has resulted in the Clinical Quality Language Specification  , a harmonization of the expressive capabilities of the Clinical Decision Support Knowledge Artifact Specification (CDS KAS)
, a harmonization of the expressive capabilities of the Clinical Decision Support Knowledge Artifact Specification (CDS KAS)  (produced by the Health eDecisions (HeD) S&I Framework Initiative), and the Health Quality Measures Format (HQMF)
(produced by the Health eDecisions (HeD) S&I Framework Initiative), and the Health Quality Measures Format (HQMF)  .
.
As part of the CQF initiative Phase II Pilot efforts, these developing specifications are being used to support knowledge artifact sharing, as well as evaluation of knowledge artifacts as part of decision support request/response and measure evaluation.
This implementation guide continues the harmonization of quality domain specifications by defining an approach to using a FHIR server as a component of a knowledge system in one of two roles:
As such, this implementation guide defines profiles that support multiple use cases in the clinical quality improvement and measurement space. From the perspective of a Knowledge Author, this IG defines profiles to support the definition of knowledge artifacts, as well as profiles for exposing existing CDS KAS artifacts.
From the perspective of a Knowledge Content Provider, this IG defines search functionality for using a FHIR server as a knowledge artifact repository.
From the perspective of a Knowledge Service Provider, this IG defines operations and profiles in support of evaluating quality measures, and defining a service for guidance request and response, consistent with the approach taken by the current Decision Support Specification.
And finally, from the perspective of a Knowledge Service Consumer, this IG defines the expected available operations and behavior of a knowledge service.

The CQIF Implementation Guide currently focuses on the Decision Support aspects of the Clinical Quality domain. However, this IG has been developed in coordination with the Clinical Quality Information Work Group sponsored project to build FHIR representations for Clinical Quality Measures. As a result of that coordination, many of the profiles defined in this implementation guide are shared by that effort. The scope of this implementation guide therefore broadly falls into two categories:
The common aspects include profiles for defining quality evaluation request/response protocols, as well as representation of knowledge modules generally. The Decision Support-specific aspects then build on those profiles to define guidance request/response protocols, and representation of Decision Support-specific artifacts including rules, order sets, and documentation templates.
This implementation guide focuses on several primary use cases:

For this ballot cycle, we are presenting this implementation guide as a comment-only ballot with the objective of gathering community feedback. We welcome any comments, criticisms and suggestions on any topic, but in particular, we seek feedback on the following areas:

At the time of this ballot, there are several issues outstanding that prevented some material from being included. The following list details these known issues:
| Issue | Description |
|---|---|
| Coverage element | The KnowledgeModule structure should contain a "coverage" element that allows categorized topics to be represented in the same way that coverage is modeled within the Clinical Decision Support Knowledge Artifact Specification. There is an issue with the knowledge module profile definition that prevents it from being included. See the Suicide Risk Order Set Example for an example of coverage elements included in a knowledge module. |
| Data Requirements Filters | The data extension used to define data requirements within a knowledge module should contain a "codeFilter" element to allow the expression of terminology restrictions on data requirements, as well as a "dateFilter" element to allow the expression of date-based restrictions on data requirements. There is an issue with the knowledge module profile definition that prevents these elements from being included. See the Knowledge Module Library Example for an example of a data requirement with a code filter applied. |
| Action Customization Expression | The action extension has a customization element that is supposed to contain a path and an expression, but only contains a path. For an example of an action with a customization expression defined, see the Respiratory Protocol Orderset Example. |
| Action Subelements | The action extension is supposed to contain an "actions" element that allows each action to contain any number of sub-actions. For an example of actions with subelements defined, see the Suicide Risk Order Set Example. |
| Missing Examples | Several of the examples could not be included in the build because they will not validate for various reasons. Specifically, a Suicide Risk Order Set, and the Guidance Request/Response examples for the guidance operation. |

This material includes SNOMED Clinical Terms ® (SNOMED CT®), which are used by permission of the International Health Terminology Standards Development Organization (IHTSDO). All rights reserved. SNOMED CT was originally created by The College of American Pathologists. "SNOMED ®" and "SNOMED CT ®" are registered trademarks of the IHTSDO.
This material contains content from LOINC® (http://loinc.org  ). The LOINC table, LOINC codes, and LOINC panels and forms file are copyright © 1995-2011, Regenstrief Institute, Inc. and the Logical Observation Identifiers Names and Codes (LOINC) Committee and available at no cost under the license at http://loinc.org/terms-of-use
). The LOINC table, LOINC codes, and LOINC panels and forms file are copyright © 1995-2011, Regenstrief Institute, Inc. and the Logical Observation Identifiers Names and Codes (LOINC) Committee and available at no cost under the license at http://loinc.org/terms-of-use  .
.
This material contains content from the Unified Code for Units of Measure (UCUM) (http://unitsofmeasure.org  ). The UCUM specification is copyright © 1999-2013, Regenstrief Institute, Inc. and available at no cost under the license at http://unitsofmeasure.org/trac/wiki/TermsOfUse
). The UCUM specification is copyright © 1999-2013, Regenstrief Institute, Inc. and available at no cost under the license at http://unitsofmeasure.org/trac/wiki/TermsOfUse  .
.
This material contains quality measure content developed by the National Committee for Quality Assurance (NCQA). The measure content is copyright (c) 2008-2013 National Committee for Quality Assurance and used in accordance with the NCQA license terms for non-commercial use.

| Author Name |
|---|
| Bryn Rhodes |
| Jason Walonoski |
| Marc Hadley |
| Lloyd McKenzie (Supporting) |
| Chris Moesel (Supporting) |